Are you looking for an answer to the topic “How do hair cells transmit signals?“? We answer all your questions at the website Chiangmaiplaces.net in category: +100 Marketing Blog Post Topics & Ideas. You will find the answer right below.
The depolarization of the cell stimulates the release of chemicals called neurotransmitters from the base of the hair cell. The neurotransmitters are absorbed by the nerve fibres located at the basal end of the hair cell, stimulating them to send an electrical signal along the cochlear nerve.In the cochlea, hair cells spiral along the basilar membrane within the organ of Corti. Airborne sounds set the eardrum in motion, which is conveyed to the cochlea by bones of the middle ear. This flexes the membrane up and down.The inner hair cells transform the sound vibrations in the fluids of the cochlea into electrical signals that are then relayed via the auditory nerve to the auditory brainstem and to the auditory cortex.

Table of Contents
How do hair cells transmit signals about hearing and equilibrium?
In the cochlea, hair cells spiral along the basilar membrane within the organ of Corti. Airborne sounds set the eardrum in motion, which is conveyed to the cochlea by bones of the middle ear. This flexes the membrane up and down.
How do hair cells function as sensors?
The inner hair cells transform the sound vibrations in the fluids of the cochlea into electrical signals that are then relayed via the auditory nerve to the auditory brainstem and to the auditory cortex.
040 The Role of Hair Cells in Hearing
Images related to the topic040 The Role of Hair Cells in Hearing

How do hair cells in the cochlea perform signal transduction?
How do hair cells in the cochlea perform signal transduction? depolarization. B) Sound vibrations activate metabotropic receptors on the hair cell, causing depolarization.
How do hair cells generate action potentials?
This mechanism transduces mechanical energy into neural impulses. An inward K+ current depolarizes the cell, and opens voltage-dependent calcium channels. This in turn causes neurotransmitter release at the basal end of the hair cell, eliciting an action potential in the dendrites of the VIIIth cranial nerve.
Where does the signal go after leaving the hair cells?
Where does the signal go after leaving the hair cells? After the signal leaves the hair cells, the signal gets sent through the auditory nerve and then to the auditory cortex of the brain.
How do hair cells in the cochlea and vestibular apparatus transduce mechanical vibrations into electrical signals?
The depolarization of the cell stimulates the release of chemicals called neurotransmitters from the base of the hair cell. The neurotransmitters are absorbed by the nerve fibres located at the basal end of the hair cell, stimulating them to send an electrical signal along the cochlear nerve.
How do hair cells stimulate the auditory nerve quizlet?
fine filaments found in both types of hair cells, In hearing, these transform the mechanical energy of sound waves into electrical signals for the hair cells, which ultimately leads to an excitation of the auditory nerve.
See some more details on the topic How do hair cells transmit signals? here:
Chapter 12: Auditory System: Structure and Function
Hair cells in the Organ of Corti in the cochlea of the ear respond to sound. Hair cells in the cristae ampullares in the semicircular ducts respond to angular …
17.4 Hearing and Vestibular Sensation – Concepts of Biology
The vestibular hair cells also send signals to the thalamus and to somatosensory cortex, but also to the cerebellum, the structure above the brainstem that …
Hair cells | Cochlea
Hair cell stereocilia are at the core of electro-mechanical transduction; the transformation of sound vibration into a neural signal that can be …
Transduction of Sound | Biology for Majors II
The inner hair cells are most important for conveying auditory information to the brain. About 90 percent of the afferent neurons carry information from inner …
How are hair cells excited?
Stimulation of the auditory hair cells
As an auditory stimulus vibrates the basilar membrane, it causes the tectorial membrane to shift in position. This motion excites the auditory hair cells by placing a shearing force upon their stereocilia (see mechanotransduction for further details about this process).
What channels are on hair cells?
In addition to the sensory MET channel, hair cells express the mechanically gated ion channel PIEZO2, which is localized near the base of stereocilia and not essential for sensory transduction. The function of PIEZO2 in hair cells is not entirely clear but it might have a role in damage sensing and repair processes.
