Are you looking for an answer to the topic “How do second generation antipsychotics work?“? We answer all your questions at the website Chiangmaiplaces.net in category: +100 Marketing Blog Post Topics & Ideas. You will find the answer right below.
Second-generation antipsychotics work by blocking D2 dopamine receptors as well as serotonin receptor antagonist action. 5-HT2A subtype of serotonin receptor is most commonly involved.First generation antipsychotics are D2 antagonists and are associated with higher risk of EPS. Second generation antipsychotics: are 5HT2A/D2 antagonists, are associated with lower risk of EPS and with higher risk of metabolic side effects.Second-generation antipsychotics generally have a lower affinity for the dopamine receptor and also block serotonin receptors, so may be associated with lower risk of these side effects.
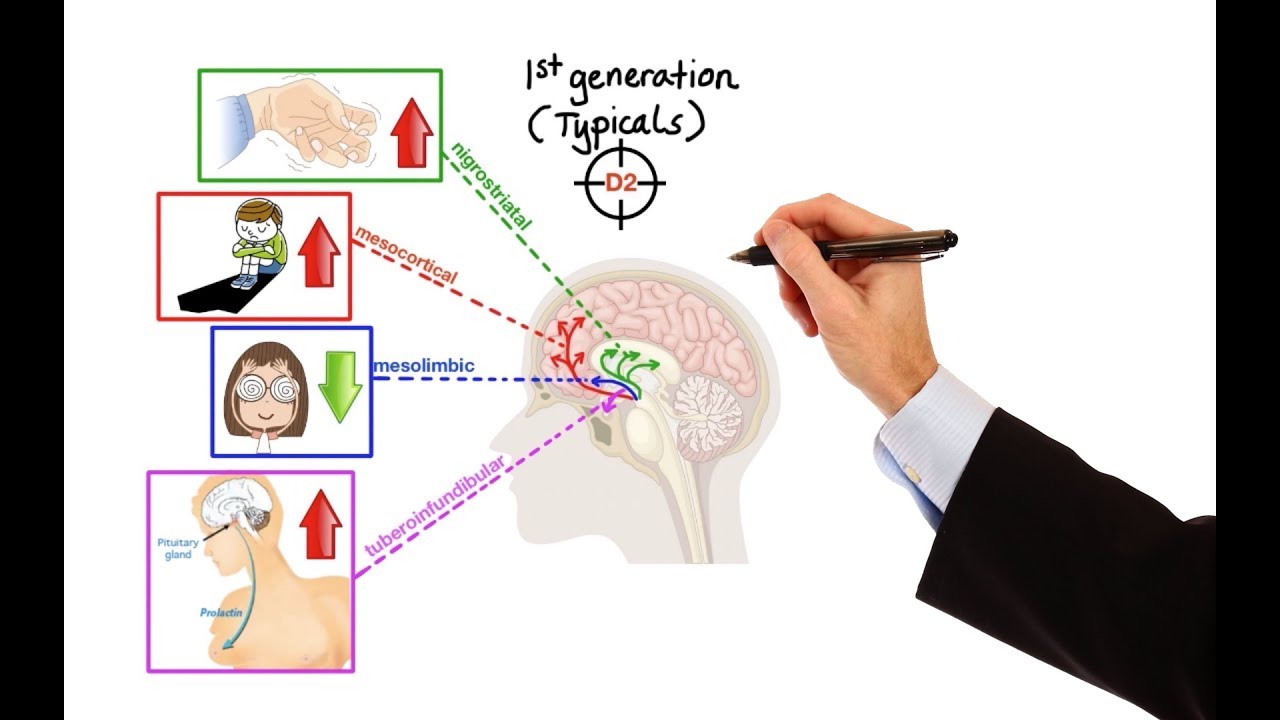
Table of Contents
What is the difference between 1st and 2nd generation antipsychotics?
First generation antipsychotics are D2 antagonists and are associated with higher risk of EPS. Second generation antipsychotics: are 5HT2A/D2 antagonists, are associated with lower risk of EPS and with higher risk of metabolic side effects.
Why are second generation antipsychotics preferred?
