Are you looking for an answer to the topic “How Can extinction be avoided with operant conditioning?“? We answer all your questions at the website Chiangmaiplaces.net in category: +100 Marketing Blog Post Topics & Ideas. You will find the answer right below.
Keep Reading
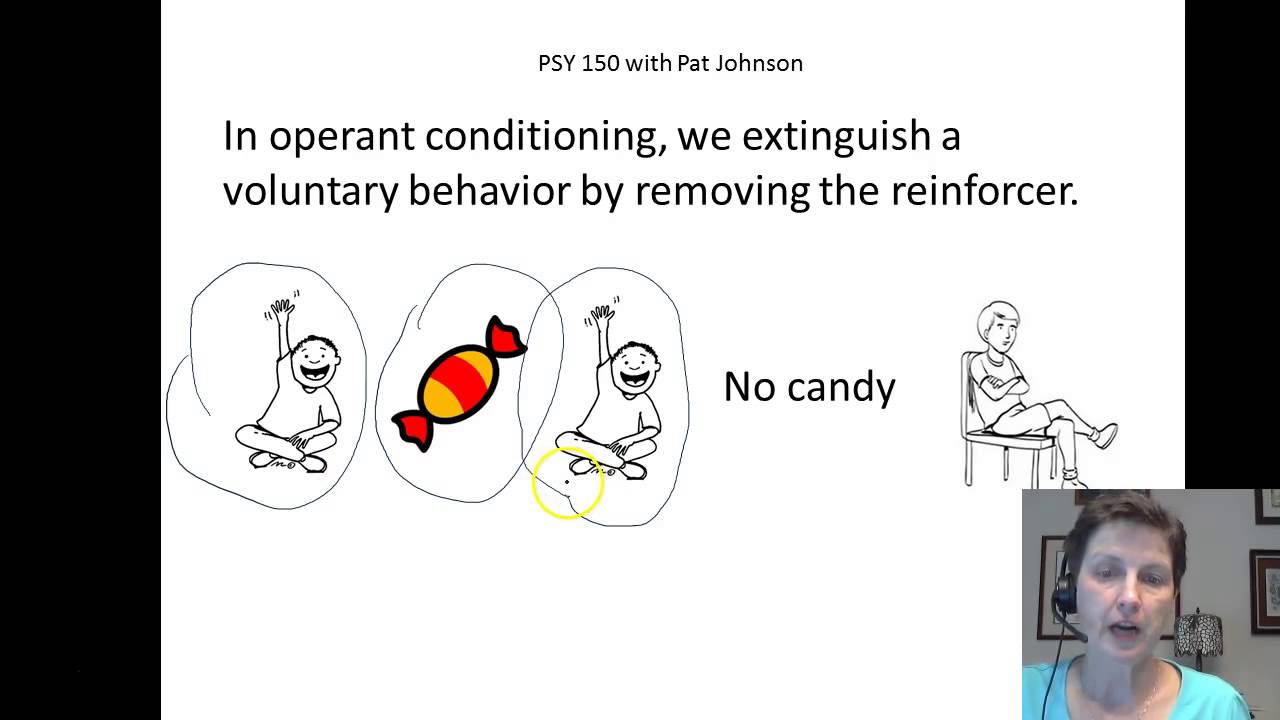
Table of Contents
Can extinction occur with operant conditioning?
In operant conditioning, extinction occurs when a response is no longer reinforced following a discriminative stimulus.
How can we prevent extinction in psychology?
The schedules of reinforcement play a significant role in how resistant a learned behavior is to extinction. A continuous schedule reinforces the conditioned response every time while a partial schedule reinforces only some of the times.
PSY 150 Operant Conditioning Extinction and Shaping
Images related to the topicPSY 150 Operant Conditioning Extinction and Shaping

Can occur after extinction in classical or operant conditioning?
Spontaneous recovery refers to the sudden reappearance of a previously extinct conditioned response after the unconditioned stimulus has been removed for some time. This phenomenon can occur after these two types of conditioning have taken place.
Which of the following is an example of the use of extinction with operant conditioning?
Which of the following is an example of the use of extinction with operant conditioning? A mother ignores her child’s temper tantrum so that the behavior ultimately goes away.
How is extinction different between classical and operant conditioning?
Classical conditioning involves associating an involuntary response and a stimulus, while operant conditioning is about associating a voluntary behavior and a consequence. In operant conditioning, the learner is also rewarded with incentives,5 while classical conditioning involves no such enticements.
What can cause extinction?
- Demographic and genetic phenomena. First of all, species with small populations face a greater risk of extinction. …
- Destruction of wild habitats. …
- Introduction of invasive species. …
- Climate change. …
- Hunting and illegal trafficking.
What are extinction strategies?
Extinction is a behavioral technique where you withhold reinforcement when the behavior occurs, so by definition you must know what the reinforcement is. Planned ignoring would only extinguish a behavior if the reinforcement was attention.
See some more details on the topic How Can extinction be avoided with operant conditioning? here:
How Extinction Is Defined in Psychology – Verywell Mind
In operant conditioning, extinction occurs when a response is no longer reinforced following a discriminative stimulus. B. F. Skinner described …
What is Extinction – Psychology – Parenting For Brain
That means a conditioned response is weakened and the target behavior eventually stops and becomes extinct. This is usually accomplished by withdrawing the …
Extinction – Conditioned Stimulus, Conditioned Response …
In classical/respondent conditioning, the learned response disappears when the association between conditioned and unconditioned stimuli is eliminated.
What Is Extinction? Psychology And Conditioning | BetterHelp
In operant conditioning, a behavior eventually becomes extinct if the reward no longer follows the behavior. For example, say you take your …
How do you deal with the extinction burst?
- Do not reinforce the maladaptive or undesirable behavior by responding to it. …
- Stay consistent in how you react or respond. …
- Be patient and don’t expect miracles overnight.
- Be prepared. …
- Get everyone on board. …
- Do not use extinction when dealing with particularly harmful habits.
What is an example of extinction in behavior?
Another form of this procedure is the extinction of behaviors maintained by negative reinforcement. This is commonly referred to as “escape extinction.” Example: Dannie throws a tantrum when she doesn’t want to eat her food. Her mom responds by sending her to a ‘corner’ for a time out.
What is extinction and how can it be recovered spontaneously?
Extinction and Spontaneous Recovery
With extinction, the behavior ceases when the conditioned stimulus is presented, or the behavior becomes sporadic when the stimulus is present. Spontaneous recovery can only happen after extinction and usually follows a rest period where no stimuli are presented.
How do you create a behavior in extinction?
- Identifying the interfering behavior. …
- Identifying data collection measures and baseline data. …
- Determining the function of the behavior. …
- Creating an intervention plan.
Under what conditions might a conditioned response become extinct?
Under what conditions might a conditioned response become extinct? If the conditioned response is no longer a reliable predictor of whatever the subject is predicting. Extinction occurs over time when you stop being confronted with a certain stimulus so your response will become extinct.
The difference between classical and operant conditioning – Peggy Andover
Images related to the topicThe difference between classical and operant conditioning – Peggy Andover

