Are you looking for an answer to the topic “How do integrins form focal adhesions?“? We answer all your questions at the website Chiangmaiplaces.net in category: +100 Marketing Blog Post Topics & Ideas. You will find the answer right below.
It is generally believed that the assembly of cell-ECM adhesion structures is initiated by interactions of cell surface integrins with multivalent adhesive ECM proteins (e.g., fibronectin), which result in integrin clustering and formation of nascent cell-ECM adhesion structures (e.g., focal complexes).Focal adhesion formation is initiated by receptor-matrix binding along the cell periphery at the leading edge. These early complexes, hitherto referred as “nascent adhesions”, initially attach to actin filaments via adaptor proteins such as talin [3][4].Focal adhesions are large structures through which integrins and scaffold proteins link the actin cytoskeleton to the extracellular matrix.

Table of Contents
How are focal adhesions formed?
Focal adhesion formation is initiated by receptor-matrix binding along the cell periphery at the leading edge. These early complexes, hitherto referred as “nascent adhesions”, initially attach to actin filaments via adaptor proteins such as talin [3][4].
Are integrins focal adhesions?
Focal adhesions are large structures through which integrins and scaffold proteins link the actin cytoskeleton to the extracellular matrix.
Focal adhesions – Mary Beckerle (Utah)
Images related to the topicFocal adhesions – Mary Beckerle (Utah)

