Are you looking for an answer to the topic “How Do Kant And Hume Differ?“? We answer all your questions at the website Chiangmaiplaces.net in category: +100 Marketing Blog Post Topics & Ideas. You will find the answer right below.
Hume locates the foundation of morality in human nature, primarily in our emotional responses to the behavior of our fellow human beings. By contrast, Kant locates the foundation of morality in the rational nature that we share with all possible finite rational beings.Kant agrees with Hume that neither the relation of cause and effect nor the idea of necessary connection is given in our sensory perceptions; both, in an important sense, are contributed by our mind.In the theoretical domain, Kant argues against Humean skepticism by treating the principles he attacks as synthetic a priori rather than a posteriori, and then arguing for the possibility of such judgments by means, in part, of the transcendental idealist claim that our knowledge does not extend to things in themselves …

Table of Contents
What did Kant and Hume agree on?
Kant agrees with Hume that neither the relation of cause and effect nor the idea of necessary connection is given in our sensory perceptions; both, in an important sense, are contributed by our mind.
What disagreement did Kant have with Hume’s philosophy?
In the theoretical domain, Kant argues against Humean skepticism by treating the principles he attacks as synthetic a priori rather than a posteriori, and then arguing for the possibility of such judgments by means, in part, of the transcendental idealist claim that our knowledge does not extend to things in themselves …
Kant’s Criticism of Hume, Lecture 1 by Hamamerud
Images related to the topicKant’s Criticism of Hume, Lecture 1 by Hamamerud

What is Kant’s Critique of Hume?
Kant writes in the Critique of Pure Reason that “the cool-headed David Hume” denied human beings the capacity to assert “a highest being” and obtain “a determinate concept” of it with the sole purpose of “bringing reason further in its self-knowledge” so as to let it admit its weaknesses (A745/B733).
What did Hume believe?
Hume was an Empiricist, meaning he believed “causes and effects are discoverable not by reason, but by experience“. He goes on to say that, even with the perspective of the past, humanity cannot dictate future events because thoughts of the past are limited, compared to the possibilities for the future.
What is Kant’s view?
Kant’s ethics are organized around the notion of a “categorical imperative,” which is a universal ethical principle stating that one should always respect the humanity in others, and that one should only act in accordance with rules that could hold for everyone.
What does Kant learn from Hume?
Kant’s discussions reflect his consistent emphasis on freedom, dignity, rationality, and purity of motive. Hume’s reflect his emphasis on utility, pleasure, and the inherently social nature of the human mind.
What in detail was Kant’s response to Hume’s problem of induction?
In short, Kant’s answer is that ‘causality’ isn’t, contra Hume, merely constant perceived conjunction. If this is the case, then the problem of induction applies and it is not possible to infer that there is a necessary connection between a cause and its effect.
See some more details on the topic How Do Kant And Hume Differ? here:
Kant and Hume on Causality
Kant then immediately refers to “David Hume, who, … This striking difference between the two editions clearly …
Kant vs Hume – Philosophy & Philosophers
By cons, according to Kant, the man is a rational being who has an autonomous will and reason …
Difference Between Kant and Hume
1. Hume was born and raised in Scotland while Kant was born and raised in present day Russia. 2.Hume’s methods were experimental and empirical whereas Kant …
Kant and Hume on Morality – Stanford Encyclopedia of …
Hume’s method of moral philosophy is experimental and empirical; Kant emphasizes the necessity of grounding morality in a priori …
Who is David Hume and Immanuel Kant?
The ethics of Immanuel Kant (1724–1804) is often contrasted with that of David Hume (1711–1776). Hume’s method of moral philosophy is experimental and empirical; Kant emphasizes the necessity of grounding morality in a priori principles.
Does Hume believe in cause and effect?
Hume therefore recognizes cause and effect as both a philosophical relation and a natural relation, at least in the Treatise, the only work where he draws this distinction. The relation of cause and effect is pivotal in reasoning, which Hume defines as the discovery of relations between objects of comparison.
KANT VS. HUME *THE BATTLE OF MORALITY*
Images related to the topicKANT VS. HUME *THE BATTLE OF MORALITY*

