Are you looking for an answer to the topic “How is hydrogen bonding an extreme version of dipole-dipole interactions?“? We answer all your questions at the website Chiangmaiplaces.net in category: +100 Marketing Blog Post Topics & Ideas. You will find the answer right below.
She said that hydrogen bonding occurs to the attraction of the lone pairs in oxygen, fluorine and nitrogen atoms to atoms with a positive partial charge. Hence this is why hydrogen bonding is much stronger than conventional dipole dipole forces.Hydrogen bonding is a special type of dipole-dipole attraction between molecules, not a covalent bond to a hydrogen atom. It results from the attractive force between a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to a very electronegative atom such as a N, O, or F atom and another very electronegative atom.A hydrogen bond is a dipole-dipole force and is an attraction between a slightly positive hydrogen on one molecule and a slightly negative atom on another molecule. Hydrogen bonds are important in the properties of water and in certain biological molecules, such as proteins.

Table of Contents
Why is hydrogen bond considered a special type of dipole-dipole interaction?
Hydrogen bonding is a special type of dipole-dipole attraction between molecules, not a covalent bond to a hydrogen atom. It results from the attractive force between a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to a very electronegative atom such as a N, O, or F atom and another very electronegative atom.
How is hydrogen bonding related to dipole-dipole interactions?
A hydrogen bond is a dipole-dipole force and is an attraction between a slightly positive hydrogen on one molecule and a slightly negative atom on another molecule. Hydrogen bonds are important in the properties of water and in certain biological molecules, such as proteins.
Intermolecular Forces – Hydrogen Bonding, Dipole-Dipole, Ion-Dipole, London Dispersion Interactions
Images related to the topicIntermolecular Forces – Hydrogen Bonding, Dipole-Dipole, Ion-Dipole, London Dispersion Interactions

