Are you looking for an answer to the topic “How Do H1 Receptor Antagonists Work?“? We answer all your questions at the website Chiangmaiplaces.net in category: +100 Marketing Blog Post Topics & Ideas. You will find the answer right below.
Histamine H1 receptor antagonists work by blocking the histamine H1 receptor, a mechanism of action different than that of any other medication for the treatment of insomnia. Administration of first-generation H1 receptor antagonists—chlorpheniramine (4.2.H1 Antagonists (second-generation antihistamines)
These agents are preferred for acute and chronic urticaria, with first-generation agents reserved for efractory cases. Commonly used H1 antagonists currently available in the United States are cetirizine, levocetirizine, desloratadine, loratadine, and fexofenadine.The H2 blockers compete with histamine for H2 receptors on the stomach’s parietal cells and thereby depress the production of hydrochloric acid. They are rapidly absorbed reaching peak blood levels in 1 to 3 hours. Acid-suppression lasts several hours thereafter and permits peptic ulcers to heal over a few weeks.
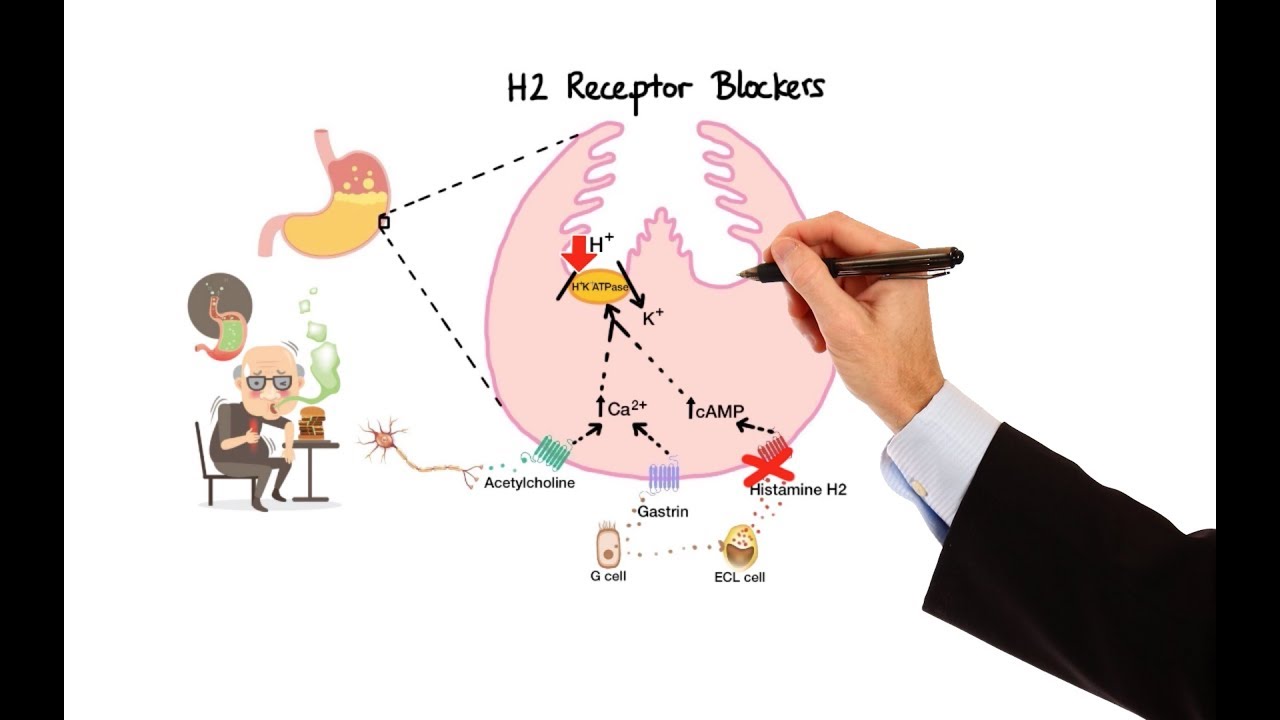
Table of Contents
What are H1 receptor antagonists?
