Are you looking for an answer to the topic “How do the cochlea hair cells convert energy into electrochemical neural activity?“? We answer all your questions at the website Chiangmaiplaces.net in category: +100 Marketing Blog Post Topics & Ideas. You will find the answer right below.
Keep Reading

Table of Contents
How does the cochlea convert sound energy into electrical impulses?
The cochlea is filled with a fluid that moves in response to the vibrations from the oval window. As the fluid moves, 25,000 nerve endings are set into motion. These nerve endings transform the vibrations into electrical impulses that then travel along the eighth cranial nerve (auditory nerve) to the brain.
How do hair cells of the cochlea translate vibration into nervous impulses?
SOUND WAVES enter the ear canal and cause the eardrum to vibrate. VIBRATIONS pass through 3 connected bones in the middle ear. This motion SETS FLUID MOVING in the inner ear. Moving fluid bends thousands of delicate hair-like cells which convert the vibrations into NERVE IMPULSES.
2-Minute Neuroscience: The Cochlea
Images related to the topic2-Minute Neuroscience: The Cochlea

How does the cochlea send neural impulses to the brain?
As the ossicles move, the stapes presses against the oval window of the cochlea, which causes fluid inside the cochlea to move. As a result, hair cells embedded in the basilar membrane become enlarged, which sends neural impulses to the brain via the auditory nerve.
How do hair cells in the cochlea perform signal transduction?
How do hair cells in the cochlea perform signal transduction? depolarization. B) Sound vibrations activate metabotropic receptors on the hair cell, causing depolarization.
How are electrical impulses from the ear sent to the brain Brainly?
Explanation: Once the sound waves reach the inner ear, they are converted into electrical impulses. The auditory nerve sends these impulses to the brain.
How are vibration in the ear converted to electrical signal?
The physical basis for hearing and mechanotransduction involves receptor cells deep in the ear that collect vibrations and convert them into electrical signals that run along nerve fibers to areas in the brain where they are interpreted as sound.
What converts sound waves into vibrations?
The sound waves are gathered by the outer ear and sent down the ear canal to the eardrum. The sound waves cause the eardrum to vibrate, which sets the middle ear’s three tiny bones into motion. The three bones’ motion causes the fluid in the inner ear, or cochlea, to move.
See some more details on the topic How do the cochlea hair cells convert energy into electrochemical neural activity? here:
COMD 400 test 2 Flashcards | Quizlet
The resulting movement of the stereocilia activates transduction mechanisms that convert mechanical energy into electrochemical activity. Hair Cell Transduction …
Chapter 12: Auditory System: Structure and Function
Hair cells in the Organ of Corti in the cochlea of the ear respond to sound. Hair cells in the cristae ampullares in the semicircular ducts respond to angular …
Anatomy, Head and Neck, Ear Organ of Corti – StatPearls – NCBI
The hair cells convert mechanical energy into electrical energy that is transmitted to the central nervous system via the auditory nerve to facilitate audition.
Transmission of sound within the inner ear | Britannica
The hair cells located in the organ of Corti transduce mechanical sound vibrations into nerve impulses. They are stimulated when the basilar membrane, …
What happens when the vibrations are passed into the cochlea of the inner ear?
The outer most part receives the sound wave and passes it to the middle ear. The middle ear then passes the vibrations to the inner ear which is known as Cochlea. This part of the ear is very sensitive and converts the stimulus to the neural signal and passes it to the brain for further action.
How are sound waves converted into action potentials?
Outer hair cells play a major role in the hearing process: they amplify the motion of the basilar membrane up to a 1000-fold and at the same time sharpen the excitation patterns. These patterns are converted by inner hair cells into action potentials of the auditory nerve.
How does the cochlea encode sound?
Hair cells in the cochlea can code sound intensity via the amount of neurotransmitter they release. Higher sound levels result in more neurotransmitter release and in turn to higher firing rates in the spiral ganglion cells of the auditory nerve.
Where does sound get converted into neural impulses quizlet?
Sound waves are bands of compressed and expanded air. Our ears detect these changes in air pressure and transform them into neural impulses, which the brain decodes as sound.
Which type of ganglion neurons connect the hair cells of the cochlea with the brain?
During the assembly of auditory circuits, spiral ganglion neurons establish precise connections that link hair cells in the cochlea to target neurons in the auditory brainstem, develop specific firing properties, and elaborate unusual synapses both in the periphery and in the CNS.
Hearing, Ear Anatomy Auditory Transduction
Images related to the topicHearing, Ear Anatomy Auditory Transduction

