Are you looking for an answer to the topic “How is aortic coarctation diagnosed?“? We answer all your questions at the website Chiangmaiplaces.net in category: +100 Marketing Blog Post Topics & Ideas. You will find the answer right below.
Coarctation of the aorta is usually diagnosed by echocardiogram (ultrasound pictures of the heart). Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging), cardiac CT (computerized tomography scan), and cardiac catheterization angiography also show aortic narrowing.Doctors often use echocardiograms to diagnose coarctation of the aorta and determine best treatment options for you. Electrocardiogram (ECG). An electrocardiogram records the electrical signals in your heart. During this test, sticky patches (electrodes) are attached to your chest and limbs.Diagnosis. Coarctation of the aorta is usually diagnosed after the baby is born. How early in life the defect is diagnosed usually depends on how mild or severe the symptoms are. Newborn screening using pulse oximetry during the first few days of life may or may not detect coarctation of the aorta.

Table of Contents
How is coarctation of aorta diagnosed?
Doctors often use echocardiograms to diagnose coarctation of the aorta and determine best treatment options for you. Electrocardiogram (ECG). An electrocardiogram records the electrical signals in your heart. During this test, sticky patches (electrodes) are attached to your chest and limbs.
When is coarctation of aorta usually diagnosed?
Diagnosis. Coarctation of the aorta is usually diagnosed after the baby is born. How early in life the defect is diagnosed usually depends on how mild or severe the symptoms are. Newborn screening using pulse oximetry during the first few days of life may or may not detect coarctation of the aorta.
Coarctation of the Aorta Nursing Pediatrics | Congenital Heart Disease Defects
Images related to the topicCoarctation of the Aorta Nursing Pediatrics | Congenital Heart Disease Defects

Can you see coarctation of aorta on ultrasound?
Diagnosis. Coarctation of the aorta can be suspected during a routine prenatal ultrasound or after a fetal echocardiogram (focused ultrasound of the fetal heart performed by a fetal cardiologist).
Which clinical finding is typical for coarctation of aorta?
Arterial pulse. Abnormal differences in the upper and lower extremity arterial pulses and blood pressures are clinical hallmarks of coarctation of the aorta.
What kind of murmur is heard with aortic stenosis?
The typical murmur of aortic stenosis is a high-pitched, “diamond shaped” crescendo-decrescendo, midsystolic ejection murmur heard best at the right upper sternal border radiating to the neck and carotid arteries (see figure below). In mild aortic stenosis, the murmur peaks in early systole.
What is the blood pressure and pulse difference that is suggestive of coarctation of the aorta?
Blood pressure in both arms and one leg must be determined; a pressure difference of more than 20 mm Hg in favor of the arms may be considered evidence of coarctation of the aorta.
What is an expected assessment finding in a child with coarctation of the aorta?
During a physical exam, a doctor may find that a child with a coarctation has higher blood pressures in the arms than in the legs. The doctor also might hear a heart murmur or notice that the pulse in the groin is weak or hard to feel.
See some more details on the topic How is aortic coarctation diagnosed? here:
Coarctation of the aorta – Diagnosis and treatment – Mayo Clinic
Tests to confirm a diagnosis of coarctation of the aorta may include: … Electrocardiogram (ECG). An electrocardiogram records the electrical …
Coarctation of the Aorta: Symptoms, Treatments & Tests
How is coarctation of the aorta diagnosed? · Electrocardiogram (ECG) · Chest X-ray · Echocardiography · Chest computed tomography (CT or CAT) scan …
Clinical manifestations and diagnosis of coarctation of the aorta
Topic Outline · Echocardiography · Cardiovascular magnetic resonance/computed tomography · Cardiac catheterization.
Coarctation of the Aorta in Children | Symptoms & Repair
The diagnosis of coarctation is confirmed with echocardiography. This can look at the anatomy of the aorta. It can also evaluate for other cardiac anomalies …
What is mild coarctation?
