Are you looking for an answer to the topic “How do hydrophobic molecules pass through the plasma membrane?“? We answer all your questions at the website Chiangmaiplaces.net in category: +100 Marketing Blog Post Topics & Ideas. You will find the answer right below.
The lipid bilayer is the main fabric of the membrane, and its structure creates a semipermeable membrane. The hydrophobic core impedes the diffusion of hydrophilic structures such as ions and polar molecules, but allows hydrophobic molecules, which can dissolve in the membrane, to cross it with ease.They are semi-permeable, which means that some molecules can diffuse across the lipid bilayer but others cannot. Small hydrophobic molecules and gases like oxygen and carbon dioxide cross membranes rapidly. Small polar molecules, such as water and ethanol, can also pass through membranes, but they do so more slowly.3 – Simple Diffusion Across the Cell (Plasma) Membrane: The structure of the lipid bilayer allows small, uncharged substances such as oxygen and carbon dioxide, and hydrophobic molecules such as lipids, to pass through the cell membrane, down their concentration gradient, by simple diffusion.
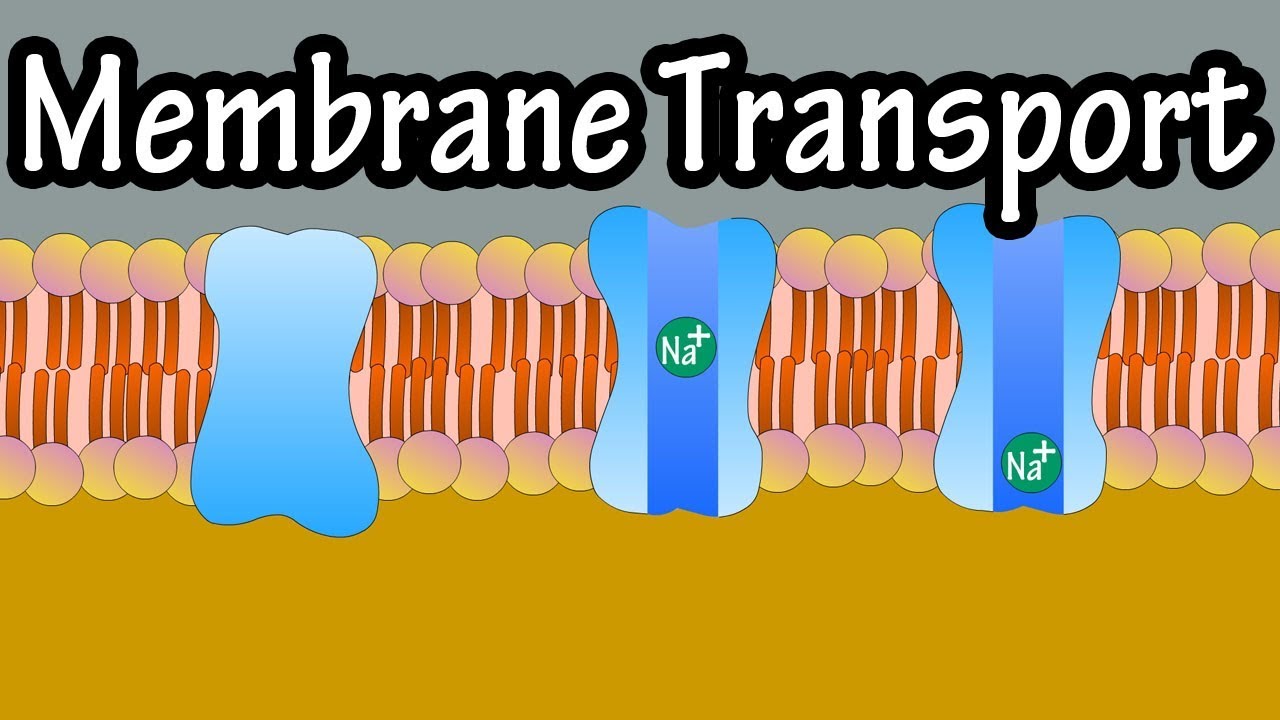
Table of Contents
Can hydrophobic molecules pass through membrane?
They are semi-permeable, which means that some molecules can diffuse across the lipid bilayer but others cannot. Small hydrophobic molecules and gases like oxygen and carbon dioxide cross membranes rapidly. Small polar molecules, such as water and ethanol, can also pass through membranes, but they do so more slowly.
How do hydrophobic molecules move across a membrane?
3 – Simple Diffusion Across the Cell (Plasma) Membrane: The structure of the lipid bilayer allows small, uncharged substances such as oxygen and carbon dioxide, and hydrophobic molecules such as lipids, to pass through the cell membrane, down their concentration gradient, by simple diffusion.
