Are you looking for an answer to the topic “How do firms in oligopoly set price and output?“? We answer all your questions at the website Chiangmaiplaces.net in category: +100 Marketing Blog Post Topics & Ideas. You will find the answer right below.
Firms in an oligopoly set prices, whether collectively—in a cartel—or under the leadership of one firm, rather than taking prices from the market. Profit margins are thus higher than they would be in a more competitive market.Price and Output under Imperfect Collusion:
Under oligopoly price and output can also be determined without any collusion among the firms. The firms may decide to follow a firm in price and output determination in the long run. Such sort of policy is called price leadership under oligopoly.(1) The oligopolistic industry consists of a large dominant firm and a number of small firms. (2) The dominant firm sets the market price. (3) All other firms act like pure competitors, which act as price takers. Their demand curves are perfectly elastic for they sell the product at the dominant firm’s price.

Table of Contents
How is price and output determined in oligopoly?
Price and Output under Imperfect Collusion:
Under oligopoly price and output can also be determined without any collusion among the firms. The firms may decide to follow a firm in price and output determination in the long run. Such sort of policy is called price leadership under oligopoly.
How do firms set price under oligopoly?
(1) The oligopolistic industry consists of a large dominant firm and a number of small firms. (2) The dominant firm sets the market price. (3) All other firms act like pure competitors, which act as price takers. Their demand curves are perfectly elastic for they sell the product at the dominant firm’s price.
Oligopolies, duopolies, collusion, and cartels | Microeconomics | Khan Academy
Images related to the topicOligopolies, duopolies, collusion, and cartels | Microeconomics | Khan Academy