Which of the following is not an effect of extinction procedures?
Which of the following is not associated with effects of extinction? Stable responding.
What is negative reinforcement in operant conditioning?
Negative reinforcement is a term described by B. F. Skinner in his theory of operant conditioning. In negative reinforcement, a response or behavior is strengthened by stopping, removing, or avoiding a negative outcome or aversive stimulus.
Who was the name behind operant conditioning?
Operant conditioning was first described by behaviorist B.F. Skinner, which is why you may occasionally hear it referred to as Skinnerian conditioning.
What is extinction in reinforcement theory?
Extinction is similar to punishment in that its purpose is to reduce unwanted behavior. The process of extinction begins when a valued behavioral consequence is withheld in order to decrease the probability that a learned behavior will continue. Over time, this is likely to result in the ceasing of that behavior.
Under which of the following circumstances should extinction not be used?
Under which of the following circumstances should extinction not be used? When it could cause harm to the individual or others in the environment. The quote “All behavior has a communicative intent” can be best explained by the statement: Behavior always serves a purpose for the person engaging in the behavior.
How does operant conditioning create the opposite effect than what was intended?
Causing the Opposite Effect
Sometimes OC can create the opposite effect than was intended. Generally this problem happens when the adult (or other person providing the reinforcement) does not look clearly at the situation, or does not understand OC.
Which of the following causes of extinction is directly brought about by human activity?
Human activities that influence the extinction and endangerment of wild species fall into a number of categories: (1) unsustainable hunting and harvesting that cause mortality at rates that exceed recruitment of new individuals, (2) land use practices like deforestation, urban and suburban development, agricultural …
How can you help protect endangered animals from extinction?
- Reduce And Reuse. …
- Don’t Use Harsh Chemicals In Your Household. …
- Dispose Of Waste Properly. …
- Prevent Soil Erosion. …
- Maintain A Healthy Backyard Habitat. …
- Support An Organization That Fights To Save Endangered Species. …
- Advocate For Conservation. …
- Vote.
What are the five extinctions?
- Ordovician-silurian Extinction: 440 million years ago.
- Devonian Extinction: 365 million years ago.
- Permian-triassic Extinction: 250 million years ago.
- Triassic-jurassic Extinction: 210 million years ago.
- Cretaceous-tertiary Extinction: 65 Million Years Ago.
Which of the following is a procedure recommended for using extinction effectively?
The first step in using extinction effectively is to identify and withhold all possible sources of reinforcement that maintain the target behavior. Extinction guidelines #2 withholding reinforcement consistently. Always withhold all reinforcers maintaining the problem behavior consistently.
Extinction in Operant Conditioning
Images related to the topicExtinction in Operant Conditioning

What is extinction in applied behavior analysis?
Extinction: When an observed behavior goes away entirely because of the reinforcement procedure that has been applied to the situation. An extinction burst, occurs when the reinforcement that caused a behavior has been removed, initially there will be an increase in the observed behavior.
How does positive reinforcement become extinction?
Behaviors maintained by positive reinforcement are placed on extinction when those behaviors do not produce the reinforcer. -Continued responding during the extinction process. All stimuli that function as reinforcers require a minimum level of an establishing operation (i.e., motivation must be present).
Related searches to How Can extinction be avoided with operant conditioning?
- pavlov is to as is to operant conditioning
- reinforcers whether they be positive or negative have the same effect on behavior which is to
- which of the following is not a step in classical conditioning?
- who would have argued that we do not need to directly be reinforced or punished to learn?
- how can extinction be avoided with operant conditioning
- can extinction occur with operant conditioning
- can operant conditioning be reversed
- why operant conditioning is bad
- which of the following produces the strongest classical conditioning outcome
- what are the consequences of operant conditioning
- is the removal of an aversive stimulus that serves to increase a behavior
- which of the following is not a step in classical conditioning
- extinction behavior example
- who would have argued that we do not need to directly be reinforced or punished to learn
- which of the following produces the strongest classical conditioning outcome?
- watson and skinner believed that
- what does extinction mean in operant conditioning
Information related to the topic How Can extinction be avoided with operant conditioning?
Here are the search results of the thread How Can extinction be avoided with operant conditioning? from Bing. You can read more if you want.
You have just come across an article on the topic How Can extinction be avoided with operant conditioning?. If you found this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much.