What is the function of the hair cells in the cochlea?
Cochlear hair cells initiate the process of hearing by converting mechanical deflections of their stereocilia bundles into electrochemical signals that are distributed throughout the rest of the auditory system.
How do hair cells generate action potentials?
This mechanism transduces mechanical energy into neural impulses. An inward K+ current depolarizes the cell, and opens voltage-dependent calcium channels. This in turn causes neurotransmitter release at the basal end of the hair cell, eliciting an action potential in the dendrites of the VIIIth cranial nerve.
How are hair cells stimulated?
The hair cells located in the organ of Corti transduce mechanical sound vibrations into nerve impulses. They are stimulated when the basilar membrane, on which the organ of Corti rests, vibrates.
Which part of human ear converts sound vibrations into electrical signals?
In the inner ear, the pressure variations are turned into electrical signals by the cochlea. These electrical signals are sent to the brain via the auditory nerve, and the brain interprets them as sound.
How are electrical impulses from the ear sent to the brain quizlet?
How are electrical impulses from the ear sent to the brain? Mechanical vibrations from the tympanic membrane directly send electrical impulses to the brain. Vibrations disturb the fluid within the cochlea that directly sends electrical impulses to the brain.
Which part of the ear carries electrical impulses to the brain?
The cochlea is shaped like a snail and is divided into two chambers by a membrane. The chambers are full of fluid which vibrates when sound comes in and causes the small hairs which line the membrane to vibrate and send electrical impulses to the brain.
How are sound waves directly translated to the cochlea?
The eardrum vibrates. The vibrations are then passed to 3 tiny bones in the middle ear called the ossicles. The ossicles amplify the sound. They send the sound waves to the inner ear and into the fluid-filled hearing organ (cochlea).
Which device converts sound into electrical signal?
A microphone is a transducer that converts sound energy (varying air pressure) into electrical energy.
How are sound waves directly translated to the cochlea quizlet?
The sound waves make the eardrum vibrate. The vibrations are amplified by the middle ear bones: the hammer, anvil and stirrup. The stirrup transfer the vibrations to the cochlea within the inner ear.
What cells are responsible for converting a sound vibration into an electric impulse?
This action is passed onto the cochlea, a fluid-filled snail-like structure that contains the organ of Corti, the organ for hearing. It consists of tiny hair cells that line the cochlea. These cells translate vibrations into electrical impulses that are carried to the brain by sensory nerves.
Action Potential in the Neuron
Images related to the topicAction Potential in the Neuron
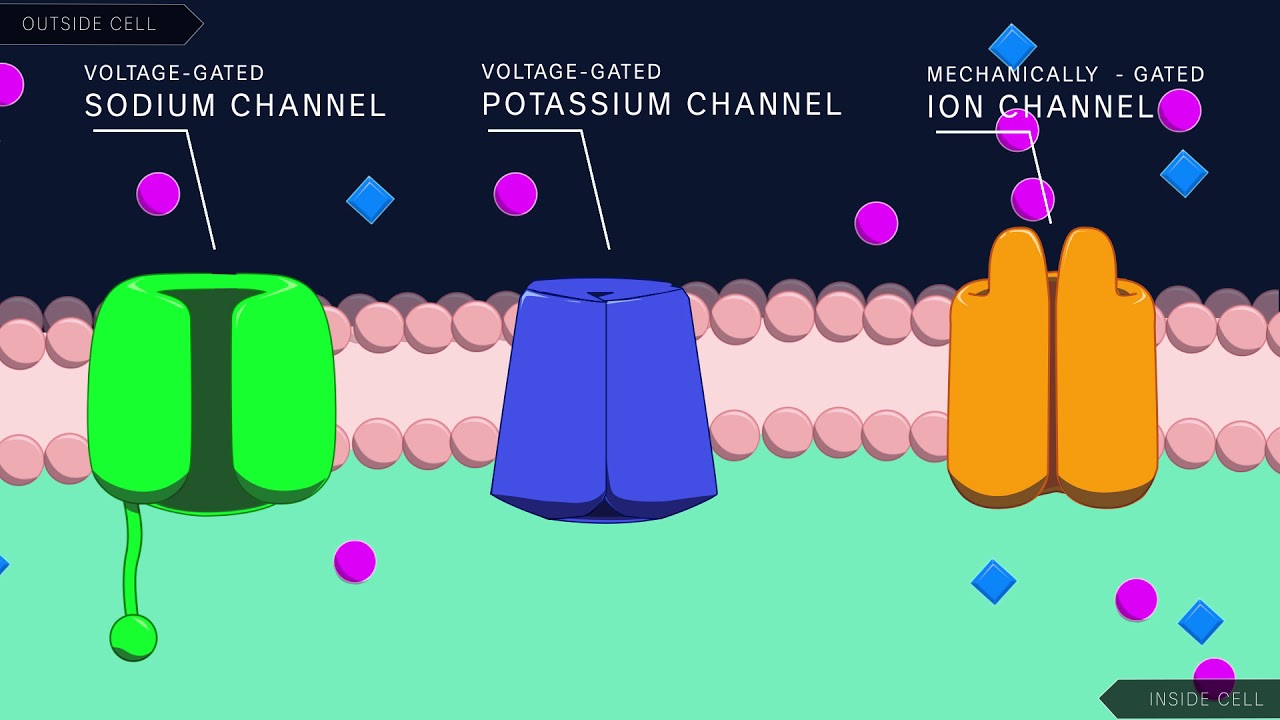
Which of the following converts sounds into neural impulses?
1 Answer. The cochlea in the inner ear.
Which part of the ear converts sound energy to mechanical energy?
The eardrum sits at an angle at the end of the ear canal. A healthy eardrum is pearly white in colour. The changes in pressure produced by the vibrating air particles will cause the eardrum to also vibrate. The acosutic energy in the sound is changed to mechanical energy in the eardrum.
Related searches to How do the cochlea hair cells convert energy into electrochemical neural activity?
- transmission of sound waves in the inner ear is known as
- how do the cochlea/hair cells convert energy into electrochemical/neural activity
- basilar membrane
- how does the auditory system work
- tectorial membrane
- auditory pathway
- organ of corti
- the two functions of the auditory system are
- basilar membrane function
Information related to the topic How do the cochlea hair cells convert energy into electrochemical neural activity?
Here are the search results of the thread How do the cochlea hair cells convert energy into electrochemical neural activity? from Bing. You can read more if you want.
You have just come across an article on the topic How do the cochlea hair cells convert energy into electrochemical neural activity?. If you found this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much.