Are you looking for an answer to the topic “How do electrons move in resonance?“? We answer all your questions at the website Chiangmaiplaces.net in category: +100 Marketing Blog Post Topics & Ideas. You will find the answer right below.
Approaches for moving electrons are move pi electrons toward a positive charge or toward an another pi bond. Move a single nonbonding electron towards a pi bond. Move lone pair electrons toward a pi bond and when electrons can be moved in more than one direction, move them to the more electronegative atom.The electrons appear to “shift” between different resonance structures and while not strictly correct as each resonance structure is just a limitation of using the Lewis structure perspective to describe these molecules.Resonance structures differ only in how the electrons are distributed between the atoms. Therefore, if we shift around the electrons in one resonance structure, then it can be transformed into other resonance structure. How to: Organic chemists use a curved arrow formalism to show the movement of a pair of electrons.

Table of Contents
What happens to electrons in resonance?
The electrons appear to “shift” between different resonance structures and while not strictly correct as each resonance structure is just a limitation of using the Lewis structure perspective to describe these molecules.
Why do electrons move in resonance?
Resonance structures differ only in how the electrons are distributed between the atoms. Therefore, if we shift around the electrons in one resonance structure, then it can be transformed into other resonance structure. How to: Organic chemists use a curved arrow formalism to show the movement of a pair of electrons.
Understanding How Electrons Move in Resonance Structure
Images related to the topicUnderstanding How Electrons Move in Resonance Structure

