Are you looking for an answer to the topic “How Do Materials Move Across Capillary Walls?“? We answer all your questions at the website Chiangmaiplaces.net in category: +100 Marketing Blog Post Topics & Ideas. You will find the answer right below.
Small molecules can cross into and out of capillaries via simple or facilitated diffusion. Some large molecules can cross in vesicles or through clefts, fenestrations, or gaps between cells in capillary walls. However, the bulk flow of capillary and tissue fluid occurs via filtration and reabsorption.Capillaries are where fluids, gasses, nutrients, and wastes are exchanged between the blood and body tissues by diffusion. Capillary walls contain small pores that allow certain substances to pass into and out of the blood vessel.Oxygen diffuses through the capillary wall, into the tissue fluid and the cells. Carbon dioxide diffuses from the cells into the tissue fluid, then across the capillary walls into the blood plasma . Glucose diffuses from the blood plasma, across the capillary walls to the tissue fluid, and then to the cells.

Table of Contents
How do materials move across the walls of capillaries?
Capillaries are where fluids, gasses, nutrients, and wastes are exchanged between the blood and body tissues by diffusion. Capillary walls contain small pores that allow certain substances to pass into and out of the blood vessel.
How do substances move in and out of capillaries?
Oxygen diffuses through the capillary wall, into the tissue fluid and the cells. Carbon dioxide diffuses from the cells into the tissue fluid, then across the capillary walls into the blood plasma . Glucose diffuses from the blood plasma, across the capillary walls to the tissue fluid, and then to the cells.
Capillary Exchange and Edema, Animation
Images related to the topicCapillary Exchange and Edema, Animation

What causes movement of substances through capillary walls?
Substances pass through the capillary wall by diffusion, filtration, and osmosis. Oxygen and carbon dioxide move across the capillary wall by diffusion. Fluid movement across a capillary wall is determined by a combination of hydrostatic and osmotic pressure.
How does water cross the capillary wall?
Water moves across capillary walls both by diffusion (osmosis) and by bulk flow.
How do substances move across capillaries quizlet?
When arterial blood reaches the capillary bed, the fluid from the capillary moves into the interstitial spaces. After arterial blood has passed through the capillaries into the venous network, fluid will flow back again into the blood from the interstitial fluid.
What forces are responsible for bulk flow across capillary walls?
- Hydrostatic Pressure. The primary force driving fluid transport between the capillaries and tissues is hydrostatic pressure, which can be defined as the pressure of any fluid enclosed in a space. …
- Osmotic Pressure. …
- Interaction of Hydrostatic and Osmotic Pressures.
What causes the transfer of materials between capillaries and tissue fluid?
The transfer of substances between capillaries and tissue fluid follows a process called pressure filtration. Pressure filtration is dependent on both hydrostatic and osmotic pressures. At the arteriole end, the high hydrostatic pressure pushes plasma out of the capillaries.
See some more details on the topic How Do Materials Move Across Capillary Walls? here:
18.8A: Capillary Dynamics – Medicine LibreTexts
Capillary exchange refers to the exchange of material between the blood and tissues in the capillaries. There are three mechanisms that …
Capillary Exchange: Process & Properties | Study.com
Capillary exchange is the transfer of materials between the blood in the capillaries and interstitial tissue. This lesson discusses methods …
Capillaries and Fluid Exchange | Veterian Key
4. Water moves across capillary walls both by diffusion (osmosis) and by bulk flow. 5. The Starling equation quantifies the interaction of …
An Illustrated Guide to Capillary Fluid Exchange – ThoughtCo
Capillaries are where fluids, gasses, nutrients, and wastes are exchanged between the blood and body tissues by diffusion. Capillary walls …
How do substances move from the blood in the capillaries into the tissue fluid?
Answer. Oxygen diffuses through the capillary wall, into the tissue fluid and the cells. Carbon dioxide diffuses from the cells into the tissue fluid, then across the capillary walls into the blood plasma . Glucose diffuses from the blood plasma, across the capillary walls to the tissue fluid, and then to the cells.
What can pass easily through the walls of the capillaries?
Capillaries are the smallest blood vessels in your body. Oxygen passes through the walls of your capillaries to your tissues. Carbon dioxide can also move into your capillaries from the tissue before entering your veins.
Do capillaries do diffusion?
Capillary Exchange Mechanisms
Diffusion, the most widely-used mechanism, allows the flow of small molecules across capillaries such as glucose and oxygen from the blood into the tissues and carbon dioxide from the tissue into the blood.
What is capillary diffusion?
(Also called capillary movement.) The movement of fluids in unsaturated porous media due to surface tension and adhesive driving forces (capillarity).
