Are you looking for an answer to the topic “How do monocytes turn into macrophages?“? We answer all your questions at the website Chiangmaiplaces.net in category: +100 Marketing Blog Post Topics & Ideas. You will find the answer right below.
Monocytes can differentiate into inflammatory or anti-inflammatory subsets. Upon tissue damage or infection, monocytes are rapidly recruited to the tissue, where they can differentiate into tissue macrophages or dendritic cells.Monocytes exit to the blood, and can enter tissues under inflammatory conditions. They give rise to subsets of macrophages and to inflammatory DCs that share many of the phenotypic features and functions of DCs, such as the ability to process and present antigen to T cells (3, 5, 26, 31, 32) (Fig.Growth factors, such as granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) and M-CSF play a principal role in their activation: GM-CSF drives the differentiation of “pro-inflammatory” monocytes to M1 macrophages, while M-CSF regulates differentiation of the “anti-inflammatory” subset of monocytes to M0 …

Table of Contents
Do monocytes give rise to macrophages?
Monocytes exit to the blood, and can enter tissues under inflammatory conditions. They give rise to subsets of macrophages and to inflammatory DCs that share many of the phenotypic features and functions of DCs, such as the ability to process and present antigen to T cells (3, 5, 26, 31, 32) (Fig.
What triggers the differentiation of monocytes into macrophages?
Growth factors, such as granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) and M-CSF play a principal role in their activation: GM-CSF drives the differentiation of “pro-inflammatory” monocytes to M1 macrophages, while M-CSF regulates differentiation of the “anti-inflammatory” subset of monocytes to M0 …
USMLE Animated Immunology – Infection Acute Inflammation – Monocytes Macrophages
Images related to the topicUSMLE Animated Immunology – Infection Acute Inflammation – Monocytes Macrophages

How are macrophages formed?
Macrophages are formed through the differentiation of monocytes, one of the major groups of white blood cells of the immune system. When there is tissue damage or infection, the monocytes leave the bloodstream and enter the affected tissue or organ and undergo a series of changes to become macrophages.
What do monocytes mature into?
Monocytes are a type of leukocyte, or white blood cell. They are the largest type of leukocyte and can differentiate into macrophages and conventional dendritic cells. As a part of the vertebrate innate immune system monocytes also influence adaptive immune responses and exert tissue repair functions.
How do monocytes perform amoeboid movement and phagocytosis?
1 Answer. Monocytes can perform phagocytosis. They do this by using intermediary or opsonising proteins such as antibodies or complement that coat the pathogen. They also bind to the microbe directly via pattern-recognition receptors that recognize pathogens.
How do monocytes become dendritic cells?
Monocytes differentiate into dendritic cells under inflammatory conditions in peripheral tissues. However, as early as the 1990s, Sallusto and Lanzavecchia15 and Romani et al. demonstrated that human monocytes differentiate into DCs in vitro by culturing with GM-CSF and IL-4.
How do monocytes differentiate into macrophages or dendritic cells?
Abstract. Monocytes can give rise to either antigen presenting dendritic cells (DCs) or scavenging macrophages. This differentiation is initiated when monocytes cross the endothelium.
See some more details on the topic How do monocytes turn into macrophages? here:
From Monocytes to M1/M2 Macrophages: Phenotypical vs …
Macrophage differentiation from monocytes occurs in the tissue in concomitance with the acquisition of a functional phenotype that depends on …
Monocyte differentiation and macrophage polarization
In response to pro-inflammatory stimuli, monocytes can be directly polarized into 3 subsets of macrophages with the pro-inflammatory M1-like phenotype; …
In vitro differentiation of Macrophages from Monocytes via M …
Tissue macrophages can be derived from monocytes. When isolated from blood and cultured in media with serum, adherent monocytes will differentiate into …
Tracing the journey of monocytes to macrophages – Axol …
Two key players in this response mechanism are: 1) circulating peripheral blood monocytes, the cells first to the site of interest; and 2) …
How are macrophages recruited?