Cell Membrane Transport – Transport Across A Membrane – How Do Things Move Across A Cell Membrane
Images related to the topicCell Membrane Transport – Transport Across A Membrane – How Do Things Move Across A Cell Membrane

How do hydrophobic molecules pass through the phospholipid bilayer?
The opposite can be said for molecules that are hydrophobic (water fearing), they are called nonpolar molecules. Here are the 5 types: Small, nonpolar molecules (e.g. oxygen and carbon dioxide): These molecules can pass through the lipid bilayer and do so by squeezing through the phospholipid bilayers.
How do molecules pass through the plasma membrane?
The simplest mechanism by which molecules can cross the plasma membrane is passive diffusion. During passive diffusion, a molecule simply dissolves in the phospholipid bilayer, diffuses across it, and then dissolves in the aqueous solution at the other side of the membrane.
Why do hydrophobic molecules pass through lipid bilayer?
The lipid bilayer is the main fabric of the membrane, and its structure creates a semipermeable membrane. The hydrophobic core impedes the diffusion of hydrophilic structures such as ions and polar molecules, but allows hydrophobic molecules, which can dissolve in the membrane, to cross it with ease.
What molecules are hydrophobic and can easily cross the plasma membrane?
Small lipids and steroids are hydrophobic and can readily cross the membrane. Molecules that are hydrophilic, on the other hand, cannot pass through the cell membrane—at least not without help—because they are water-loving like the exterior of the membrane, and are therefore excluded from the interior of the membrane.
Why can’t hydrophilic molecules cross the plasma membrane?
Molecules that are hydrophilic, on the other hand, cannot pass through the plasma membrane—at least not without help—because they are water-loving like the exterior of the membrane, and are therefore excluded from the interior of the membrane.
See some more details on the topic How do hydrophobic molecules pass through the plasma membrane? here:
2.5: Phospholipid Bilayers – Biology LibreTexts
Molecules that are hydrophobic can easily pass through the plasma membrane, if they are small enough, because they are water-hating like the …
The Plasma Membrane
The plasma membrane is selectively permeable; hydrophobic molecules and small polar molecules can diffuse through the lipid layer, but ions and large polar …
Cell Membranes | Learn Science at Scitable – Nature
Small polar molecules, such as water and ethanol, can also pass through membranes, but they do so more slowly. On the other hand, cell membranes restrict …
The Cell Membrane – Anatomy and Physiology – BC Open …
The structure of the lipid bilayer allows small, uncharged substances such as oxygen and carbon dioxide, and hydrophobic molecules such as lipids, to pass …
Is hydrophobic polar or nonpolar?
Hydrophobes are nonpolar molecules and usually have a long chain of carbons that do not interact with water molecules. The mixing of fat and water is a good example of this particular interaction.
What is responsible for lipophilic molecules to cross across plasma membrane?
Phospholipid bilayer is responsible fo lipophilic molecules to cross across plasma membrane.
Which one of the following molecules can most easily pass through the plasma membrane unassisted?
Water is a small molecule that easily diffuses through a cell membrane despite the lipid tails. Water diffusion is called osmosis. Oxygen is a small molecule and it’s nonpolar, so it easily passes through a cell membrane.
Why do hydrophobic molecules repel water?
Water does not tend to wet hydrophobic surfaces; rather, the droplets stay beaded up with high values of contact angle. Hydrophobic molecules called hydrophobes repel bodies of water and, owing to the fact that hydrophobes are non-polar, they attract other neutral molecules and non-polar solvents.
What part of the plasma membrane is hydrophobic?
The heads, which form the outer and inner linings, are “hydrophilic” (water loving) while the tails that face the interior of the cell membrane are “hydrophobic” (water fearing).
