Are you looking for an answer to the topic “How is hydrogen bonding different from dipole-dipole forces?“? We answer all your questions at the website Chiangmaiplaces.net in category: +100 Marketing Blog Post Topics & Ideas. You will find the answer right below.
An ion-dipole force is a force between an ion and a polar molecule. A hydrogen bond is a dipole-dipole force and is an attraction between a slightly positive hydrogen on one molecule and a slightly negative atom on another molecule.Hydrogen bonds are typically stronger than other dipole-dipole forces.The main difference between dipole-dipole and London dispersion forces is that dipole-dipole forces occur among molecules with dipole moment whereas London dispersions occur due to instantaneous dipoles that form in atoms or nonpolar molecules.

Table of Contents
Is dipole-dipole or hydrogen bonding stronger?
Hydrogen bonds are typically stronger than other dipole-dipole forces.
What are the differences between London dispersion forces dipole-dipole forces and hydrogen bonding?
The main difference between dipole-dipole and London dispersion forces is that dipole-dipole forces occur among molecules with dipole moment whereas London dispersions occur due to instantaneous dipoles that form in atoms or nonpolar molecules.
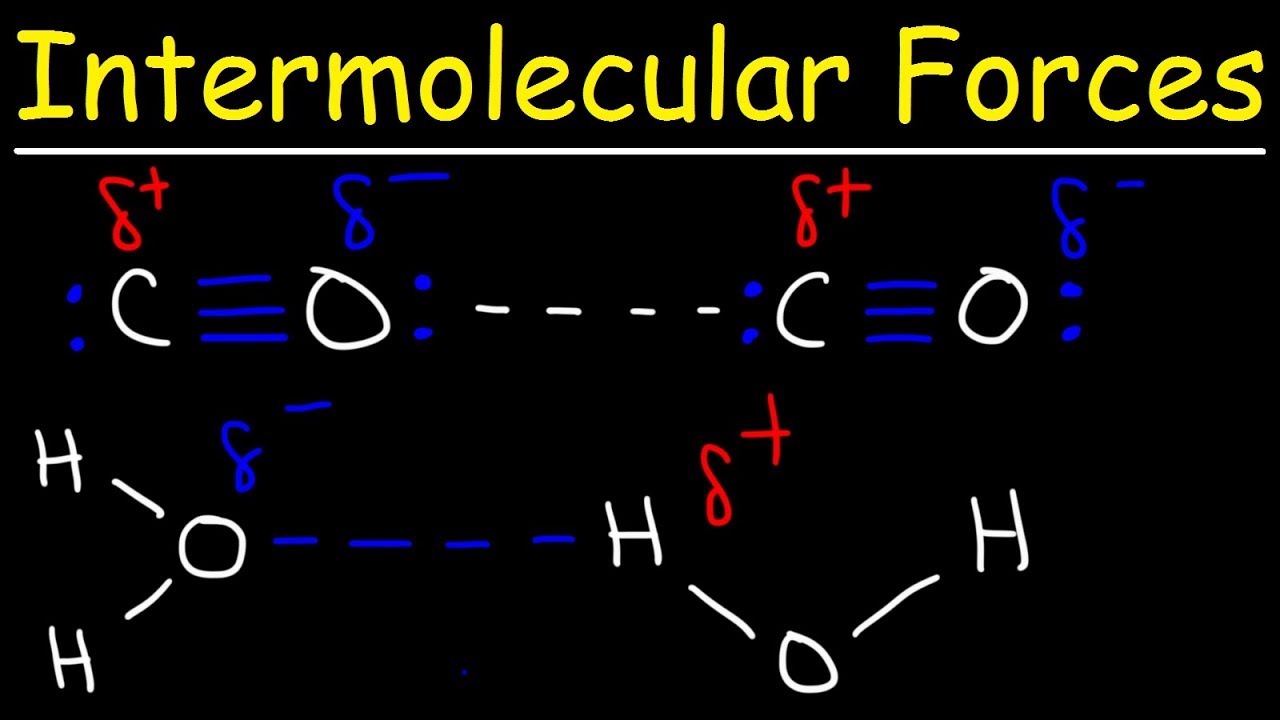
Intermolecular Forces – Hydrogen Bonding, Dipole-Dipole, Ion-Dipole, London Dispersion Interactions
Images related to the topicIntermolecular Forces – Hydrogen Bonding, Dipole-Dipole, Ion-Dipole, London Dispersion Interactions

Why is hydrogen bonding the strongest among intermolecular forces?
Hydrogen bonding is so strong among dipole-dipole interactions because it itself is a dipole-dipole interaction with one of the strongest possible electrostatic attractions.
Why is hydrogen bonding considered as a very strong type of dipole-dipole force?
