Are you looking for an answer to the topic “How do histamine receptors work?“? We answer all your questions at the website Chiangmaiplaces.net in category: +100 Marketing Blog Post Topics & Ideas. You will find the answer right below.
Histamine receptors are 7-transmembrane receptors which mediate cellular responses to the biogenic amine histamine. Histamine may be released as a transmitter in neuronal preparations or as a mediator of an inflammatory response by mast cells. Currently, four histamine receptors have been identified.Histamine action at these receptors stimulates the release of gastric acid, excess of which can result in gastroenteritis. These receptors are also found on heart, uterus and vascular smooth muscle cells. Histamine reacting with the receptor at these places encourages smooth muscle relaxation.This receptor is activated by the biogenic amine histamine. It is expressed in smooth muscles, on vascular endothelial cells, in the heart, and in the central nervous system.

Table of Contents
What happens when histamine receptors are stimulated?
Histamine action at these receptors stimulates the release of gastric acid, excess of which can result in gastroenteritis. These receptors are also found on heart, uterus and vascular smooth muscle cells. Histamine reacting with the receptor at these places encourages smooth muscle relaxation.
What activates histamine receptor?
This receptor is activated by the biogenic amine histamine. It is expressed in smooth muscles, on vascular endothelial cells, in the heart, and in the central nervous system.
Histamine and Antihistamines, Pharmacology, Animation
Images related to the topicHistamine and Antihistamines, Pharmacology, Animation