Second-generation antipsychotics generally have a lower affinity for the dopamine receptor and also block serotonin receptors, so may be associated with lower risk of these side effects.
Pharmacology – ANTIPSYCHOTICS (MADE EASY)
Images related to the topicPharmacology – ANTIPSYCHOTICS (MADE EASY)

What is second generation antipsychotic drug?
Second generation antipsychotics (SGAs), also known as atypical antipsychotics, are a newer class of antipsychotic medications used to treat schizophrenia, bipolar disorder and related psychiatric conditions.
How do D2 antagonists work?
First-generation or conventional antipsychotics are D2 antagonists, they lower dopaminergic neurotransmission in the four dopamine pathways. In addition, they can also block other receptors such as histamine-1, muscarinic-1 and alpha-1. Second-generation antipsychotics are also known as “atypical” antipsychotics.
How do antipsychotic drugs work in the brain?
Blocking the action of dopamine.
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter, which means that it passes messages around your brain. Most antipsychotic drugs are known to block some of the dopamine receptors in the brain. This reduces the flow of these messages, which can help to reduce your psychotic symptoms.
Do second gen antipsychotics treat negative symptoms?
While these antipsychotics are effective against the positive symptoms of Schizophrenia, they have been considered to be ineffective in treating negative symptoms. Such symptoms particularly play a critical role in producing the severe social and vocational disabilities experienced by many patients with Schizophrenia.
Why do psychiatrists use second-generation antipsychotic medication to manage schizophrenia instead of first-generation antipsychotic medication?
Both first- and second-generation antipsychotic medications can effectively reduce psychotic symptoms associated with schizophrenia and improve overall quality of life. Second-generation antipsychotics are associated with a lower risk of neurological symptoms, such as tremors, than first-generation drugs.
See some more details on the topic How do second generation antipsychotics work? here:
Antipsychotics, Second Generation: Drug Class, Uses, Side …
Second generation antipsychotics work by blocking the excitatory activity of dopamine and serotonin, chemicals (neurotransmitters) released by nerve cells ( …
First versus second generation – NeuRA Library
Second-generation antipsychotics generally have a lower affinity for the dopamine receptor and also block serotonin receptors, so may be …
Antipsychotic drugs for schizophrenia: Second-generation and …
Drs. Sedlak and Shinn explained that in addition to disrupting dopamine signaling, second-generation medications also affect serotonin levels.
Antipsychotics – What you need to know. – Rethink Mental Illness
The older first generation and newer second generation. … You should not stop taking antipsychotics suddenly. … How do antipsychotics work?
What can happens if you take antipsychotics and don’t need them?
If you stop antipsychotics suddenly it can cause ‘rebound psychosis‘. This means that the symptoms of your illness return suddenly, and you may become unwell again.
Do second-generation antipsychotics increase serotonin?
Second‐generation antipsychotic drugs were intended to cause fewer side effects (e.g., extrapyramidal symptoms) than first‐generation antipsychotics. These drugs are known to antagonize the dopamine (D2) and serotonin (5‐HT2A) receptors, but many also act as partial agonists at the 5‐HT1A and/or 5‐HT1B receptors.
What is the mechanism of action of antipsychotics?
Mechanism of Action
The first-generation antipsychotics work by inhibiting dopaminergic neurotransmission; their effectiveness is best when they block about 72% of the D2 dopamine receptors in the brain. They also have noradrenergic, cholinergic, and histaminergic blocking action.
How do atypical antipsychotics work?
Typical and some atypical antipsychotics are dopamine antagonists, which means that they impede chemical messengers in the brain known as dopamine. In people with psychosis, dopamine signals are typically abnormal. Antipsychotics block those messages.
2nd Generation Antipsychotics (Psychiatry) (Pharmacology) – USMLE Step 1
Images related to the topic2nd Generation Antipsychotics (Psychiatry) (Pharmacology) – USMLE Step 1

Why do antipsychotics target D2 receptors?
Traditional antipsychotics remain attached to D2 receptors for days, preventing relapse, but allowing accumulation that can lead to tardive dyskinesia. Future goals include imaging D2High receptors and desensitizing them in early-stage psychosis.