In which way is the mechanism of hair cell transduction distinct from sensory transduction mechanisms that occur outside the ear?
In which of the following ways is the mechanism of hair-cell transduction distinct from sensory transduction mechanisms that occur outside the ear? Potassium influx from the endolymph depolarizes the hair cell. Potassium efflux into the perilymph repolarizes the hair cell.
What happens when a hair cell is stimulated?
As hair cells depolarize, voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels near basolateral synapses open; elevated Ca2+ levels stimulate the neurotransmitter release at the glutamatergic synapses, initiating signal propagation to afferent neurons (Ottersen et al., 1998).
2-Minute Neuroscience: The Cochlea
Images related to the topic2-Minute Neuroscience: The Cochlea

Do inner hair cells transmit frequency information to the brain?
Inner hair cells synapse with type I auditory nerve fibers, and depolarization of the inner hair cells increases the probability of action potential generation in these fibers. This provides the main route for transmission of information along the auditory nerve to the central auditory system.
What neurotransmitter do outer hair cells release?
Abstract. The dominant efferent innervation of the cochlea terminates on outer hair cells (OHCs), with acetylcholine (ACh) being its principal neurotransmitter.
What neurotransmitter is released from depolarized hair cells?
The calcium entry through these channels results in the increased release of neurotransmitter (glutamate) from the base of the hair cells, exciting the peripheral terminals of afferent fibers of the vestibulocochlear nerve.
How is sound transmitted and heard?
Sound waves enter the ears and travel down a canal at the end of which is a thin, tightly stretched membrane called eardrum. As the sound wave strikes the eardrum, it vibrates and the vibrations reach the inner ear which sends signals to the brain. The brain interprets the signals and we hear the sound.
What are the 6 steps of hearing?
- Step 1: Hearing history. …
- Step 2: Visual exam of the external ear canal (otoscopy) …
- Step 3: Middle ear check. …
- Step 4: Sound detection. …
- Step 5: Word recognition. …
- Step 6: Results and recommendations.
How does the ear send messages to the brain?
Our hearing system has many working parts. The outer ear collects the sounds which vibrate the eardrum in the middle ear. The inner ear gets these vibrations and sends them to the auditory nerve. These impulses go to our brain, which translates them into what we hear.
How do the cochlea hair cells convert energy into electrochemical neural activity?
so that the motion of the traveling wave in the cochlear fluids creates shearing forces on the hair cells. The resulting movement of the stereocilia activates transduction mechanisms that convert mechanical energy into electrochemical activity.
How do outer hair cells amplify sound?
Outer hair cells contract and elongate with each cycle of sound as their intracellular voltage changes. This amplifies the vibration of the organ of Corti, permitting exquisite hearing sensitivity and frequency selectivity. OHCs have an intracellular turgor pressure to help maintain their shape.
How does signal transduction occur in the ear?
Vibrating objects, such as vocal cords, create sound waves or pressure waves in the air. When these pressure waves reach the ear, the ear transduces this mechanical stimulus (pressure wave) into a nerve impulse (electrical signal) that the brain perceives as sound.
How do hair cells stimulate the auditory nerve psychology?
The basilar membrane is a thin strip of tissue within the cochlea. The activation of hair cells is a mechanical process: the stimulation of the hair cell ultimately leads to activation of the cell. As hair cells become activated, they generate neural impulses that travel along the auditory nerve to the brain.