Coarctation (say “ko-ark-TAY-shun”) means that a section of this blood vessel is narrowed or pinched. The heart has to work extra hard to pump the blood through it. If the narrowing gets worse, the heart may have to work harder.
How long can you live with coarctation?
Individuals with coarctation of the aorta have historically had poor long-term out- comes with a mean life expectancy of 35 years. Natural history studies demon- strated 90% of individuals dying before age 50 years.
What is the difference between coarctation of the aorta and aortic stenosis?
This spectrum is dichotomized by the idea that aortic coarctation occurs in the aortic arch, at or near the ductus arteriosus, whereas aortic stenosis occurs in the aortic root, at or near the aortic valve.
Is coarctation of the aorta genetic?
The exact cause of coarctation of the aorta is unknown. It results from abnormalities in development of the aorta prior to birth. Aortic coarctation is more common in people with certain genetic disorders, such as Turner syndrome.
How do you prevent coarctation of the aorta?
Prevention. Coarctation of the aorta can’t be prevented, because it’s usually present at birth.
A case of coarctation of the aorta: ECG,echo and treatment.
Images related to the topicA case of coarctation of the aorta: ECG,echo and treatment.

What does a PDA sound like?
The murmur of a PDA is described as a medium pitched high-grade continuous murmur heard best at the pulmonic position, with a harsh machinelike quality that often radiates to the left clavicle.
Can adults have coarctation of the aorta?
Aortic coarctation may be recognized in the adult, usually because of systemic arterial hypertension and discrepant upper– and lower–extremity pulses. Patients may complain of exertional headaches, leg fatigue or claudication.
When does PDA close?
After birth, the ductus arteriosus normally closes within two or three days. In premature infants, the opening often takes longer to close. If the connection remains open, it’s referred to as a patent ductus arteriosus. The abnormal opening causes too much blood to flow to the baby’s lungs and heart.
How do you diagnose aortic stenosis?
- Echocardiogram. This test uses sound waves to create images of your heart in motion. …
- Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG). …
- Chest X-ray. …
- Exercise tests or stress tests. …
- Cardiac computerized tomography (CT) scan. …
- Cardiac MRI . …
- Cardiac catheterization.
What pulse is typical for aortic stenosis?
In severe aortic stenosis, the carotid arterial pulse typically has a delayed and plateaued peak, decreased amplitude, and gradual downslope (pulsus parvus et tardus). Other symptoms of aortic stenosis include the following: Pulsus alternans: Can occur in the presence of left ventricular systolic dysfunction.
How do you assess aortic stenosis?
Echocardiography is the main method to assess AS severity. It relies on three parameters, namely the peak velocity (PVel), the mean pressure gradient (MPG) and the aortic valve area (AVA).
When should you intervene on coarctation?
Intervention for coarctation is recommended in the following circumstances: (1) Peak-to-peak coarctation gradient of at least 20 mm Hg (level of evidence: C) and (2) peak-to-peak coarctation gradient below 20 mm Hg in the presence of anatomic imaging evidence of significant coarctation with radiologic evidence of …
What is the most common congenital heart defect?
The most common type of heart defect is a ventricular septal defect (VSD).
What does aortic regurgitation sound like?
On auscultation, the typical murmur of aortic regurgitation is a soft, high-pitched, early diastolic decrescendo murmur heard best at the 3rd intercostal space on the left (Erb’s point) on end expiration, with the patient sitting up and leaning forward.
Does coarctation cause murmur?
The typical heart murmur that is associated with a coarctation is a systolic murmur that is loudest in the back below the left shoulder blade (scapula). If a prominent back murmur is not heard and the child has a blood pressure difference between arms and legs a coarctation located in the abdomen should be considered.