Capillary Exchange (diffusion, filtration, reabsorption)
Images related to the topicCapillary Exchange (diffusion, filtration, reabsorption)
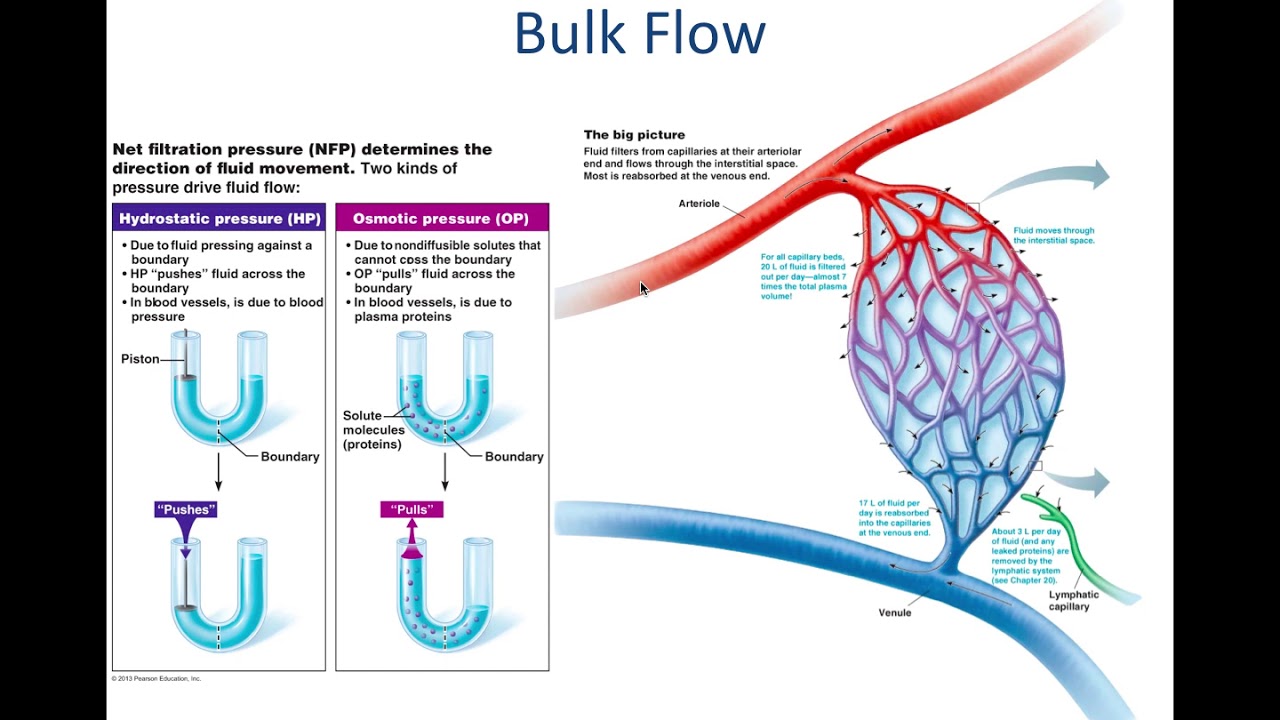
Which cell can pass through the capillary wall?
That’s about four ten-thousandths of one inch, or the width of a single cotton fiber. Red blood cells have to pass through continuous capillaries in a single-file line. Continuous capillaries consist of: Endothelial cells that line the capillary walls.
What is the function of capillary wall?
The capillary wall performs an important function by allowing nutrients and waste substances to pass across it. Molecules larger than 3 nm such as albumin and other large proteins pass through transcellular transport carried inside vesicles, a process which requires them to go through the cells that form the wall.
What controls blood flow through a capillary?
Blood flow through the capillary beds is controlled by precapillary sphincters to increase and decrease flow depending on the body’s needs and is directed by nerve and hormone signals.
What is hydrostatic pressure in capillaries?
The pressure that blood exerts in the capillaries is known as blood pressure. The force of hydrostatic pressure means that as blood moves along the capillary, fluid moves out through its pores and into the interstitial space.
What causes the movement of substances from the blood into the interstitial fluid?
Blood hydrostatic pressure pushes fluid out of capillaries (filtration), and blood colloid osmotic pressure pulls fluid into capillaries (reabsorption).
What is bulk flow in capillaries?
Bulk flow is a process used by small lipid-insoluble proteins to cross the capillary wall. Capillary structure plays a large role in the rate of bulk flow, with continuous capillaries limiting flow and discontinuous capillaries facilitating the greatest amount of flow.
What two forces control the movement of fluid through the capillary wall?
What two forces control movement of fluid through the capillary wall? Blood pressure– causes fluids in the blood to move from capillary to tissue spaces. Osmotic pressure- tends to cause water to move in the opposite direction.
What is the most important force causing net water flow across capillary walls?
Hydrostatic pressure of capillary blood. What is the most important force causing net outward water flow across capillary walls? Electrolytes have greater osmotic power than nonelectrolytes and therefore have the greatest ability to cause fluid shifts.
What pressure pulls water into capillaries?
Hydrostatic pressure pushes water out of the capillary and colloid osmotic pressure pulls water into the capillary. The difference between these gradients is the net filtration pressure (NFP). At the capillary’s arteriolar end, the NFP is? 13 mm Hg.