When chemoattractant factors are released by tumor cells, monocytes extravasate, migrate into the tumor, and differentiate into mature macrophages. The combination of chemokine receptors (on monocytes) and chemokines (by tumor cells) plays a central role in monocyte/macrophage recruitment.
What is the difference between macrophages and monocytes?
Monocyte and macrophage are two types of cells found in the immune system of organisms. They are considered as the front line of host defense. Monocytes are bean-shaped small cells whereas macrophages are irregular-shaped large cells. Both monocytes and macrophages are capable of secreting cytokines and chemokines.
Where do macrophages develop from?
Macrophages develop in the bone marrow from cells known as monocytes. Monocytes arise from precursor cells under the influence of the granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. They then leave the bone marrow and circulate in the blood.
Are monocytes macrophages?
Put simply, monocytes are macrophages in the blood; macrophages are monocytes in tissue.
When do macrophages develop?
It is now well accepted that murine macrophages are produced during three consecutive waves of hematopoietic development. The first wave of macrophage formation takes place during primitive hematopoiesis, which occurs in the yolk sac, and gives rise to primitive erythroid, megakaryocyte and macrophage progenitors.
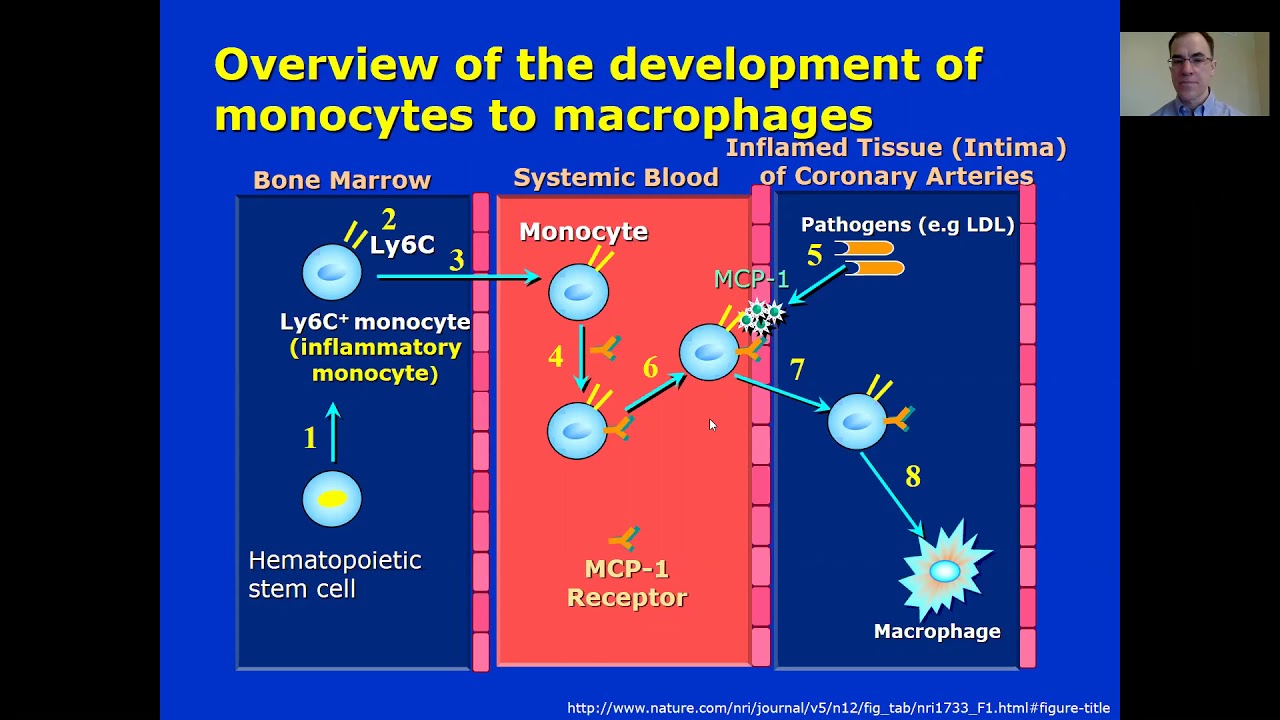
Lesson 2.2 Overview of the development of monocytes to macrophages
Images related to the topicLesson 2.2 Overview of the development of monocytes to macrophages
What do monocytes become when they leave the blood and travel to the site of an infection?