H1 Antagonists (second-generation antihistamines)
These agents are preferred for acute and chronic urticaria, with first-generation agents reserved for efractory cases. Commonly used H1 antagonists currently available in the United States are cetirizine, levocetirizine, desloratadine, loratadine, and fexofenadine.
How do histamine antagonists work?
The H2 blockers compete with histamine for H2 receptors on the stomach’s parietal cells and thereby depress the production of hydrochloric acid. They are rapidly absorbed reaching peak blood levels in 1 to 3 hours. Acid-suppression lasts several hours thereafter and permits peptic ulcers to heal over a few weeks.
Pharmacology – ANTIHISTAMINES (MADE EASY)
Images related to the topicPharmacology – ANTIHISTAMINES (MADE EASY)

How does H1 receptor work?
The H1-receptor drives cellular migration, nociception, vasodilatation, and bronchoconstriction (39), whereas the H2-receptor modifies gastric acid secretion, airway mucus production, and vascular permeability (40). The H3-receptor plays an important role in neuro-inflammatory diseases (37).
What happens when histamine 1 receptors are blocked?
Histamine is an important neurotransmitter. Old (first-generation) H1-receptor antagonists such as chlorpheniramine, diphenhydramine, or triprolidine produce histamine blockade at H1-receptors in the central nervous system (CNS) and frequently cause somnolence or other CNS adverse effects.
Why do H1 antagonists cause sedation?
Antihistamines are medications that target the H1 histamine receptor. First-generation antihistamines block peripheral H1 receptors, but also cross the blood – brain barrier and block central nervous system H1 and cholinergic receptors as well. This produces the unwanted side effect of sedation.
What do H2 antagonists do?
Histamine H2-receptor antagonists, also known as H2-blockers, are used to treat duodenal ulcers and prevent their return. They are also used to treat gastric ulcers and for some conditions, such as Zollinger-Ellison disease, in which the stomach produces too much acid.
How do H2 blockers help with allergic reactions?
These agents block effects of released histamine at H2 receptors, thereby treating vasodilation, possibly some cardiac effects, and glandular hypersecretion. H2 blockers with H1 blockers have additive benefit over H1 blockers alone in treating anaphylaxis.
See some more details on the topic How Do H1 Receptor Antagonists Work? here:
Histamine H1 Receptor Antagonist – an overview
H1-receptor antagonists competitively inhibit the interaction of histamine with the H1-receptor, thereby inhibiting the vasodilator effects of histamine and …
H1 antagonist – Wikipedia
H1 antagonists, also called H1 blockers, are a class of medications that block the action of histamine at the H1 receptor, helping to relieve allergic …
Antihistamines – American Osteopathic College of Dermatology
Mechanism: H1-antihistamines competitively block histamines from attaching to histamine receptors that are located on nerves, smooth muscle, endothelium, …
Urticaria Medication: H1-receptor antagonist antihistamines …
These agents block the histamine response in sensory nerve endings and blood vessels. They act by competitive inhibition of histamine at the H1 …
What happens when histamine binds to the H2 receptor?
Histamine binds to the H2-receptors located on the acid-secreting gastric parietal cells. This initiates a cascade that eventually increases the intracellular cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP). Cyclic AMP activates the hydrogen-potassium pump, causing secretion of hydrogen ions.
What are the differences between the H2-receptor antagonists?
On a weight basis, famotidine is approximately eight times more potent than ranitidine and 40 times more potent than cimetidine. Cimetidine, ranitidine and famotidine are competitive antagonists, while the long-acting H2-receptor antagonists, e.g. loxtidine and lamitidine, are insurmountable H2-receptor blockers.
How do histamines work?
Histamine works with nerves to produce itching. In food allergies it can cause vomiting and diarrhea. And it constricts muscles in the lungs, making it harder to breathe. Most worrisome is when histamine causes anaphylaxis, a severe reaction that is potentially fatal.
Is histamine a vasodilator or vasoconstrictor?
Histamine (HA) is a potent mediator in many physiological processes: it causes vasodilation or vasoconstriction, stimulates heart rate and contractility, and contraction of smooth muscles in the intestine and airways. It works as a neurotransmitter, immunomodulator, and regulator of haematopoiesis and angiogenesis.
