Are you looking for an answer to the topic “How do taste receptor cells work?“? We answer all your questions at the website Chiangmaiplaces.net in category: +100 Marketing Blog Post Topics & Ideas. You will find the answer right below.
Taste receptors activate when chewed food mixes with saliva, then flows over and around the papillae like a mushy river. The receptor proteins ignore most of the mix, but when they detect their target food particles they react, notifying their cells that a taste substance has been detected.When taste cells are stimulated by binding of chemicals to their receptors, they depolarize and this depolarization is transmitted to the taste nerve fibers resulting in an action potential that is ultimately transmitted to the brain.When taste receptor cells are stimulated, they send signals through three cranial nerves to taste regions in the brainstem — the facial, glossopharyngeal, and vagus nerves. These impulses get routed through the thalamus, which relays sensory information to other brain regions.
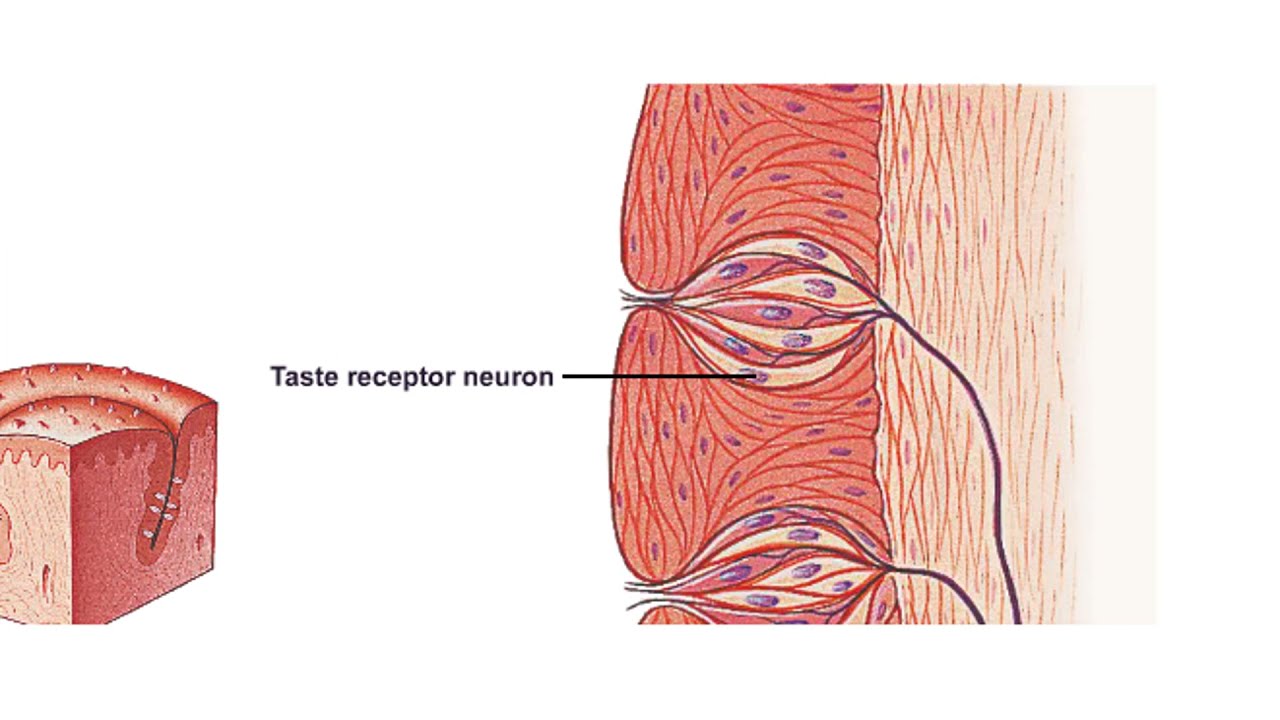
Table of Contents
How are taste cells stimulated?
When taste cells are stimulated by binding of chemicals to their receptors, they depolarize and this depolarization is transmitted to the taste nerve fibers resulting in an action potential that is ultimately transmitted to the brain.
How does taste work in the brain?
When taste receptor cells are stimulated, they send signals through three cranial nerves to taste regions in the brainstem — the facial, glossopharyngeal, and vagus nerves. These impulses get routed through the thalamus, which relays sensory information to other brain regions.
What are Taste Receptors? How Does it Work? Animation
Images related to the topicWhat are Taste Receptors? How Does it Work? Animation