What are focal adhesion complexes?
Focal adhesions are large, dynamic protein complexes through which the cytoskeleton of a cell connects to the ECM. They are limited to clearly defined ranges of the cell, at which the plasma membrane closes to within 15 nm of the ECM substrate.
Are integrins cell adhesion molecules?
In blood cells, as we have seen, integrins also serve as cell-cell adhesion molecules, helping the cells bind to other cells, as well as to the extracellular matrix.
What are focal adhesions made of?
Abstract. Focal adhesions (FAs) are complex plasma membrane-associated macromolecular assemblies that engage with the surrounding extracellular matrix (ECM) via integrin receptors and physically connect with the actin cytoskeleton through the recruitment of numerous FA-associated proteins.
How do integrins work?
Integrins bind cell-surface ligands to promote cellular interactions with the ECM and with other cells in the transduction of complex signals that modulate many cellular processes, such as adhesion, migration, and differentiation.
What do focal adhesions do?
Focal adhesions are large macromolecular assemblies that form mechanical links between intracellular actin bundles and the ECM. Thus, cell adhesion to the ECM at focal adhesions allows cells to crawl during migration. Nascent adhesions form at the leading edge and grow into focal complexes in lamellipodia.
See some more details on the topic How do integrins form focal adhesions? here:
What are focal adhesions? | MBInfo
Focal adhesions are integrin-containing, multi-protein structures that form mechanical links between intracellular actin bundles and the extracellular …
Integrin adhesions – PMC – NCBI
Sites of integrin clustering form distinct types of adhesions: nascent adhesions, focal complexes, focal …
Focal Adhesion – an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
Focal adhesions (FAs) are complex plasma membrane-associated macromolecular assemblies that engage with the surrounding extracellular matrix (ECM) via integrin …
Focal adhesion – Wikipedia
In cell biology, focal adhesions are large macromolecular assemblies through which mechanical force and regulatory signals are transmitted between the …
What is the major membrane receptor involved with focal adhesions quizlet?
=The main integral membrane protein involved with focal adhesions is focal adhesion kinase.
What is the difference between focal adhesions and Hemidesmosomes?
Focal Adhesion and Hemidesmosome
Focal adhesion mediates the adhesion between cells and the extracellular matrix. Hemidesmosomes anchor the epidermal keratin filament cytoskeleton to the extracellular matrix. They are crucial for the mechanical integrity of the skin.
What are the 2 main differences between adherens junctions and focal adhesions What do they have in common?
1. Adherens junctions and desmosomes hold cells together and are formed by transmembrane adhesion proteins that belong to the cadherin family. 2. Focal adhesions and hemidesmosomes bind cells to the extracellular matrix and are formed by transmembrane adhesion proteins of the integrin family.
Integrin Activation Signalling | PAR-1 Receptor
Images related to the topicIntegrin Activation Signalling | PAR-1 Receptor
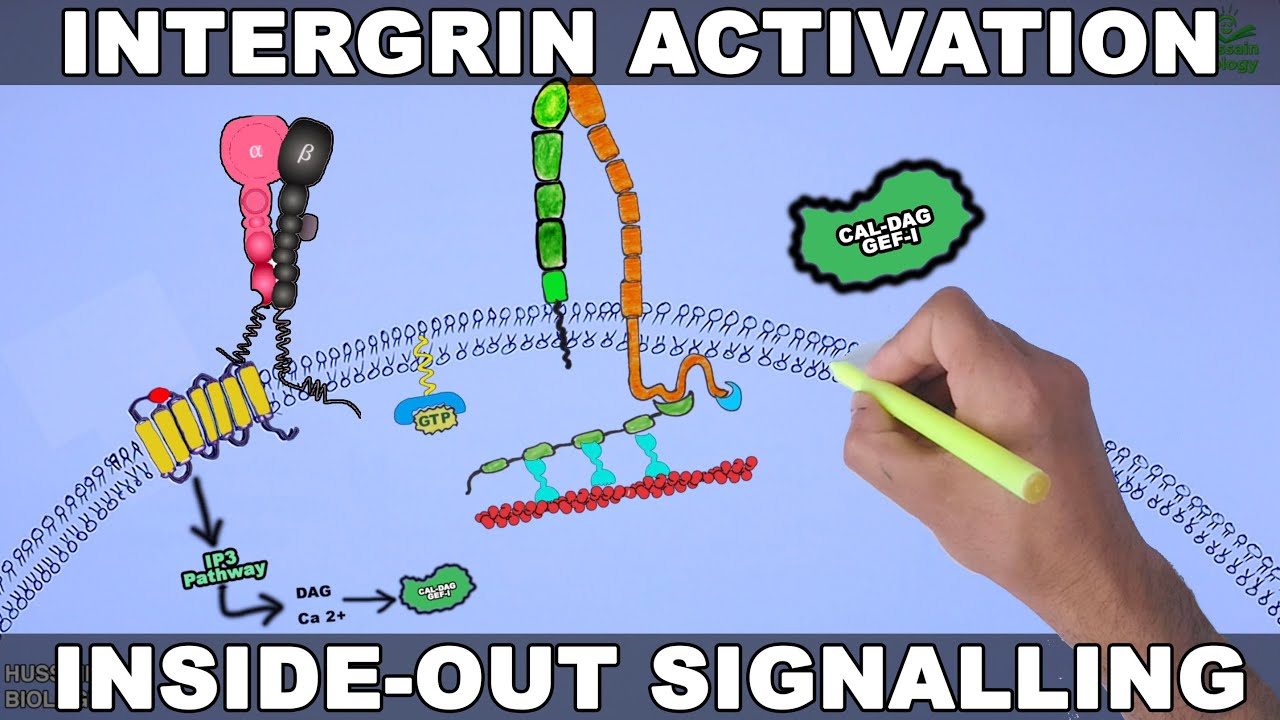
What does focal adhesion kinase do?
Focal-adhesion kinase (FAK) is a non-receptor tyrosine kinase that provides signalling and scaffolding functions at sites of integrin adhesion. It is involved in the regulation of turnover of these adhesion sites, a process that is crucial in the control of cell migration.
Which protein is involved in focal contacts?
…
| Protein | Function | References |
|---|---|---|
| ERK/MAP kinase | Fincham et al, 2000; | |
| FAK | Focal adhesion kinase | |
| Integrin | A family of trans-membranous adhesions molecules |
How are integrin receptors involved in cell adhesion and why is the RGD sequence important to the integrin extracellular matrix ligands?
The integrin receptor family regulates cell adhesion, migration, invasion, and cell survival. Integrin receptors are heterodimeric molecules consisting of combinations of α and β subunits. Each combination dictates the spectrum of extracellular matrix components to which these receptors bind.
How are integrins activated?
Integrin can be activated from two directions, from the inside by the regulated binding of proteins to the cytoplasmic tails, and from the outside by multivalent ligand binding. In either case, talin binding to the integrin β tails is an essential and the final common step ([10], reviewed in [11]).
What contains binding sites for integrins?
The binding site is composed of the β-propeller domain of the α subunit and the I-like domain of the β subunit. The original crystal structure of integrin αVβ3 revealed a bent conformation of the head region associated with low affinity for ligand [4, 5].
How do cells adhere to one another?
Cells adhere to each other and to the extracellular matrix through cell-surface proteins called cell adhesion molecules (CAMs)—a category that includes the transmembrane adhesion proteins we have already discussed. CAMs can be cell-cell adhesion molecules or cell-matrix adhesion molecules.
What is used for cell adhesion?
Cadherins are essential for cell–cell adhesion and cell signalling in multicellular animals and can be separated into two types: classical cadherins and non-classical cadherins.
Where are adhesion junctions found?
Adherens junctions (or zonula adherens, intermediate junction, or “belt desmosome”) are protein complexes that occur at cell–cell junctions, cell–matrix junctions in epithelial and endothelial tissues, usually more basal than tight junctions.
How do integrins communicate signal inside cell?
Integrins link the actin cytoskeleton of a cell to various external structures. The cytoplasmic portion of each integrin molecule binds to adaptor proteins that connect to the actin filaments inside the cell.
Integrin protein structure and signaling
Images related to the topicIntegrin protein structure and signaling

What is the role of integrins and actin in cell migration?
The connection between integrins and actin is driving the field of cell migration in new directions. Integrins and actin are coupled through a physical linkage, which provides traction for migration. Recent studies show the importance of this linkage in regulating adhesion organization and development.
What is the role of integrin in cell migration?
Integrins are essential for cell migration and invasion, not only because they directly mediate adhesion to the extracellular matrix, but also because they regulate intracellular signalling pathways that control cytoskeletal organization, force generation and survival.
Related searches to How do integrins form focal adhesions?
- focal adhesion pathway
- how do integrins form focal adhesions in dna
- focal adhesions function
- focal adhesion formation
- focal adhesions vs hemidesmosomes
- focal adhesion integrin
- where are focal adhesions found
- how do integrins form focal adhesions in proteins
- how do integrins form focal adhesions in dna replication
- what are focal adhesions
- focal adhesion diagram
- how do integrins form focal adhesions in a cell
Information related to the topic How do integrins form focal adhesions?
Here are the search results of the thread How do integrins form focal adhesions? from Bing. You can read more if you want.
You have just come across an article on the topic How do integrins form focal adhesions?. If you found this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much.