Are you looking for an answer to the topic “How do forces act on sodium in resting cells quizlet?“? We answer all your questions at the website Chiangmaiplaces.net in category: +100 Marketing Blog Post Topics & Ideas. You will find the answer right below.
Keep Reading
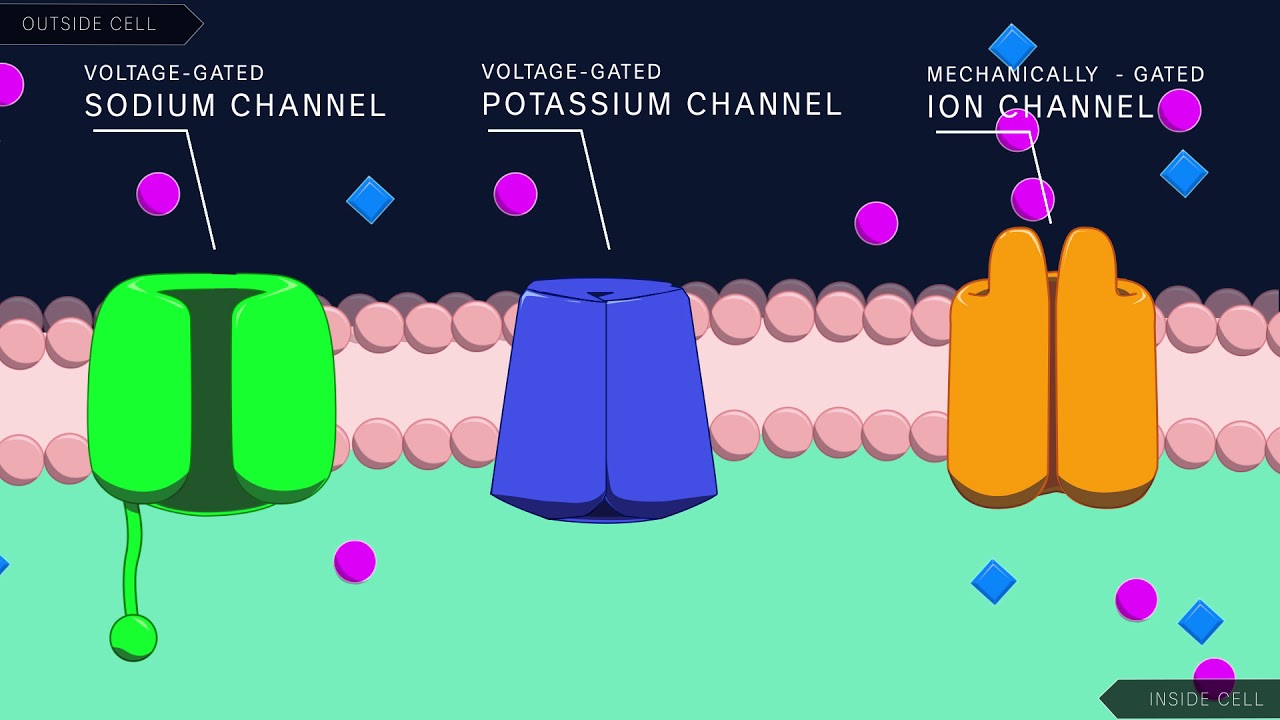
Table of Contents
Which of the following makes sodium want to enter a resting cell?
Sodium ions (Na+) are attracted to the inside of neurons at rest by two forces. The high concentration of (Na+) outside the cell pushes this ion into the cell down the concentration gradient. Likewise, the electrostatic pressure due to the negative charge within the neuron attracts the positively charged (Na+) inside.
When the membrane is at rest What are the forces acting on potassium ions quizlet?
When the membrane is at rest, what are the forces acting on potassium ions? The concentration gradient tends to move potassium ions out of the cell, and the electrical gradient tends to move them into the cell.
Action Potential in the Neuron
Images related to the topicAction Potential in the Neuron

What is the direction of the driving forces for the movement of potassium ions at resting membrane potential?
Because the membrane is permeable to potassium ions, they will flow down their concentration gradient; i.e. towards the outside of the cell. There is also a concentration gradient favouring sodium diffusion in the opposite direction but the membrane is not permeable to sodium.
Which force pushes potassium ions into the cell?
Potassium is in higher concentration inside the cell—the chemical driving force tends to push potassium out of the cell.
When a membrane is at rest what attracts sodium ions to the inside of the cell?
The voltage-dependent sodium gates have opened, so sodium can move freely. Sodium is attracted to the inside of the cell by both an electrical and a concentration gradient.
Does sodium move in or out of the cell?
The sodium-potassium pump transports sodium out of and potassium into the cell in a repeating cycle of conformational (shape) changes. In each cycle, three sodium ions exit the cell, while two potassium ions enter. This process takes place in the following steps: To begin, the pump is open to the inside of the cell.