Can oligopolies set their own prices?
Key Points. Firms in an oligopoly may collude to set a price or output level for a market in order to maximize industry profits. At an extreme, the colluding firms can act as a monopoly. Oligopolists pursuing their individual self-interest would produce a greater quantity than a monopolist, and charge a lower price.
How do oligopolistic company determine its price and earn profit in the market?
When oligopoly firms in a certain market decide what quantity to produce and what price to charge, they face a temptation to act as if they were a monopoly. By acting together, oligopolistic firms can hold down industry output, charge a higher price, and divide the profit among themselves.
How price and output is determined?
The market price and output is determined on the basis of consumer demand and market supply under perfect competition. In other words, the firms and industry should be in equilibrium at a price level in which quantity demand is equal to the quantity supplied.
How is price determined in price leadership model of oligopoly?
The collusive price leadership model may emerge within markets that have oligopolistic conditions. Collusive price leadership occurs as a result of an explicit or implicit agreement among a handful of dominant firms to keep their prices in mutual alignment.
What is oligopoly determine price and output under oligopoly with the help of kinked demand curve model?
Answer: In an oligopolistic market, the kinked demand curve hypothesis states that the firm faces a demand curve with a kink at the prevailing price level. The curve is more elastic above the kink and less elastic below it. This means that the response to a price increase is less than the response to a price decrease.
See some more details on the topic How do firms in oligopoly set price and output? here:
Oligopoly Pricing Models – thisMatter.com
The contestable market model is an oligopolistic model based on barriers to entry and barriers to exit that determine the firm’s price and output. If the …
Oligopoly – Principles of Economics 2e – BC Open Textbooks
When oligopoly firms in a certain market decide what quantity to produce and what price to charge, they face a temptation to act as if they were a monopoly. By …
Price Determination under Oligopoly – MA Economics Karachi …
The firms may agree on a price, or divide the total market, or assign quota, or merge themselves into one unit and form a monopoly or try to differentiate their …
Oligopoly – Economics Help
An oligopoly is an industry dominated by a few large firms. … If the firm restricts output (sets the High price), and then the other firm …
How price and output is determined under monopoly?
The monopolist will select the profit-maximizing level of output where MR = MC, and then charge the price for that quantity of output as determined by the market demand curve. If that price is above average cost, the monopolist earns positive profits.
How does oligopoly affect output decisions?
When firms in an oligopoly individually choose production to maximize profit, they produce a quantity of output greater than the level produced by monopoly and less than the level produced by competition. The oligopoly price is less than the monopoly price but greater than the competitive price.
Why are prices stable in oligopoly?
The model of the kinked demand curve suggests prices will be stable. Firms don’t want to increase prices because they will see a sharp fall in demand. Firms don’t want to cut prices because they will start a price war, where they don’t gain market share, but do get lower prices and lower revenue.
What are three models used to study pricing and output by oligopolies?
The kinked-demand curve model. Price leadership model. Benefits to oligopolies from collusion: It increases profits.
Price and output determination under Oligopoly ( Price Rigidity)
Images related to the topicPrice and output determination under Oligopoly ( Price Rigidity)
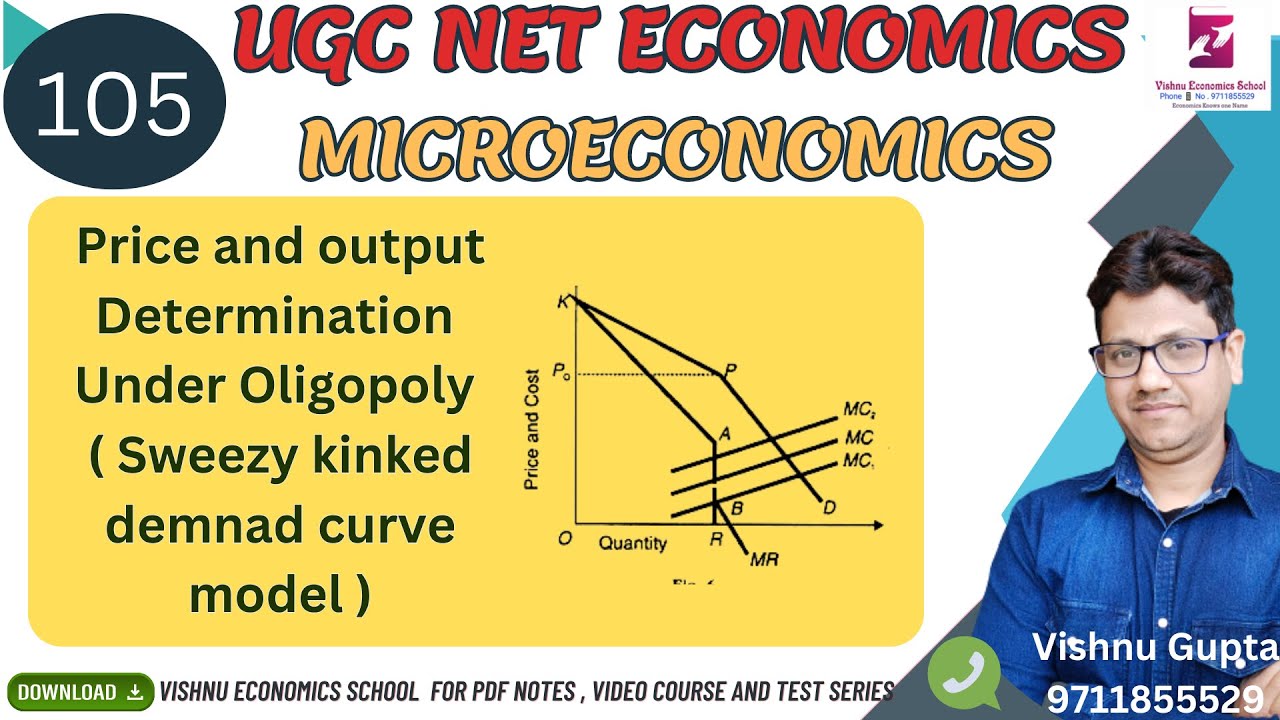
What is oligopoly explain the price output determination process under price leadership in oligopoly?
An oligopoly exists between two extreme market structures, perfect competition, and monopoly. When a few firms dominate the market for a good or service is called oligopoly.
What is the pricing power of oligopoly?
Firms in oligopolistic and monopolistic competition markets have some pricing power depending on the size, information access, and other characteristics of their competitors, and thus have some power to set prices without losing significant market share. Performance is measured primarily by profits.
How does the number of firms in an oligopoly affect its outcome on price product place and promotion?
How does the number of firms in an oligopoly affect the outcome in its market? As the number of sellers in an oligopoly grows larger, an oligopolistic market looks more and more like a competitive market. Price approaches marginal cost, and quantity produced approaches the socially efficient level.
Why do oligopolies not compete on price?
Competitive oligopolies
When competing, oligopolists prefer non-price competition in order to avoid price wars. A price reduction may achieve strategic benefits, such as gaining market share, or deterring entry, but the danger is that rivals will simply reduce their prices in response.
How the price and output is determined by a firm under perfect competition?
In perfect competition, the price of a product is determined at a point at which the demand and supply curve intersect each other. This point is known as equilibrium point as well as the price is known as equilibrium price. In addition, at this point, the quantity demanded and supplied is called equilibrium quantity.
What do you mean by oligopoly define price determination under it?
Price Determination under Oligopoly. Oligopoly is that market situation in which the number of firms is small but each firm in the industry takes into consideration the reaction of the rival firms in the formulation of price policy. The number of firms in the industry may be two or more than two but not more than 20.
Why do oligopoly firms engage in price leadership?
Oligopolists seek to maximize market profits while minimizing market competition through non-price competition and product differentiation. read more. That is, there should be very few firms in the market. One firm among them should be big enough to control the price.
What are the characteristics of oligopoly?
- A Few Firms with Large Market Share. …
- High Barriers to Entry. …
- Interdependence. …
- Each Firm Has Little Market Power In Its Own Right. …
- Higher Prices than Perfect Competition. …
- More Efficient.
What is price leadership explain price leadership with the help of real world examples?
What is an example of price leadership? The most common example of price leadership in an industry when a large business in an industry where their only competition is small business. The large business can lower prices as much as they want without worrying about getting into a losing price war with their rivals.
When firms get together to make price and output decisions it is called?
A cartel is defined as a group of firms that gets together to make output and price decisions.
How to Solve a Cournot Oligopoly Problem
Images related to the topicHow to Solve a Cournot Oligopoly Problem

How does it help in explaining price rigidity under oligopoly?
The low elasticity does not increase the demand significantly as a result of the price cut. This asymmetrical behavioral pattern results in a kink in the demand curve and hence there is price rigidity in oligopoly markets.
How is an oligopoly market different from monopolistic competitive market in respect of price and output determination?
Oligopoly: An Overview. A monopoly and an oligopoly are market structures that exist when there is imperfect competition. A monopoly is when a single company produces goods with no close substitute, while an oligopoly is when a small number of relatively large companies produce similar, but slightly different goods.
Related searches to How do firms in oligopoly set price and output?
- who sets price in an oligopoly
- oligopoly example
- oligopoly features
- how does an oligopoly set prices
- oligopoly barriers to entry
- oligopoly market structure pdf
- how is price determined in oligopoly market
- how do firms in an oligopolistic market set their prices
- oligopoly definition and examples
- how do oligopolies set prices
- how do firms in oligopoly set price and output
- oligopolistic competition
- types of oligopoly
- monopoly and oligopoly examples
Information related to the topic How do firms in oligopoly set price and output?
Here are the search results of the thread How do firms in oligopoly set price and output? from Bing. You can read more if you want.
You have just come across an article on the topic How do firms in oligopoly set price and output?. If you found this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much.