Journey of Sound to the Brain
Images related to the topicJourney of Sound to the Brain
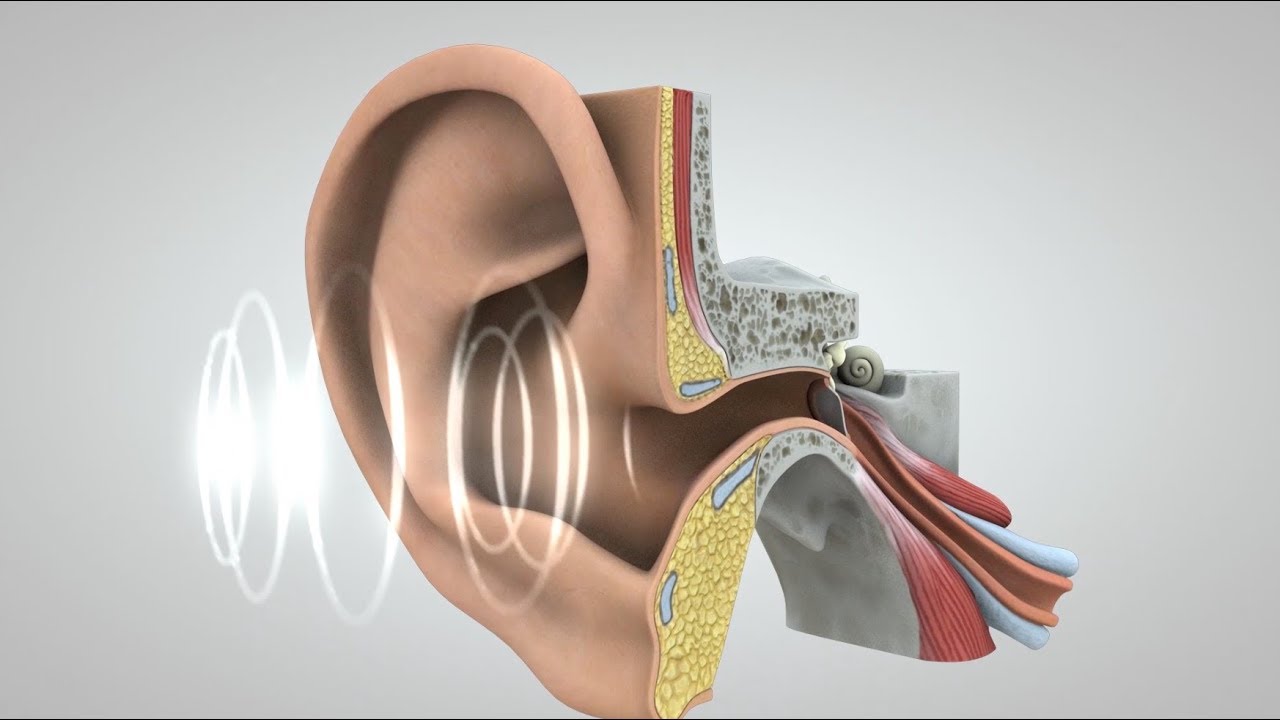
What is the name of the neurotransmitter released by hair cells in the cochlea quizlet?
Hair cells: Cells that support the stereocilia that transduce mechanical movement in the cochlea and vestibular labyrinth into neural activity sent to the brain stem; some hair cells also receive inputs from the brain, when they are bent they release the neurotransmitter glutamate which cause nearby auditory neurons to …
Which of the following cues does her brain use to locate where the sounds of the other players are coming from?
Which of the following cues does her brain use to locate where the sounds of the other players are coming from? Correct Answers: The intensity of the sound in each ear.
Related searches to How do hair cells transmit signals?
- transmission of sound waves in the inner ear is known as
- how do cells receive signals
- how do hair cells stimulate the auditory nerve
- how are signals transmitted
- inner vs outer hair cells
- how do cells recognize signals
- how do cells process signals
- how do hair cells transmit signals about hearing and equilibrium
- stimulation of hair cells
- damage to inner hair cells
- inner hair cells function
- what is the function of hair cells outer and inner
- how do cells send signals
- pathway of sound waves through the ear
Information related to the topic How do hair cells transmit signals?
Here are the search results of the thread How do hair cells transmit signals? from Bing. You can read more if you want.
You have just come across an article on the topic How do hair cells transmit signals?. If you found this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much.