Are you looking for an answer to the topic “How do you distribute voltage in series?“? We answer all your questions at the website Chiangmaiplaces.net in category: +100 Marketing Blog Post Topics & Ideas. You will find the answer right below.
The sum of the voltages across components in series is equal to the voltage of the supply. The voltages across each of the components in series is in the same proportion as their resistances . This means that if two identical components are connected in series, the supply voltage divides equally across them.Voltage: The supply voltage in a series circuit is equal to the sum of the individual voltage drops.“Voltage is the same across each component of the parallel circuit.” You may remember from the last section that the voltage drops across a resistor in series. Not so with a parallel circuit. The voltage will be the same anywhere in the circuit.

What is the rule for voltage in series?
Voltage: The supply voltage in a series circuit is equal to the sum of the individual voltage drops.
How is voltage distributed in a parallel and series circuit?
“Voltage is the same across each component of the parallel circuit.” You may remember from the last section that the voltage drops across a resistor in series. Not so with a parallel circuit. The voltage will be the same anywhere in the circuit.
Voltage distribution in series circuit|Current distribution in circuit|Voltage in parallel circuits
[su_youtube url=”https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NDMX2hXEzwI”]
Images related to the topicVoltage distribution in series circuit|Current distribution in circuit|Voltage in parallel circuits

Why is voltage divided in series connection?
That is due to the laws of nature. A series circuit has only one pathway for current to flow. There is NO other pathway for current to flow. If that pathway are a series of loads (resistors) then the voltage must be divided across each resistor according to the resistance.
How does voltage in series add?
Batteries correctly placed in series, positive to negative, will add their output voltages, producing a greater voltage. If two 1.5 volt batteries are connected head to tail, the total voltage is 3.0 volt.
How do you calculate voltage in a series circuit?
How do you calculate voltage in a series circuit? Voltage for each circuit element in a series circuit can be calculated by applying Ohm’s law: V=R*I. Also, if the element’s resistance is unknown, the Kirchhoff loop rule helps to calculate the voltage across such a circuit element.
What are the 3 rules for series circuits?
From this definition, three rules of series circuits follow: all components share the same current; resistances add to equal a larger, total resistance; and voltage drops add to equal a larger, total voltage.
How is current distributed in a series circuit?
In a series circuit, the current is the same at each resistor. If the light bulbs are identical, then the resistance is the same for each resistor. The voltage drop (I•R) will be the same for each resistor since the current at and the resistance of each resistor is the same.
See some more details on the topic How do you distribute voltage in series? here:
Voltage in Series Circuits (Sources, Formula & How To Add)
In the case of AC voltage sources in series, the voltage sources can be added or combined together to form a single source provided that the …
Distribution of current and voltage in parallel and series
Here is a brief explanation to know about the distribution of current and voltage in series and parallel connections.
Parallel Circuits – Basic Electricity – BCcampus Pressbooks
In the above circuit, the voltage in each branch is 120 V. Current. A parallel circuit has more than one path for current flow. The number of current paths is …
Why does voltage change in a series circuit?
As current passes through each resistor in a series circuit, it establishes a difference in potential across each individual resistance. This is commonly called voltage drop, and its magnitude is in direct proportion to the value of resistance.
Is voltage constant in series?
The voltage across each resistor in a series circuit is different depending on the resistance value. So, voltage is not constant in series. Only equal-valued resistors can yield the same voltage drop. We use the word ‘constant’ to specify a fixed value of a quantity that remains unchanged.
How do you divide voltages?
When we place 2 resistors of the same value in series, voltage will divide equally among them. Voltage is directly proportional to resistance, according to ohm’s law by the following formula, Voltage= Current * Resistance (V= IR).