When a membrane is at rest what attracts sodium ions quizlet?
When a membrane is at rest, what attracts sodium ions to the inside of the cell? The sodium gates in the membrane close.
See some more details on the topic How do forces act on sodium in resting cells quizlet? here:
lecture quiz 3 Flashcards | Quizlet
How do forces act on sodium in resting cells? Electrical gradient pushes in; concentration gradient pushes in.
the cell Flashcards | Quizlet
How do forces act on sodium in resting cells? a. Electrical gradient pushes in; concentration gradient pushes in b. Electrical gradient pushes in; …
Physiology Exam 3 pt. 1 Flashcards | Quizlet
Because there is a high concentration of sodium outside the cell, there is a chemical driving force tending to push sodium ions into the cell. Potassium is in …
KIN 270 Cell Biology Flashcards | Quizlet
How do forces act on sodium in resting cells? Electrical gradient pushes in; concentration gradient pushes in.
When the neuronal membrane is at rest where are the sodium ions and potassium ions most concentrated?
For a typical neuron at rest, sodium, chloride, and calcium are concentrated outside the cell, whereas potassium and other anions are concentrated inside. This ion distribution leads to a negative resting membrane potential.
Which direction does the sodium-potassium pump move ions?
The Sodium-Potassium Pump
Active transport is the energy-requiring process of pumping molecules and ions across membranes “uphill” – against a concentration gradient. To move these molecules against their concentration gradient, a carrier protein is needed.
What two forces are at work attempting to push sodium ions into the cell?
Sodium is positively charged and the inside of the cell is negatively charged. Opposite electrical charges attract, so the electrical gradient tends to pull sodium into the cell. Second, consider the concentration gradient, the difference in distribution of ions across the membrane.
What happens to the resting membrane potential when the extracellular Na+ concentration is increased?
A change in extracellular Na+ results in little change to resting membrane potential because the plasma membrane of a neuron is only slightly permeable to Na+ because it contains relatively few Na+ leakage channels. This inhibits net diffusion of Na+ into or out of the cell.
Why does NA enter the cell during the action potential?
Because sodium is a positively charged ion, it will change the relative voltage immediately inside the cell relative to immediately outside. The resting potential is the state of the membrane at a voltage of −70 mV, so the sodium cation entering the cell will cause it to become less negative.
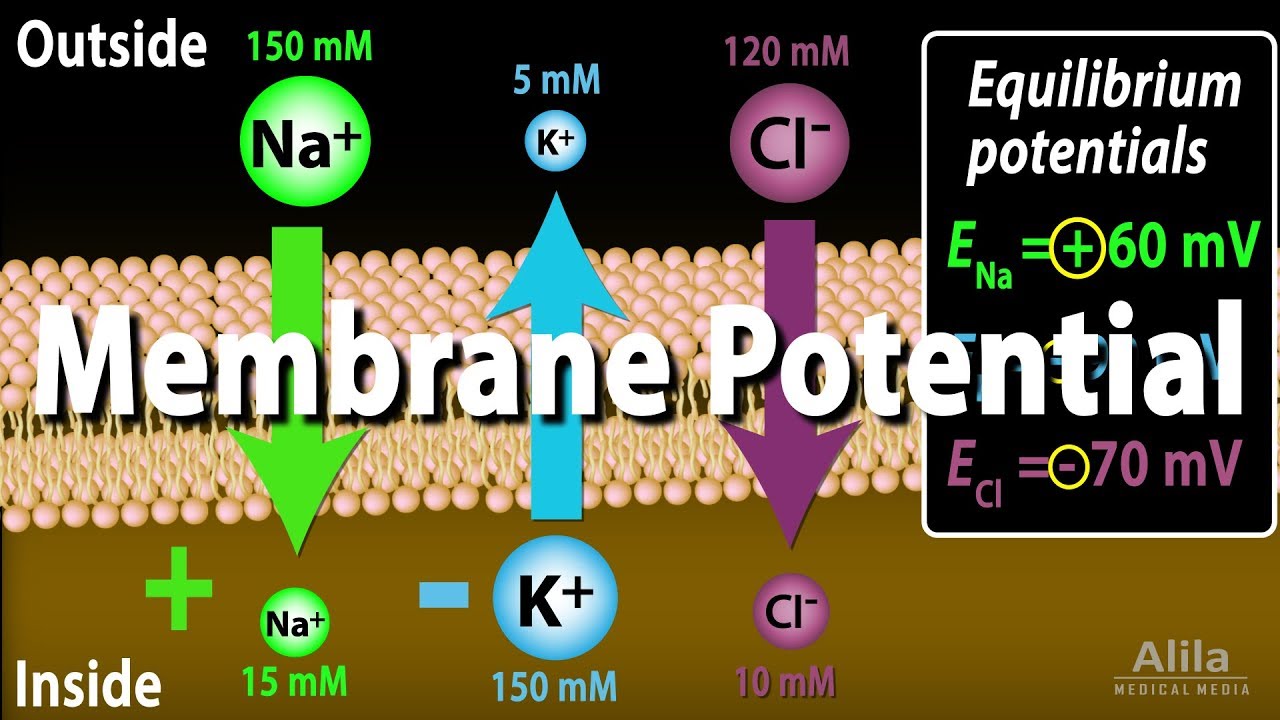
Membrane Potential, Equilibrium Potential and Resting Potential, Animation
Images related to the topicMembrane Potential, Equilibrium Potential and Resting Potential, Animation
How does sodium move through the cell membrane?