Does Kant believe in cause and effect?
Kant calls this the ‘law of causality’ or the ‘law of the connection of cause and effect’ (see note 16). It states that necessarily, in every event there is something that is preceded and determined (according to a rule) by something else, i.e. that every event involves a cause.
Who disagrees with David Hume?
In the mid eighteenth century the debate became fiercely personal during a public quarrel between two philosophical luminaries: David Hume and Jean-Jacques Rousseau.
What was Kant known for?
Immanuel Kant was a German philosopher and one of the foremost thinkers of the Enlightenment. His comprehensive and systematic work in epistemology (the theory of knowledge), ethics, and aesthetics greatly influenced all subsequent philosophy, especially the various schools of Kantianism and idealism.
What is Hume known for?
David Hume, (born May 7 [April 26, Old Style], 1711, Edinburgh, Scotland—died August 25, 1776, Edinburgh), Scottish philosopher, historian, economist, and essayist known especially for his philosophical empiricism and skepticism. Hume conceived of philosophy as the inductive, experimental science of human nature.
Does Hume believe in free will?
It is widely accepted that David Hume’s contribution to the free will debate is one of the most influential statements of the “compatibilist” position, where this is understood as the view that human freedom and moral responsibility can be reconciled with (causal) determinism.
What is an example of Kantian ethics?
For example, if you hide an innocent person from violent criminals in order to protect his life, and the criminals come to your door asking if the person is with you, what should you do? Kantianism would have you tell the truth, even if it results in harm coming to the innocent person.
What are two of Kant’s important ideas about ethics?
What are two of Kant’s important ideas about ethics? One idea is universality, we should follow rules of behaviors that we can apply universally to everyone. and one must never treat people as a means to an end but as an end in themselves.
Hume and Kant
Images related to the topicHume and Kant
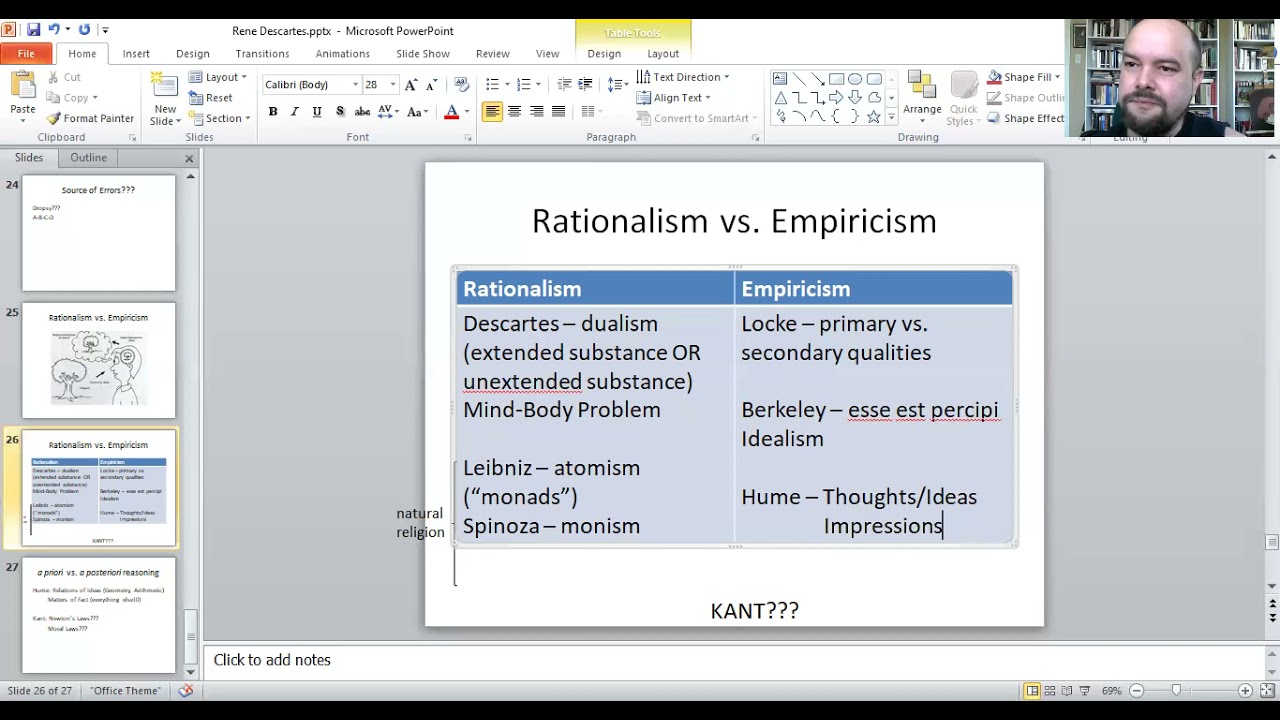
Does Kant believe God?
Kant maintains that underlying all the traditional proofs for God’s existence is the concept of the ens realissimum, the most real being. Reason comes to the idea of this being through the principle that every individuated object is subject to the “principle of complete determination”.
Does Hume believe in God?
I offer a reading of Hume’s writings on religion which preserves the many criticisms of established religion that he voiced, but also reveals that Hume believed in a genuine theism and a true religion. At the heart of this belief system is Hume’s affirmation that there is a god, although not a morally good.
Related searches to How Do Kant And Hume Differ?
- kant on causality
- kant vs hume ethics
- difference between hume and kant
- hume morality summary
- hume vs kant aesthetics
- kant philosophy
- did kant meet hume
- kant hume dogmatic slumber
- similarities between kant and hume
- categorical imperative
- kant, hume dogmatic slumber
- how do kant and hume differ
- david hume cause and effect essay
- david hume causality
Information related to the topic How Do Kant And Hume Differ?
Here are the search results of the thread How Do Kant And Hume Differ? from Bing. You can read more if you want.
You have just come across an article on the topic How Do Kant And Hume Differ?. If you found this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much.