Voltage and current division in series parallel circuit
[su_youtube url=”https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9pZQNSerftg”]
Images related to the topicVoltage and current division in series parallel circuit
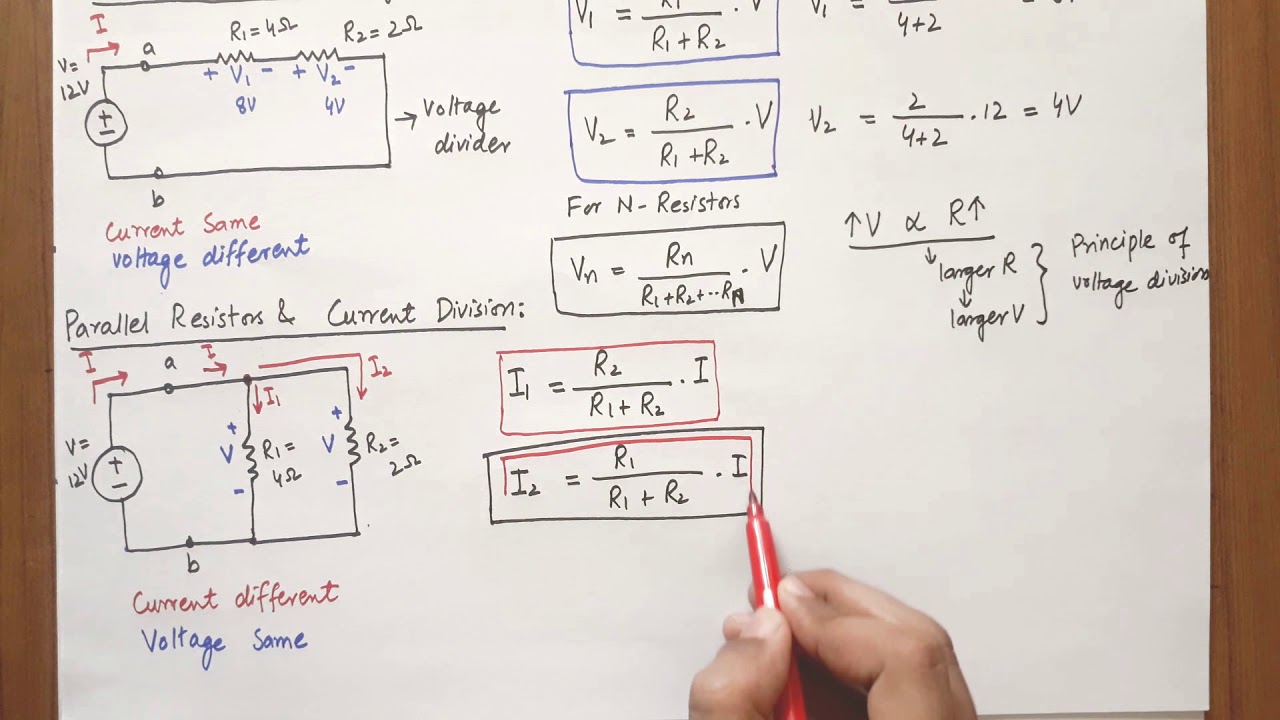
What happens to voltage in series?
Voltage applied to a series circuit is equal to the sum of the individual voltage drops. The voltage drop across a resistor in a series circuit is directly proportional to the size of the resistor. If the circuit is broken at any point, no current will flow.
How is voltage divided in parallel?
In a parallel circuit, the voltage across each of the components is the same, and the total current is the sum of the currents flowing through each component.
Does voltage double in series?
When connecting your batteries in Series you are doubling the voltage while maintaining the same capacity rating (amp hours).
How do you combine series voltages?
Voltage Source in Series
In the example above, the two voltages of 10V and 5V of the first circuit can be added, for a VS of 10 + 5 = 15V. So the voltage across terminals A and B is 15 volts.
How do two 12v batteries produce 12v at high current?
To join batteries in parallel, use a jumper wire to connect both the positive terminals, and another jumper wire to connect both the negative terminals of both batteries to each other. Negative to negative and positive to positive. You CAN connect your load to ONE of the batteries, and it will drain both equally.
Is voltage constant in parallel?
All parallel components have the same voltage because you have connected them together with wires that are assumed to have no resistance. The voltage at each end of a wire should be the same for all the components.
Why the voltage is same in parallel circuit?
Once the charges get out of the resistors, the electric field of the battery is enough to drive them mad (as the wire has relatively lower resistance). And, the charges get back their energy once again. This is the reason why we say voltage is the same in parallel circuits3.
What are the rules for series and parallel circuits?
All components share the same (equal) voltage. Branch currents add to equal total current. Resistances diminish to equal total resistance.
How current is distributed in parallel?
In a parallel circuit, charge divides up into separate branches such that there can be more current in one branch than there is in another.