What do taste cells do?
Taste receptor cells are responsible for reporting the sense of taste to the brain. It used to be believed that the tongue was divided like a map into sections responsible for tasting things that are salty, sweet, bitter, and sour.
What stimulates the receptors that determine taste?
A nociceptor is stimulated by tissue damage. ________4. Taste receptors are stimulated by the pressure of food on the tongue.
How does taste work step by step?
Taste buds have very sensitive microscopic hairs called microvilli (say: mye-kro-VILL-eye). Those tiny hairs send messages to the brain about how something tastes, so you know if it’s sweet, sour, bitter, or salty. The average person has about 10,000 taste buds and they’re replaced every 2 weeks or so.
What is the stimulus for taste?
The stimuli for taste are chemical substances dissolved in water or other fluids. Taste can be described as four basic sensations, sweet, sour, salty, and bitter, which can be combined in various ways to make all other taste sensations.
What is the taste receptor?
A taste receptor is a type of cellular receptor which facilitates the sensation of taste. When food or other substances enter the mouth, molecules interact with saliva and are bound to taste receptors in the oral cavity and other locations.
See some more details on the topic How do taste receptor cells work? here:
Physiology of Taste – Vivo.Colostate.edu
The sense of taste is mediated by taste receptor cells which are bundled in clusters called taste buds. Taste receptor cells sample oral concentrations of a …
How do our tastebuds work? – Curious – Australian Academy …
The receptors for sweet, bitter, sour and umami tastes are proteins (produced and coded for by particular genes in our DNA) found on the surface …
How does our sense of taste work? – InformedHealth.org – NCBI
It activates the cell by changing specific proteins in the wall of the sensory cell. This change causes the sensory cell to transmit messenger …
Taste Receptor – an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
Taste receptor cells sense various chemical compounds in foods and transmit these signals through gustatory nerve fibers to the central nervous system. These …
What part of the brain controls your taste and smell?
Parietal lobe
It figures out the messages you receive from the five senses of sight, touch, smell, hearing and taste.
What is the neural pathway for taste?
The three nerves associated with taste are the facial nerve (cranial nerve VII), which provides fibers to the anterior two-thirds of the tongue; the glossopharyngeal nerve (cranial nerve IX), which provides fibers to the posterior third of the tongue; and the vagus nerve (cranial nerve X), which provides fibers to the …
Taste Receptors
Images related to the topicTaste Receptors

Can you taste without smell?
Can you taste without smell? Smell and taste are closely related. Your tongue can detect sweet, sour, salty and bitter tastes. But without your sense of smell, you wouldn’t be able to detect delicate, subtle flavors.
Are taste receptor cells neurons?
Taste cells are primary receptor cells that are derived from local epithelium rather than from neuronal precursors [3]. Yet, many taste cells possess electrical properties similar to neurons and are capable of firing action potentials either spontaneously or in response to electrical or chemical stimulation.
What are the 4 taste receptors?
On the basis of physiologic studies, there are generally believed to be at least four primary sensations of taste: sour, salty, sweet, and bitter.
What causes sense of taste?
When our taste buds encounter food and other substances, the taste cells inside send messages to the brain that help us make sense of what we are tasting. These taste cells work in conjunction with chemical and physical senses to produce what we know as “flavor.”
What helps the food to taste it by our tongue?
Each taste bud is made up of taste cells, which have sensitive, microscopic hairs called microvilli (say: mye-kro-VILL-eye). Those tiny hairs send messages to the brain, which interprets the signals and identifies the taste for you.
What nerve supplies taste to tongue?
The glossopharyngeal (IX) is the most important nerve for the sense of taste. It provides sensory innervation to the base of the tongue and both motor and sensory innervation to part of the pharynx.
Where are the taste receptors?
Taste receptors are found on the upper surface of special cells called taste cells. Many taste cells group together to form an onion-like structure known as a taste bud. Thousands of taste buds are found in nipple-like structures (called papillae) on the upper surface of the tongue.
2-Minute Neuroscience: Taste
Images related to the topic2-Minute Neuroscience: Taste

What are receptor cells in the tongue?
taste bud. Taste receptor cells, with which incoming chemicals from food and other sources interact, occur on the tongue in groups of 50–150. Each of these groups forms a taste bud, which is grouped together with other taste buds into taste papillae.
How does taste work on a molecular level?
Taste arises from chemical substances dissolved in saliva interacting with specific proteins, i.e. taste receptors, which trigger the activation of taste receptor cells (TRCs) located on gustatory papillae, modified epithelial cells distributed throughout the oral mucosa, especially on the tongue.
Related searches to How do taste receptor cells work?
- how long do olfactory receptor cells live
- where are taste receptor cells located
- how do taste receptor cells work
- taste buds
- taste receptor cell function
- physiology of taste
- physiology of taste ppt
- what are taste receptor cells
- how do cell receptors work
- give the termination of the sense of taste
- taste sensation
- which area of the tongue is most sensitive to tastes
- gustatory cells
Information related to the topic How do taste receptor cells work?
Here are the search results of the thread How do taste receptor cells work? from Bing. You can read more if you want.
You have just come across an article on the topic How do taste receptor cells work?. If you found this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much.