How does histamine work in the immune system?
Histamine affects the maturation of immune system cells and alters their activation, polarization, chemotaxis, and effector functions. Histamine also regulates antigen-specific TH1 and TH2 cells, as well as related antibody isotype responses.
What are histamines and how do they work?
Histamine – a chemical found in some of the body’s cells – causes many of the symptoms of allergies, such as a runny nose or sneezing. When a person is allergic to a particular substance, such as a food or dust, the immune system mistakenly believes that this usually harmless substance is actually harmful to the body.
What triggers histamine release?
Histamine is a chemical created in the body that is released by white blood cells into the bloodstream when the immune system is defending against a potential allergen. This release can result in an allergic reaction from allergy triggers such as pollen, mold, and certain foods.
What happens when histamine receptors are blocked?
Inhibition of H1 receptors leads to decreased alertness and subjective sedation. In addition to their effects on histamine, these medications can also have anticholinergic effects. The effect of specific antihistamines on sleep and alertness varies with the degree to which they cross the blood–brain barrier.
What does histamine do during inflammation?
Histamine increases the vasodilatation, and also increases the vascular permeability in the immediate transient phase of the acute inflammatory reaction. This act as a chemical mediator in acute inflammation.
See some more details on the topic How do histamine receptors work? here:
The Role of Histamine and Histamine Receptors in Mast Cell …
Histamine and its receptors (H1R–H4R) play a crucial and significant role in the development of various allergic diseases.
Histamine and its receptors – PMC – NCBI
Histamine H3 receptors act as presynaptic autoreceptors that inhibit the synthesis and release of histamine in the histaminergic neurones in the …
The role of histamine H1 and H4 receptors in allergic … – Nature
Histamine has a key role in allergic inflammatory conditions. The inflammatory responses resulting from the liberation of histamine have long been thought to be …
Histamine receptor – Wikipedia
The histamine receptors are a class of G protein–coupled receptors which bind histamine as their primary endogenous ligand. There are four known histamine …
What are the main actions of histamine?
Once released from its granules, histamine produces many varied effects within the body, including the contraction of smooth muscle tissues of the lungs, uterus, and stomach; the dilation of blood vessels, which increases permeability and lowers blood pressure; the stimulation of gastric acid secretion in the stomach; …
Does histamine trigger mast cells?
Histamine-mediated mast cell activation plays a critical role in various allergic diseases. Histamine may induce the release of leukotrienes, cytokines, and chemokines via H4R in CD34+ cord blood-derived human mast cells (33).
Pharmacology – ANTIHISTAMINES (MADE EASY)
Images related to the topicPharmacology – ANTIHISTAMINES (MADE EASY)
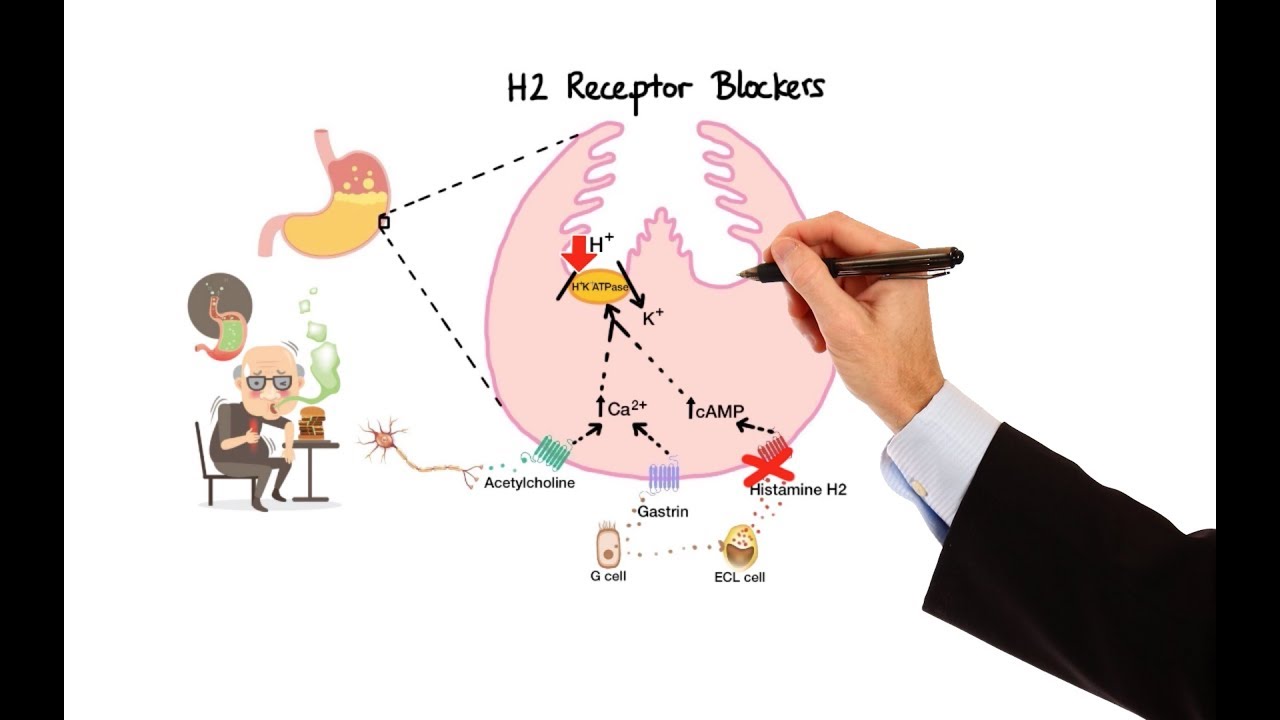
What is the role of histamines in human body?
Histamine regulates a plethora of pathophysiological and physiological processes, such as secretion of gastric acid, inflammation, and the regulation of vasodilatation and bronchoconstriction (29, 30). In addition, it can also serve as a neurotransmitter (31).
Do histamines help fight viruses?
There are numerous studies showing that mast cells and basophils can respond to viruses by releasing mediators such as histamine and cytokines [20].
Why does histamine cause itching?
Scientists say histamine acts on the itch receptors in your skin, initiating the itch. For example, when a mosquito bites your arm, the mosquito’s irritating saliva triggers the release of histamine. The histamine tickles your skin’s itch receptors, which rush this message to your brain: Scratch.
What causes the body to produce too much histamine?
Bacterial overgrowth is another contributing factor for developing a histamine intolerance. Bacteria grows when food isn’t digested properly, causing histamine overproduction. Normal levels of DAO enzymes can’t break down the increased levels of histamine in your body, causing a reaction.
What stimulates mast cells to release histamine?
In the skin, antigens, via IgE, activate mast cells in the deep layers of connective tissue. Mast cells release histamine as well as other vasoactive molecules, which cause urticaria (hives). If the antigen activates mast cells in deeper tissue, this can lead to angioedema.
Does exercise release histamine?
The histamine released during exercise appears to result from mast cell degranulation, as well as de novo synthesis of histamine. This response, a fundamental element of exercise, seems to comprise an anaphylactoid reaction and not an allergic reaction to exercise.
How do you remove histamine from your body?
Vitamin C is a natural antihistamine, which means it can lower histamine levels and mitigate allergic reactions and symptoms. Consume plenty of Vitamin C rich foods, like tropical fruits, citrus fruits, broccoli and cauliflower, and berries.
Can too much histamine cause inflammation?
When they leave the mast cells, histamines boost blood flow in the area of your body the allergen affected. This causes inflammation, which lets other chemicals from your immune system step in to do repair work.
Histamine and its Actions – Quick Review!
Images related to the topicHistamine and its Actions – Quick Review!

Does B12 increase histamine?
Folic acid (with vitamin B12) can help to raise the histamine level.
Does histamine cause vasoconstriction or vasodilation?
Histamine (HA) is a potent mediator in many physiological processes: it causes vasodilation or vasoconstriction, stimulates heart rate and contractility, and contraction of smooth muscles in the intestine and airways. It works as a neurotransmitter, immunomodulator, and regulator of haematopoiesis and angiogenesis.
Related searches to How do histamine receptors work?
- role of histamine in inflammation
- h1 receptor
- h1 receptor function
- types of histamine receptors
- what are histamine receptors
- what do histamine receptors do
- what blocks histamine receptors
- histamine mechanism of action
- histamine receptors location and function
- what are the histamine receptors
- what does blocking histamine receptors do
- histamine receptors in stomach
- how do histamine receptors work
- histamine receptor location
Information related to the topic How do histamine receptors work?
Here are the search results of the thread How do histamine receptors work? from Bing. You can read more if you want.
You have just come across an article on the topic How do histamine receptors work?. If you found this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much.