Is hydrogen bonding a strong type of dipole-dipole interaction?
Hydrogen bonds are a strong type of dipole-dipole interaction. As a Rule of Thumb, they are weaker than covalent and ionic (“intramolecular”) bonds”, but stronger than most dipole-dipole interactions. There are two requirements for hydrogen bonding.
Are hydrogen bonds an example of dipole-dipole?
Hydrogen bonds are a type of dipole-dipole interactions that occur between hydrogen and either nitrogen, fluorine, or oxygen.
Why hydrogen bonding is the strongest intermolecular force?
Hydrogen bonding is so strong among dipole-dipole interactions because it itself is a dipole-dipole interaction with one of the strongest possible electrostatic attractions. Remember that hydrogen bonding cannot occur unless hydrogen is covalently bonded to either oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine.
Is hydrogen bonding the strongest intermolecular force?
Hydrogen bonds are a special case of dipole-dipole interactions. H-bonds are the strongest intermolecular force.
Can hydrogen bonding occur without dipole-dipole?
…
Hydrogen bonding in alcohols.
| ethanol (with hydrogen bonding) | 78.5°C |
|---|---|
| methoxymethane (without hydrogen bonding) | -24.8°C |
See some more details on the topic How is hydrogen bonding an extreme version of dipole-dipole interactions? here:
Types of interactions – Chemistry 301
Hydrogen Bonding. This is a special case of extreme dipole-dipole forces that occurs when a hydrogen atom is bonded to a highly electronegative atom.
Hydrogen Bonding, Dipole-Dipole & Ion-Dipole Forces – Study …
A hydrogen bond is a dipole-dipole force and is an attraction between a slightly positive hydrogen on one molecule and a slightly negative atom on another …
8.1: Intermolecular Interactions – Chemistry LibreTexts
Finally, CH3CH2OH has an −OH group, and so it will experience the uniquely strong dipole-dipole attraction known as hydrogen bonding. So the ordering in terms …
Intermolecular Forces | Van der Waals & Ion-Dipole | ChemTalk
Hydrogen bonding is a special type of dipole-dipole interaction. It can only occur when the molecules in question have a highly …
Can hydrogen bonding exist without dipole-dipole?
…
| element | electronegativity value |
|---|---|
| O | 3.5 |
| F | 4.1 |
How are dipole dipole interactions London dispersion forces and hydrogen bonding similar?
How are dipole-dipole attractions, London dispersion forces, and hydrogen bonding similar? They are all forces of attraction between molecules. In all cases there is an attraction between the slightly negatively-charged portion of one molecule and the slightly positively charged portion of another molecule.
Intermolecular Forces – Hydrogen Bonding, Dipole Dipole Interactions – Boiling Point Solubility
Images related to the topicIntermolecular Forces – Hydrogen Bonding, Dipole Dipole Interactions – Boiling Point Solubility
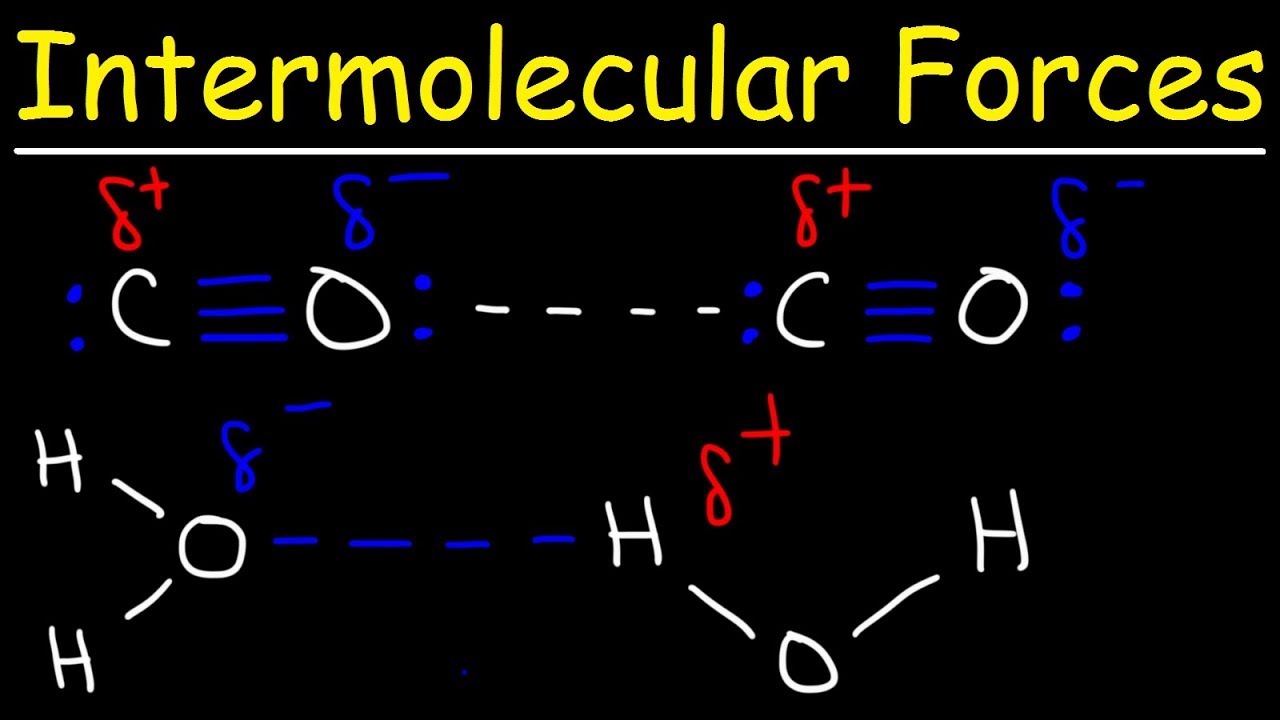
Which is stronger dipole-dipole or hydrogen bonding or London dispersion?
All molecules, whether polar or nonpolar, are attracted to one another by London dispersion forces in addition to any other attractive forces that may be present. In general, however, dipole–dipole interactions in small polar molecules are significantly stronger than London dispersion forces, so the former predominate.
How do dipole-dipole differ from hydrogen bonding in what ways are they similar?
Explanation: Typical dipole-dipole forces are strong bonds between atoms, some of them usually quite electronegative. Hydrogen Bonding is between molecules and is a weak bond that usually requires the presence of hydrogen.
Which intermolecular force is the strongest?
Dipole-dipole interactions are the strongest intermolecular force of attraction.
How does dipole-dipole interaction happen?
Dipole-Dipole interactions result when two dipolar molecules interact with each other through space. When this occurs, the partially negative portion of one of the polar molecules is attracted to the partially positive portion of the second polar molecule.
What makes hydrogen bonding the strongest?
So if we increase the polarization between the atoms involved in the hydrogen bond, the hydrogen bond should become much stronger. Fluorine is the most electronegative element (3.98 on the Pauling scale) and because of this fluorine forms some of the strongest hydrogen Page 3 bonds.
Why are hydrogen bonds stronger than Van der Waals?
Hydrogen bonds are stronger than the van der Waals forces because H-bonds are considered as an extreme form of dipole-dipole interaction.
Why is dipole-dipole the strongest?
The dipole dipole force is defined as the intermolecular force, which are present in the susbtance made up of polar molecules. We can say, the strongest dipole dipole forces are the strongest intermolecular force of attraction. The strongest dipole dipole force can often seen in the compounds with the hydrogen bonding.
Why does hydrogen bonding occur?
The reason hydrogen bonding occurs is because the electron is not shared evenly between a hydrogen atom and a negatively charged atom. Hydrogen in a bond still only has one electron, while it takes two electrons for a stable electron pair.
How to Identify the Intermolecular Force a Compound Has: London Dispersion, Dipole Dipole, H-Bonding
Images related to the topicHow to Identify the Intermolecular Force a Compound Has: London Dispersion, Dipole Dipole, H-Bonding

Why is hydrogen bonding only possible with hydrogen?
Hydrogen bonds are only possible with hydrogen because hydrogen is small. When hydrogen is bonded to an electronegative atom like nitrogen or oxygen…
What are the conditions for hydrogen bonding?
- The molecule must contain a highly electronegative atom linked to the hydrogen atom. The higher the electronegativity more is the polarization of the molecule.
- The size of the electronegative atom should be small. The smaller the size, the greater is the electrostatic attraction.
Related searches to How is hydrogen bonding an extreme version of dipole-dipole interactions?
- how to identify hydrogen bonding
- hydrogen bonding intermolecular forces
- intermolecular hydrogen bonding
- ion-dipole forces
- ion dipole forces
- explain how hydrogen bonding is an extreme version of dipole dipole interactions
- are dipole dipole forces stronger than hydrogen bonds
- hydrogen bonding types
- how do typical dipole dipole forces similar from hydrogen bonding
- dipole-dipole interaction example
- dipole dipole interaction example
Information related to the topic How is hydrogen bonding an extreme version of dipole-dipole interactions?
Here are the search results of the thread How is hydrogen bonding an extreme version of dipole-dipole interactions? from Bing. You can read more if you want.
You have just come across an article on the topic How is hydrogen bonding an extreme version of dipole-dipole interactions?. If you found this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much.