Their diffusion is facilitated by membrane proteins that form sodium channels (or “pores”), so that Na+ ions can move down their concentration gradient from outside the cells to inside the cells.
How does the sodium and potassium pump work?
The sodium-potassium pump uses active transport to move molecules from a high concentration to a low concentration. The sodium-potassium pump moves sodium ions out of and potassium ions into the cell. This pump is powered by ATP. For each ATP that is broken down, 3 sodium ions move out and 2 potassium ions move in.
Is sodium active or passive transport?
The sodium-potassium pump carries out a form of active transport—that is, its pumping of ions against their gradients requires the addition of energy from an outside source. That source is adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the principal energy-carrying molecule of the cell.
When sodium ions move into a cell through embedded proteins What happens to the membrane potential?
In response to stimulus, voltage-gated ion channels in the membrane suddenly open and permit the sodium ions on the outside to rush into the cell. As the positively charged sodium ions rush in, the charge on the cell membrane becomes depolarized (from -70 toward 0 mV).
What will be the effect on membrane potential of Na+ ions move into the cell?
The membrane depolarizes above a certain threshold potential. Influx of Na+ ions into the neuron can lead to membrane depolarization above the threshold potential; this event triggers the creation of an action potential.
What effect did decreasing the extracellular sodium have on the resting membrane potential?
The resting membrane potential disappeared. The resting membrane potential became less negative. Only a small change occurred, because the resting neuron is not very permeable to sodium. Only a small change occurred, because the sodium channels were mostly open.
How does the sodium-potassium pump contribute to the resting membrane potential?
Increased activity of the sodium-potassium ATPase pump increases the concentration of potassium intracellularly and decreases the concentration of sodium. This results in a more strongly negative resting membrane potential.
Why do sodium ions need channels to move in and out of cells?
Sodium need channels to move into cell because if cell will let every ion to move into it then it will become toxic. In order to prevent this nerve cells regulated the entry of ions via ion gated channels. Another reason is that sodium cannot cross the cell via simple diffusion,it needs to be facilitated via channels.
How does the sodium-potassium pump restore resting potential?
After about half a millisecond, the sodium channels close again and potassium channels open, allowing positive potassium ions to move to the outside of the cell. The cell is quickly repolarized. The sodium-potassium pump works to restore the proper concentrations of the ions inside and outside the cell.
When the potential across the membrane reaches threshold the sodium channels?
The rising phase is caused by the opening of voltage-gated sodium channels. These ion channels are activated once the cell’s membrane potential reaches threshold and open immediately. The electrochemical gradients drive sodium into the cell causing the depolarization. Animation 6.3.
Resting membrane potential – definition, examples
Images related to the topicResting membrane potential – definition, examples
Is sodium more concentrated on the inside or outside of the cell membrane quizlet?
the sodium concentration is higher outside the cell than inside the cell and the potassium concentration is higher inside the cell than outside the cell. The sodium-potassium exchange pump transports potassium and sodium ions in which direction(s)?
What is one major cause for the resting potential of a neuron’s membrane?
What generates the resting membrane potential is the K+ that leaks from the inside of the cell to the outside via leak K+ channels and generates a negative charge in the inside of the membrane vs the outside. At rest, the membrane is impermeable to Na+, as all of the Na+ channels are closed.
Related searches to How do forces act on sodium in resting cells quizlet?
- all hyperosmotic solutions are hypertonic
- the portion of a cell membrane that forms the core (inside) of a lipid bilayer consists primarily of
- many choice sources of chemical potential energy in the body include
- how do forces act on sodium in resting cells quizlet answers
- many choice by which of the following methods does a cell control the rate of a chemical reaction
- many choice: sources of chemical potential energy in the body include
- a basic nervous system
- sodium is moved from the inside of a cell to the outside of a cell by
- moving potassium into a cell would
- moving sodium out of a cell
- a basic nervous system ________.
- how do forces act on sodium in resting cells quizlet lab
- the portion of a cell membrane that forms the core inside of a lipid bilayer consists primarily of
Information related to the topic How do forces act on sodium in resting cells quizlet?
Here are the search results of the thread How do forces act on sodium in resting cells quizlet? from Bing. You can read more if you want.
You have just come across an article on the topic How do forces act on sodium in resting cells quizlet?. If you found this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much.