Inside the Cell Membrane
Images related to the topicInside the Cell Membrane
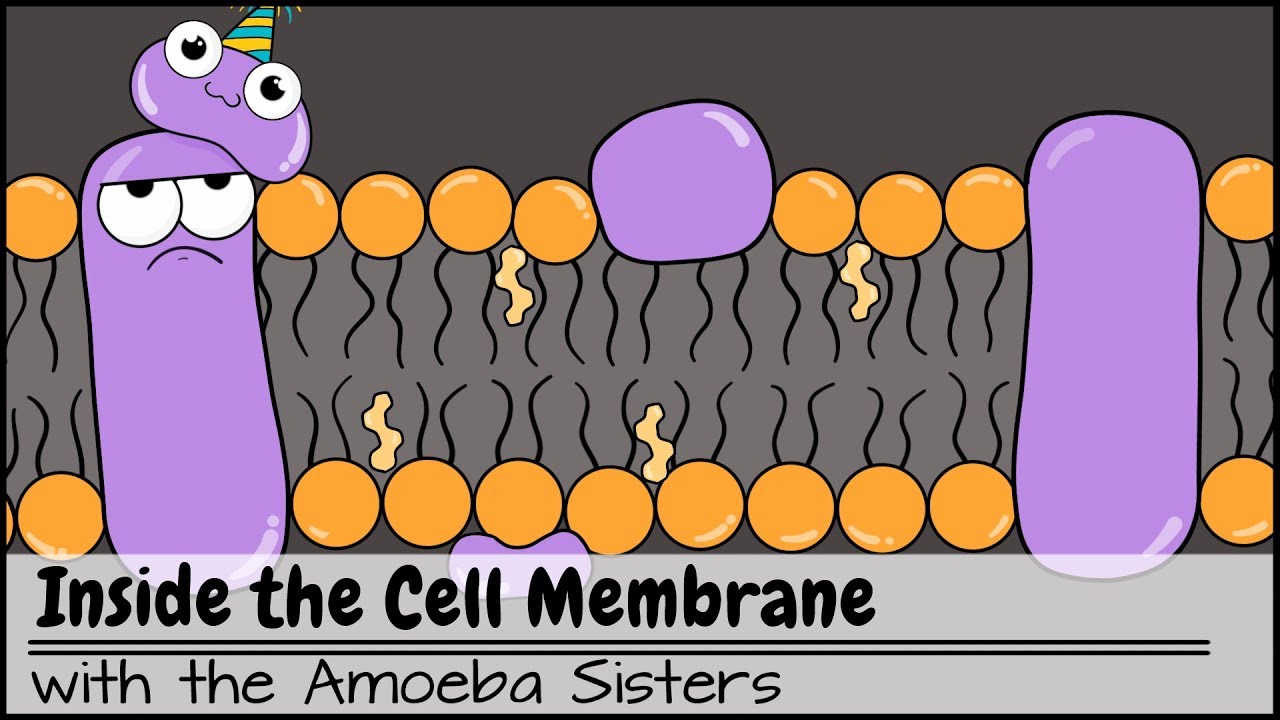
What are the three ways that the molecules can cross the cell membrane?
Examples include the diffusion of oxygen and carbon dioxide, osmosis of water, and facilitated diffusion. Types of passive transport.
What molecules can diffuse across the plasma membrane?
Small nonpolar molecules, such as O2 and CO2, are soluble in the lipid bilayer and therefore can readily cross cell membranes. Small uncharged polar molecules, such as H2O, also can diffuse through membranes, but larger uncharged polar molecules, such as glucose, cannot.
How did the molecules pass through enter the membrane osmosis?
Water(solvent) molecules travel from A across the cell membrane / semi permeable membrane to B until the concentrations of A and B become equal. Water can move through the cell membrane directly through the membrane (simple diffusion ) or through protein channels called aquaporins.
Why can lipids pass through lipid bilayers?
Because of the chemical and structural nature of the phospholipid bilayer (hydrophobic core), only lipid-soluble molecules and some small molecules are able to freely pass through the lipid bilayer.
Which of the following would likely move through the lipid bilayer of a plasma membrane most rapidly?
Of these molecules, it is likely that CO2 moves by far faster than any other molecule through the lipid bilayer.
Is the phospholipid bilayer hydrophobic?
Phospholipids. Phospholipids, arranged in a bilayer, make up the basic fabric of the plasma membrane. They are well-suited for this role because they are amphipathic, meaning that they have both hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions.
What molecules are hydrophobic and can easily cross the plasma membrane quizlet?
Small, nonpolar molecules are hydrophobic, so they can easily cross the phospholipid bilayer of the plasma membrane.
Why can generally only very small hydrophobic molecules cross the cell membrane by simple diffusion?
Very small polar molecules, such as water, can cross via simple diffusion due to their small size. Charged atoms or molecules of any size cannot cross the cell membrane via simple diffusion as the charges are repelled by the hydrophobic tails in the interior of the phospholipid bilayer.
What molecules Cannot easily pass through the membrane?
Answer and Explanation: Large molecules, polar molecules, and ions, cannot easily pass through the cell membrane.
Why hydrophobic water hating molecules can easily cross the plasma membrane while hydrophilic water loving molecules Cannot?
Hydrophobic molecules can pass though the membrane because they are water-hating like the interior of the membrane. Hydrophilic molecules can’t pass through because they are water-loving like the exterior of the membrane.