Fluid Exchange in Capillaries | Starling Forces | Capillary Filtration | General Physiology
Images related to the topicFluid Exchange in Capillaries | Starling Forces | Capillary Filtration | General Physiology
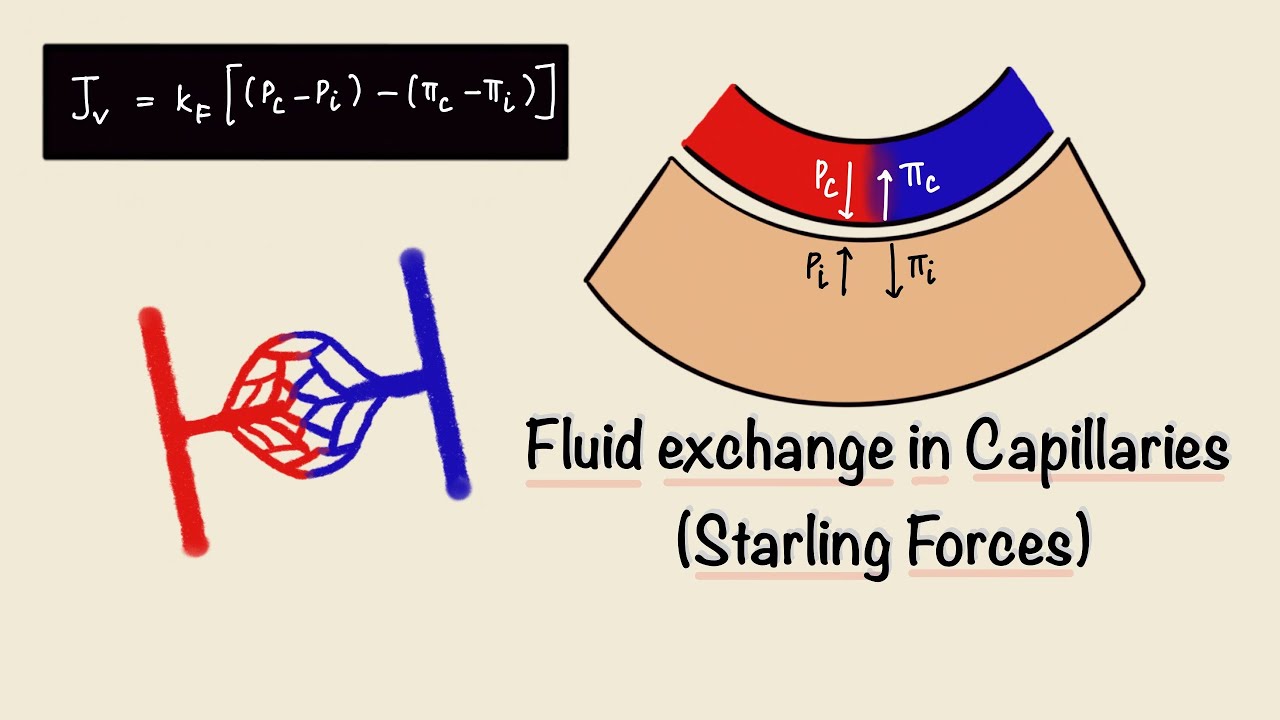
How do oxygen and carbon dioxide cross capillary walls?
How do oxygen and carbon dioxide cross capillary walls? Oxygen diffuses down its concentration gradient (from high to low concentration) from the capillary into the interstitial fluid; carbon dioxide diffuses down its concentration gradient from the interstitial fluid into the capillary.
How do materials get from the blood to the surrounding tissues?
Capillaries, the smallest and most numerous of the blood vessels, form the connection between the vessels that carry blood away from the heart (arteries) and the vessels that return blood to the heart (veins). The primary function of capillaries is the exchange of materials between the blood and tissue cells.
Related searches to How Do Materials Move Across Capillary Walls?
- explain the process of fluid movement at both the arterial and venous side of the capillary
- what would happen if the plasma protein, albumin, could easily cross capillary walls?
- what does not move substances across capillary walls
- the most important force causing net outward water flow across capillary walls is
- describe the fate of fluid that is not reabsorbed from the tissues into the vascular capillaries.
- at the arteriolar end of the capillary which pressure is the greatest
- describe the fate of fluid that is not reabsorbed from the tissues into the vascular capillaries
- capillary exchange quizlet
- how do materials move across capillary walls
- why is painting a wall a physical change
- how does water move up a capillary tube
- how do materials enter and leave capillaries
- explain the process of fluid movement at both the arterial and venous side of the capillary.
- how are materials exchanged across capillary walls
- which net pressure draws fluid into the capillary
- what would happen if the plasma protein albumin could easily cross capillary walls
- capillary exchange
- capillary hydrostatic pressure
- which way up does capillary matting go
Information related to the topic How Do Materials Move Across Capillary Walls?
Here are the search results of the thread How Do Materials Move Across Capillary Walls? from Bing. You can read more if you want.
You have just come across an article on the topic How Do Materials Move Across Capillary Walls?. If you found this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much.