What electrons participate in resonance?
Resonance contributors involve the ‘imaginary movement’ of pi-bonded electrons or of lone-pair electrons that are adjacent to (i.e. conjugated to) pi bonds.
How do resonance structures work?
Resonance structures have the same number of electrons and therefore have the same overall charge. Resonance structures differ only in the arrangement of electrons; the atoms keep the same connectivity and arrangement.
What is resonance effect?
Resonance Effect Or Mesomeric Effect In Chemistry
The concept of resonance effect tells about the polarity induced in a molecule by the reaction between a lone pair of electron and a pi bond. It also occurs by the interaction of 2 pi bonds in the adjacent atoms.
What is resonance explain in detail?
Resonance is a phenomenon that occurs when the matching vibrations of another object increase the amplitude of an object’s oscillations.
Can lone pairs move in resonance?
Rules to remember for recognising resonance structures:
You can only move electrons in π bonds or lone pairs (that are in p orbitals) The overall charge of the system must remain the same. The bonding framework of a molecule must remain intact.
See some more details on the topic How do electrons move in resonance? here:
MOVE ELECTRONS TO TRANSFORM ONE … – HOW TO
Resonance structures differ only in how the electrons are distributed between the atoms. Therefore, if we shift around the electrons in one resonance structure, …
2.6: Drawing Resonance Forms – Chemistry LibreTexts
Organic chemistry has developed a system to show how electrons move between resonance structures. This system will also be used to help describe …
Ch 1 : Resonance – Chemistry
Rules to remember for recognising resonance structures: Atoms never move. You can only move electrons in π bonds or lone pairs (that are in p orbitals); The …
Resonance Tutorial
Instead of starting to move electrons from the blue oxygen in structure 1, could you start drawing new resonance structures by moving a lone pair on the …
Why do some molecules have resonance?
A molecule can have resonance structures when it has a lone pair or a double bond on the atom next to a double bond.
What is Hyperconjugation explain?
Hyperconjugation is the stabilising interaction that results from the interaction of the electrons in a σ-bond (usually C-H or C-C) with an adjacent empty or partially filled p-orbital or a π-orbital to give an extended molecular orbital that increases the stability of the system.
Is positive charge involved in resonance?
The best resonance form has a new π bond that has been formed through the donation of a pair of electrons on the adjacent atom (O, N, Cl, F). In the process we put a positive charge on that atom.
Electron Pushing Arrows in Resonance and Organic Mechanisms
Images related to the topicElectron Pushing Arrows in Resonance and Organic Mechanisms
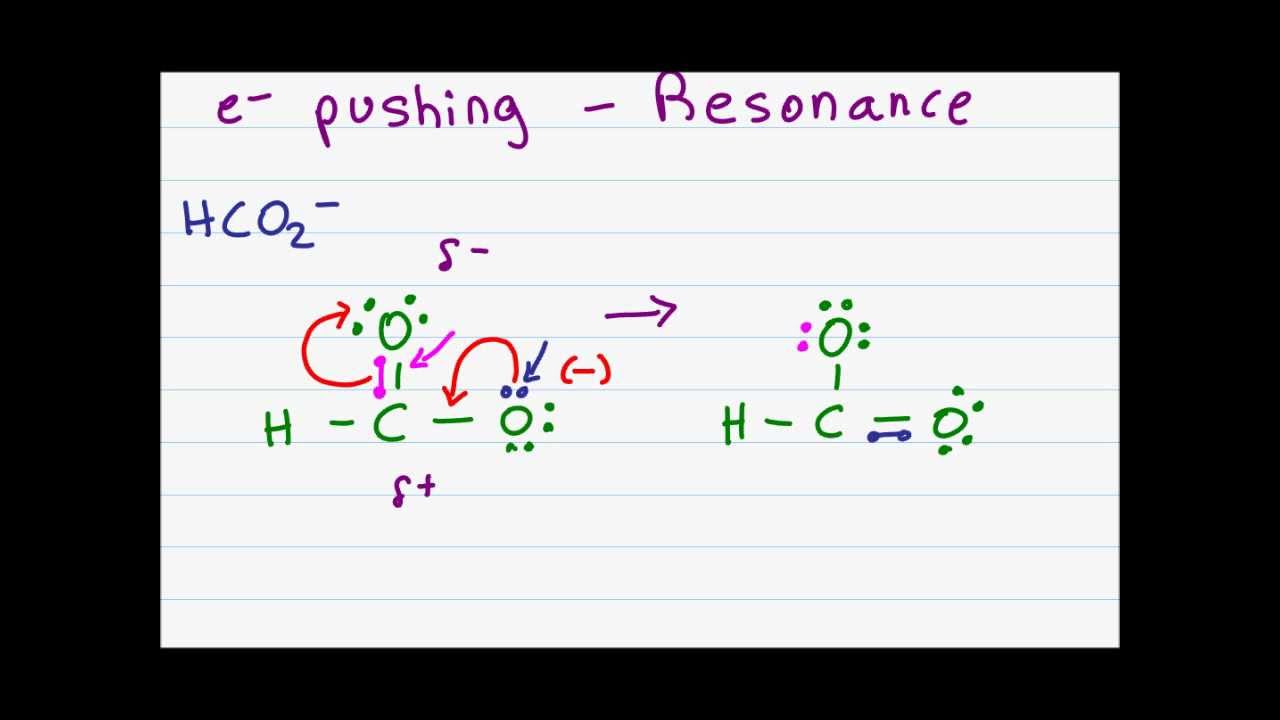
Why are pi bonds required for resonance?
Since pi bonds are higher energy than sigma bonds, they are more easily broken and may re-form elsewhere on the molecule. This movement of electrons between each resonance structure helps to delocalize any formal charges. The more resonance forms a structure has, the more stable the compound.
Which lone pairs participate in resonance?
It means that only one, either π bond or lone pair will participate in resonance if the atom has both. For example, in pyridine, the nitrogen has lone pair as well as is attached with a π bond.
Do resonance structures have to follow the octet rule?
Rules for Estimating Stability of Resonance Structures
The resonance structures in which all atoms have complete valence shells is more stable. This means most atoms have a full octet. In the example below structure A has a carbon atom with a positive charge and therefore an incomplete octet.
How does resonance affect polarity?
Resonance is the phenomenon which causes a polarity to be produced in the molecule. This could happen either by the interaction of two π-bonds or between a π-bond and lone pair of electrons present on an adjacent atom. The delocalisation of π-electrons is what causes this effect.
What does resonance mean in physics?
resonance, in physics, relatively large selective response of an object or a system that vibrates in step or phase, with an externally applied oscillatory force. Resonance was first investigated in acoustical systems such as musical instruments and the human voice.
What are the conditions for resonance?
The conditions to produce resonance in an object are: The object must have a minimum of one natural frequency of vibration. The object must be driven by an external force of vibration. The frequency of the external vibrating force must be similar to the object’s natural frequency of vibration.
How does resonance stabilize a molecule?
Resonance stabilization
Because resonance allows for delocalization, in which the overall energy of a molecule is lowered since its electrons occupy a greater volume, molecules that experience resonance are more stable than those that do not. These molecules are termed resonance stabilized.
How do you know when electrons are delocalized?
The easiest way to spot delocalized electrons is to compare electron locations in two resonance forms. If a pair appears in one place in one form, and in a different place in another form, the pair is delocalized.
How does the electron move around the atom?
Images related to the topicHow does the electron move around the atom?

What does it mean when an electron is delocalized?
Electron delocalization (delocalization): Distribution of electron density beyond a fixed place such as a single atom, lone pair, or covalent bond via resonance or inductive effects.
How do you distinguish between resonance and isomers?
Resonance structures are not isomers. Isomers have different arrangement of both atoms and electrons. Resonance forms differ only in arrangement of electrons. Resonance structures are a better depiction of a Lewis dot structure because they clearly show bonding in molecules.
Related searches to How do electrons move in resonance?
- how to draw resonance structures
- 7 rules of resonance
- how many resonance structure of benzene
- how to draw resonance structures for rings
- resonance structures rules
- resonance energy
- resonance structure of benzene pdf
- draw resonance structure of benzene
- how do electrons move in resonance structures
Information related to the topic How do electrons move in resonance?
Here are the search results of the thread How do electrons move in resonance? from Bing. You can read more if you want.
You have just come across an article on the topic How do electrons move in resonance?. If you found this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much.