Fluid Mosaic Model of the Plasma Membrane – Phospholipid Bilayer
Images related to the topicFluid Mosaic Model of the Plasma Membrane – Phospholipid Bilayer
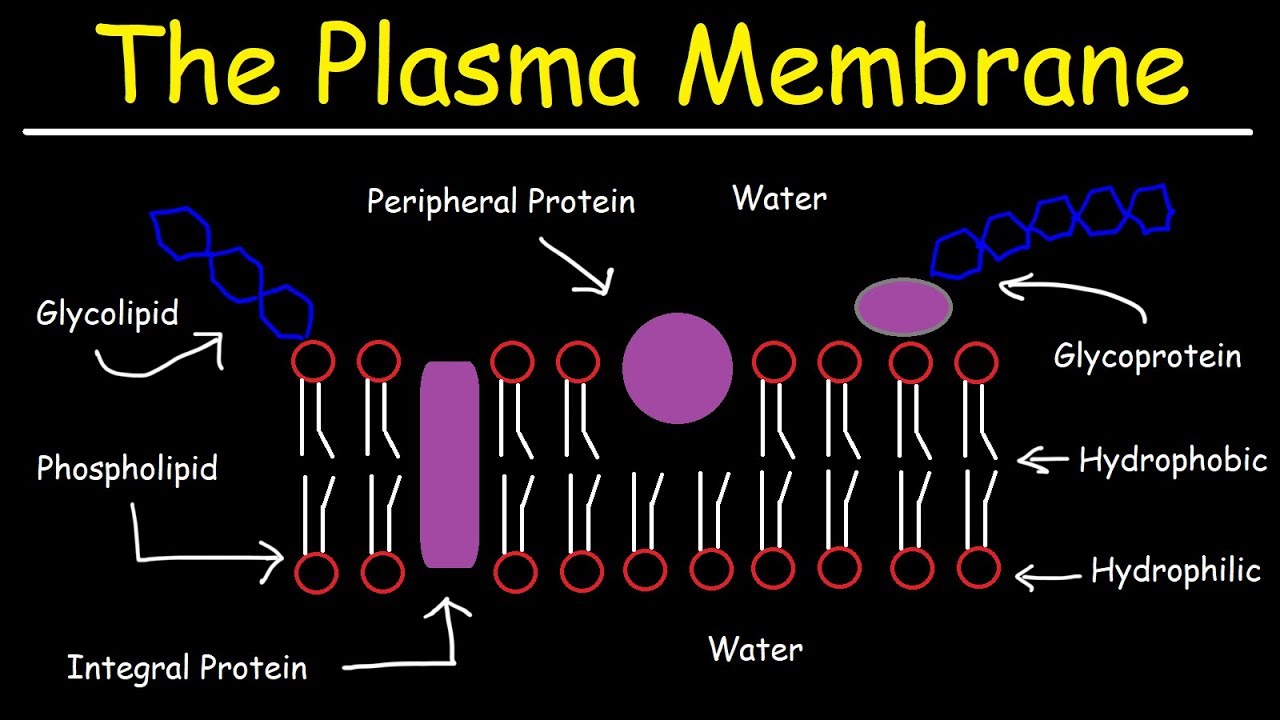
Why is it difficult for polar hydrophilic molecules to cross a cell membrane?
Polar or charged molecules have a difficult time crossing the membrane because of the hydrophobic core – water molecules “hydrate” the surface of polar molecules, and the hydrophobic core of the membrane strongly resists water. See the answer. Ions can use facilitated diffusion or active transport.
Which of the following are hydrophobic molecules that can diffuse directly through the plasma membrane?
Small nonpolar (hydrophobic) molecules, such as dissolved gases (O2, CO2, N2) and small lipids, can pass directly through the membrane.
Related searches to How do hydrophobic molecules pass through the plasma membrane?
- can non polar molecules pass through cell membrane
- what kind of molecules pass through a cell membrane most easily
- which portion of the bilayer is hydrophobic
- phospholipid bilayer
- how do charged molecules pass through the plasma membrane
- phospholipid bilayer structure
- why cant polar molecules pass through membrane
- how do small polar molecules pass through the plasma membrane
- how do hydrophobic molecules pass through the plasma membrane
- how can some large molecules and charged ions get through the cell membrane
Information related to the topic How do hydrophobic molecules pass through the plasma membrane?
Here are the search results of the thread How do hydrophobic molecules pass through the plasma membrane? from Bing. You can read more if you want.
You have just come across an article on the topic How do hydrophobic molecules pass through the plasma membrane?. If you found this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much.