Coarctation of the Aorta – Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Images related to the topicCoarctation of the Aorta – Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
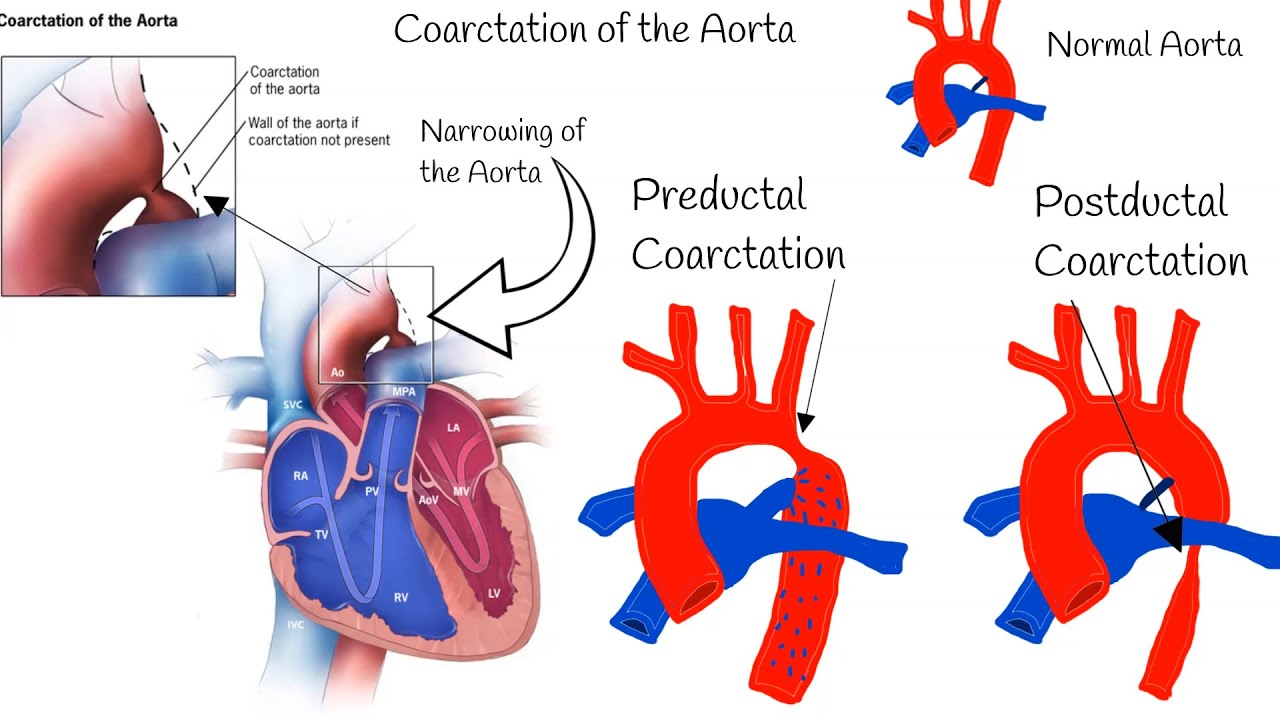
How many babies are born with coarctation of the aorta?
Causes of coarctation of the aorta
Coarctation occurs in 1 out of 2,500 babies born in the United States. About 6-8% of people with congenital heart disease have coarctation of the aorta. The cause is unknown, though it is more common in babies who also have genetic conditions such as Turner syndrome.
How long does surgery for coarctation of the aorta take?
The procedure takes about three to four hours. Your child will be admitted to the hospital the morning of the procedure and may return home the following morning. To perform cardiac catheterization, a tiny incision is made in the groin to insert thin, flexible tubes, called catheters.
Related searches to How is aortic coarctation diagnosed?
- coarctation of aorta murmur
- coarctation of aorta blood pressure difference
- living with coarctation of the aorta
- coarctation of aorta signs
- how is coarctation of the aorta diagnosed
- aortic coarctation treatment
- aortic coarctation life expectancy
- coarctation of aorta in adults
- signs of coarctation of the aorta in infants
Information related to the topic How is aortic coarctation diagnosed?
Here are the search results of the thread How is aortic coarctation diagnosed? from Bing. You can read more if you want.
You have just come across an article on the topic How is aortic coarctation diagnosed?. If you found this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much.