What does the D2 receptor do?
Abstract. Signalling through dopamine D2 receptors governs physiological functions related to locomotion, hormone production and drug abuse1,2,3,4,5,6,7. D2 receptors are also known targets of antipsychotic drugs that are used to treat neuropsychiatric disorders such as schizophrenia8.
What happens to D2 receptors in schizophrenia?
While the pre-synaptic release of dopamine is normal in stable patients with schizophrenia, brain imaging studies find that D2 receptors are increased by an average of 5.8% in antipsychotic-free schizophrenia patients.
How do antipsychotics work D2 receptors?
The mesolimbic pathway is one of four major dopamine-related pathways in the brain that is associated with pleasurable feelings, with addiction—and with psychosis. Generally speaking, antipsychotic medications work by blocking a specific subtype of the dopamine receptor, referred to as the D2 receptor.
How does Abilify work on dopamine?
Abilify is a “dopamine stabilizer,” meaning it can act as a dopamine receptor antagonist when the dopamine system is overactive, and a partial agonist when dopamine levels are low. It is able to do this because it has a very high affinity for dopamine receptors, so it binds to the receptor in place of dopamine.
How do antipsychotics work for bipolar?
Antipsychotic drugs help regulate the functioning of brain circuits that control thinking, mood, and perception. It is not clear exactly how these drugs work, but they usually improve manic episodes quickly.
How do antipsychotics work from receptors to reality?
Antipsychotics improve psychosis by diminishing this abnormal transmission by blocking the dopamine D2/3 receptor (not D1 or D4), and although several brain regions may be involved, it is suggested that the ventral striatal regions (analog of the nucleus accumbens in animals) may have a particularly critical role.
What happens when dopamine receptors are blocked?
Dopamine receptor blocking agents are known to induce parkinsonism, dystonia, tics, tremor, oculogyric movements, orolingual and other dyskinesias, and akathisia from infancy through the teenage years. Symptoms may occur at any time after treatment onset.
Does your brain go back to normal after antipsychotics?
For neurological, neuropsychological, neurophysiological, and metabolic abnormalities of cerebral function, in fact, there is evidence suggesting that antipsychotic medications decrease the abnormalities and return the brain to more normal function.
Why are atypical antipsychotics better than typical?
Atypical antipsychotics seem to be preferable than conventional agents in treating psychological symptoms of dementia (BPSD), because they have substantially lower risks of extrapyramidal neurological effects with lower reported rates of parkinsonism and tardive dyskinesia.
Lecture 28 Second Generation Antipsychotic Medications
Images related to the topicLecture 28 Second Generation Antipsychotic Medications

What does Second-generation drug mean?
Second-generation antipsychotics (SGAs), also known as atypical antipsychotics, generally have lower risk of extrapyramidal symptoms and tardive dyskinesia compared with first-generation antipsychotics (FGAs).
Why do atypical antipsychotics cause less EPS?
Abstract. Atypical antipsychotic drugs (APDs) have been hypothesized to show reduced extrapyramidal side effects (EPS) due to their rapid dissociation from the dopamine D2 receptor.
Related searches to How do second generation antipsychotics work?
- why are second generation antipsychotics preferred
- first-generation antipsychotics
- side effects of first generation antipsychotics
- atypical antipsychotics
- how do 2nd generation antipsychotics work
- what is a second generation antipsychotic
- how do atypical antipsychotics work
- what do second generation antipsychotics treat
- how do second generation antipsychotics work
- list of second generation antipsychotics
- second-generation antipsychotics vs first-generation
- typical antipsychotics
- first generation antipsychotics
- second generation antipsychotics vs first generation
- 3rd generation antipsychotics
- 2nd generation antipsychotics side effects
- using two second generation antipsychotics
- list of second-generation antipsychotics
Information related to the topic How do second generation antipsychotics work?
Here are the search results of the thread How do second generation antipsychotics work? from Bing. You can read more if you want.
You have just come across an article on the topic How do second generation antipsychotics work?. If you found this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much.