Voltage in a series circuit with resistors. Basic Electrical Learning
[su_youtube url=”https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gxro5dhJMDo”]
Images related to the topicVoltage in a series circuit with resistors. Basic Electrical Learning
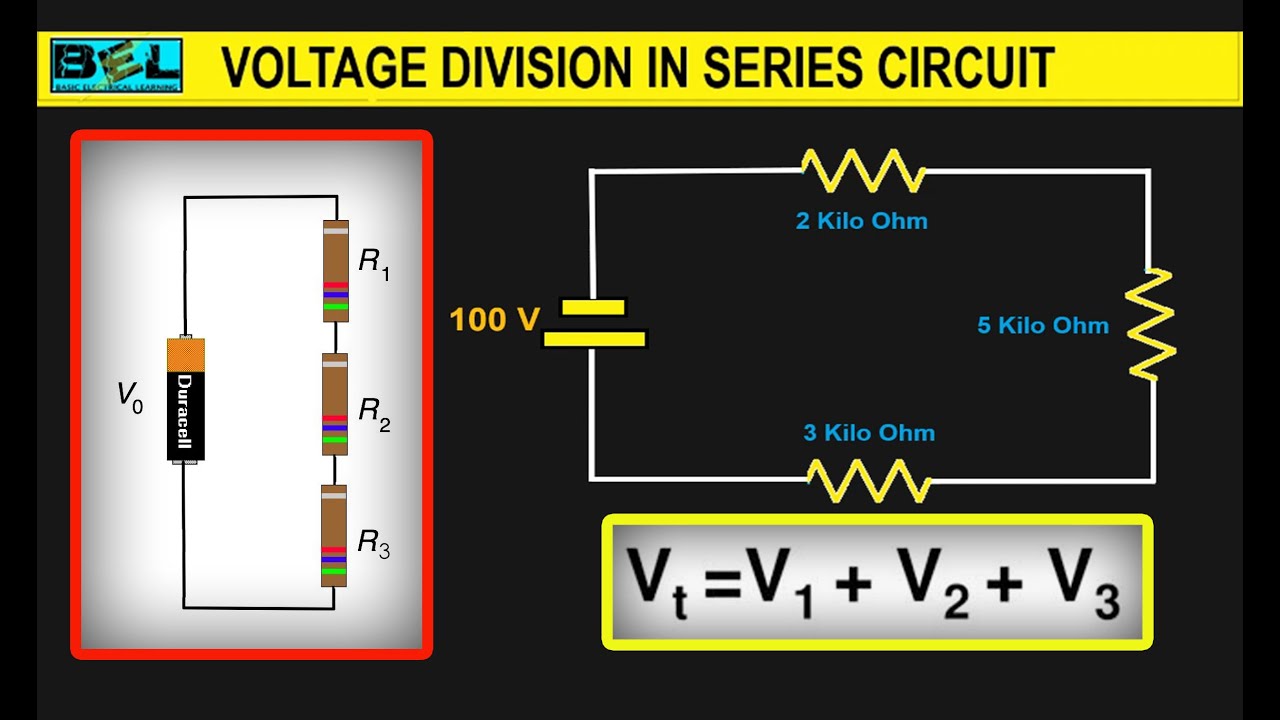
Why is current distributed in a parallel circuit?
A parallel circuit is often called a current divider for its ability to proportion—or divide—the total current into fractional parts. Once again, it should be apparent that the current through each resistor is related to its resistance, given that the voltage across all resistors is the same.
What happens to the voltage drop in a parallel circuit?
In a parallel circuit, all the circuit components are connected between the same points on the circuit. This gives them their branching structure in which current divides itself among each branch but the voltage drop across each branch remains the same.
Related searches to How do you distribute voltage in series?
- voltage in parallel
- voltage distribution in parallel circuit
- voltage in series and parallel
- how do you distribute voltage in series circuit
- current in series
- voltage distribution in series circuit
- distribution of current in parallel circuit
- how do you distribute voltage in series and parallel circuits
- how do you distribute voltage in series and parallel
- how to add voltage in series
- voltage in series formula
Information related to the topic How do you distribute voltage in series?
Here are the search results of the thread How do you distribute voltage in series? from Bing. You can read more if you want.
You have just come across an article on the topic How do you distribute voltage in series?. If you found this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much.
Leave a Reply