Histamine and Antihistamines, Pharmacology, Animation
Images related to the topicHistamine and Antihistamines, Pharmacology, Animation

What effect is associated with a first-generation H1 receptor antagonist?
The older, first-generation H1 antagonists (eg, diphenhydramine, hydroxyzine) are effective in reducing the lesions and pruritus but can produce adverse effects, such as drowsiness and anticholinergic effects. These are no longer first-line treatments, but can be helpful when sedation is needed.
What is the difference between H1 and H2 antihistamines?
H1 receptor antagonists are typically utilized to suppress the body’s histamine-mediated effects in anaphylactoid or anaphylactic reactions. H2 antagonists are competitive antagonists at the parietal cell H2 receptor and are typically used to suppress gastric acid secretion.
Why do antihistamines make people sleepy?
They can cross the blood-brain barrier and inhibit one of the other functions of histamines, which is the role they play in regulating sleep and wakefulness. This disruption of the action of histamines in the brain results in drowsiness.
What happens when antihistamines cross the blood-brain barrier?
First-generation H1 antihistamines cross the blood-brain barrier, and in usual doses, they potentially cause sedation and impair cognitive function and psychomotor performance. These medications, some of which have been in use for more than 6 decades, have never been optimally investigated.
Why do antihistamines cause anticholinergic effects?
Older adults are especially sensitive to the central nervous system- and anticholinergic-related side effects of sedating antihistamines because of decreased cholinergic neurons or receptors in the brain, reduced hepatic and renal function, and increased blood-brain permeability.
What is the difference between an H2 blocker and a proton pump inhibitor?
“H2 blockers work by blocking the histamine receptors in parietal cells to decrease the amount of acid produced (although there are other stimuli so that some acid is still produced).” PPIs work by “shutting down the proton pumps in these cells and preventing the acid from being secreted into the stomach.”
What are H1 and H2 blockers?
H1-antihistamines are used to treat allergy symptoms. Within this group are two generations called the first generation and second generation antihistamines. H2-antihistamines are used to treat gastrointestinal conditions.
How does histamine affect stomach acid?
Histamine 2 blockers (also called H2 blockers) target a substance called histamine. The result is that your stomach makes less acid, which cuts down on heartburn.
How do H2-receptor antagonists reduce the secretion of acids?
Histamine-2 receptor antagonists (H2RAs) decrease acid secretion by inhibiting histamine-2 receptors on gastric parietal cells. Historically, cimetidine was the first H2RA available. Ranitidine, famotidine and nizatidine are the most popular, although very poorly studied in children.
Pharmacology of Histamine , Histamine receptors and Anti-histamine Drugs : Part 1
Images related to the topicPharmacology of Histamine , Histamine receptors and Anti-histamine Drugs : Part 1

What is the difference between H1 and H2 receptors?
The key difference between H1 and H2 receptors is that the H1 receptor couples with Gq/11 stimulating phospholipase C while the H2 receptor interacts with Gs to activate adenylyl cyclase. Histamine is an organic nitrogenous compound that involves local immune responses.
How do proton pump inhibitors work?
PPIs work by inhibiting certain stomach cells from “pumping” acid into the stomach. When taken 30 to 60 minutes before a meal, PPIs can prevent or reduce heartburn. However, they do not work as well when taken on demand as they do when taken over a period of time.
Related searches to How Do H1 Receptor Antagonists Work?
- what are h1 receptor antagonist
- h1 receptor antagonist side effects
- h2 receptor antagonist function
- h3 receptor antagonist mechanism of action
- how do h1 receptor antagonists work
- how do h1 blockers work
- h1 receptor antagonist examples
- h1 receptor agonist examples
- 4th generation antihistamine
- h1 and h2 blockers list
- h1 receptor antagonist uses
- how do serotonin receptor antagonists work
- h1 receptor antagonist effects
- h1 receptor agonist
- is benadryl an h1 blocker
- uses of h1 receptor antagonist
- h1 antagonist classification
Information related to the topic How Do H1 Receptor Antagonists Work?
Here are the search results of the thread How Do H1 Receptor Antagonists Work? from Bing. You can read more if you want.
You have just come across an article on the topic How Do H1 Receptor Antagonists Work?. If you found this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much.