Monocytes are a type of white blood cell in your immune system. Monocytes turn into macrophage or dendritic cells when an invading germ or bacteria enters your body. The cells either kill the invader or alert other blood cells to help destroy it and prevent infection.
When monocytes migrate from the blood out to the tissues they are transformed by inflammatory?
Monocytes move from flowing blood to the tissues after 1–2 days. When monocytes enter the tissue, they become known as macrophages and are responsible for fighting foreign bodies or pathogen and debris by engulfing and inactivating and digesting them in a process known as phagocytosis.
Can monocytes Phagocytose?
Monocytes can phagocytose and present antigens, secrete chemokines, and proliferate in response to infection and injury. Once recruited to tissues, monocytes are capable of differentiating into macrophages and dendritic cells.
Why do white blood cells show amoeboid movement?
Amoeboid movement in WBC
It helps to pass through the cells without any obstacles. If any obstacle occurs the kills the pathogens enter into the body.
What is meant by amoeboid movement?
Amoeboid movement is the most typical mode of locomotion in adherent eukaryotic cells. It is a crawling-like type of movement accomplished by protrusion of cytoplasm of the cell involving the formation of pseudopodia (“false-feet”) and posterior uropods.
Which cell is responsible for phagocytosis?
Macrophages, neutrophils, monocytes, dendritic cells, and osteoclasts are among these dedicated cells. These professional phagocytes express several phagocytic receptors that activate signaling pathways resulting in phagocytosis.
What is the difference between dendritic cells and macrophages?
Macrophages refer to a type of white blood cells that surround and kill microorganisms, remove dead cells, and stimulate the activity of other immune system cells. Dendritic cells refer to a special type of immune cells that boost immune responses by showing antigens on its surface to other cells of the immune system.
What are monocyte-derived dendritic cells?
Monocyte-derived Dendritic cells (Mo-DC) are a distinct DC subset, involved in inflammation and infection, they originate from monocytes upon stimulation in the circulation and their activation and function may vary in autoimmune diseases.
Are dendritic cells derived from macrophages?
Classifying mouse dendritic cells
We propose that DCs should be classified as a separate lineage of mononuclear phagocytes on the basis of the fact that they arise from adult haematopoietic stem cell (HSC)-derived precursors that are distinct from the precursors of monocytes and macrophages (Fig. 1).
What is the difference between monocytes and macrophages quizlet?
What is the difference between monocytes and macrophages? Macrophages are tissue fixed, whereas monocytes are in circulation.
Immunology – Monocytes and Macrophages
Images related to the topicImmunology – Monocytes and Macrophages

Do monocytes mature into dendritic cells?
Mature dendritic cells derived from human monocytes within 48 hours: a novel strategy for dendritic cell differentiation from blood precursors. J Immunol.
Which cell is the precursor of the macrophage?
3.2 Monocytes. Monocytes are white blood cells that have a fundamental role in the inflammatory process [112] and are the circulating precursors of macrophages.
Related searches to How do monocytes turn into macrophages?
- how to increase macrophages and monocytes
- role of monocytes in inflammation
- monocyte function
- how do monocytes modify into macrophages
- macrophages are derived from
- do macrophages turn back into monocytes
- monocytes and macrophages function
- how do monocytes become dendritic cells
- how do monocytes turn into macrophages
- do monocytes make macrophages
- how to differentiate monocytes into macrophages in vitro
- types of macrophages
- monocyte differentiation to macrophages protocol
- monocytes differentiate into which kind of phagocytic cells
Information related to the topic How do monocytes turn into macrophages?
Here are the search results of the thread How do monocytes turn into macrophages? from Bing. You can read more if you want.
You have just come across an article on the topic How do monocytes turn into macrophages?. If you found this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much.