Because a hydrogen atom is so small, these dipoles can also approach one another more closely than most other dipoles. The combination of large bond dipoles and short dipole–dipole distances results in very strong dipole–dipole interactions called hydrogen bonds, as shown for ice in Figure 12.6.
What is the difference between London dispersion forces and dipole-dipole forces chegg?
Explanation: London dispersion forces occur between nonpolar molecules and are extremely weak. Dipole-dipole forces are between polar molecules, and since polar molecules have slight charges, their force is more similar to ions, giving them a moderately strong bond.
What’s the difference between dipole-dipole and LDF?
Dipole-dipole and London dispersion forces are two attraction forces found between molecules or atoms; they directly affect the boiling point of the atom /molecule. The key difference between Dipole-Dipole and London Dispersion forces is their strength and where they can be found.
What is the difference between London forces and dipole-dipole forces?
Solution : Dipole-dipole forces arise between two polar molecules. London forces on the other hand result from the presence of temkporary dipole moments caused by the unsymmetrical distribution of electrons.
See some more details on the topic How is hydrogen bonding different from dipole-dipole forces? here:
What is the difference between hydrogen bonds and … – Socratic
Hydrogen bonds are a specific type of dipole dipole interaction commonly found in water molecules. Dipole dipole interactions occur between …
Hydrogen Bonding – Liquids Help Page
Hydrogen bonding is a special type of dipole-dipole attraction between molecules, not a covalent bond to a hydrogen atom. It results from the attractive force …
Intramolecular and intermolecular forces (article) – Khan …
Hydrogen bonding: This is a special kind of dipole-dipole interaction that occurs specifically between a hydrogen atom bonded to either an oxygen, nitrogen, …
Intermolecular Forces
Hydrogen bonds are typically stronger than other dipole-dipole forces. Clicking on the right will take you to the debriefing for this module.
What is hydrogen bonding intermolecular forces?
A hydrogen bond is an intermolecular force (IMF) that forms a special type of dipole-dipole attraction when a hydrogen atom bonded to a strongly electronegative atom exists in the vicinity of another electronegative atom with a lone pair of electrons. Intermolecular forces (IMFs) occur between molecules.
What causes hydrogen bonding?
Hydrogen bonding is a special type of dipole-dipole attraction between molecules, not a covalent bond to a hydrogen atom. It results from the attractive force between a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to a very electronegative atom such as a N, O, or F atom and another very electronegative atom.
Intermolecular Forces – Hydrogen Bonding, Dipole Dipole Interactions – Boiling Point Solubility
Images related to the topicIntermolecular Forces – Hydrogen Bonding, Dipole Dipole Interactions – Boiling Point Solubility
What is meant by dipole-dipole forces?
Dipole-dipole forces are attractive forces between the positive end of one polar molecule and the negative end of another polar molecule. Dipole-dipole forces have strengths that range from 5 kJ to 20 kJ per mole.
Why is dipole-dipole the strongest?
The dipole dipole force is defined as the intermolecular force, which are present in the susbtance made up of polar molecules. We can say, the strongest dipole dipole forces are the strongest intermolecular force of attraction. The strongest dipole dipole force can often seen in the compounds with the hydrogen bonding.
Is dipole-dipole the strongest intermolecular force?
Types of intermolecular forces that exist between molecules
Dipole-dipole interactions are the strongest intermolecular force of attraction.
What makes hydrogen bonding the strongest?
So if we increase the polarization between the atoms involved in the hydrogen bond, the hydrogen bond should become much stronger. Fluorine is the most electronegative element (3.98 on the Pauling scale) and because of this fluorine forms some of the strongest hydrogen Page 3 bonds.
Which intermolecular force is the strongest?
The strongest intermolecular forces are dipole-dipole interactions. A dipole-dipole force is when the positive side of a polar molecule attracts the negative side of another polar molecule. For this kind of bond to work, the molecules need to be very close to each other as they are in a liquid.
What is the difference between intermolecular and intramolecular forces?
Both types of forces determine the chemical and physical characteristics of substances. The main difference between intermolecular and intramolecular forces is that intermolecular forces exist between the molecules themselves, whereas intramolecular forces exist between atoms within a molecule.
Is water dipole-dipole or hydrogen bonding?
Water has polar O-H bonds. The negative O atoms attract the positive H atoms in nearby molecules, leading to the unusually strong type of dipole-dipole force called a hydrogen bond. Since water has hydrogen bonds, it also has dipole-induced dipole and London dispersion forces.
What is the difference between a polar covalent bond and dipole forces?
Polar molecules align so that the positive end of one molecule interacts with the negative end of another molecule. Unlike covalent bonds between atoms within a molecule ( intramolecular bonding), dipole-dipole interactions create attractions between molecules of a substance ( intermolecular attractions).
How to Identify the Intermolecular Force a Compound Has: London Dispersion, Dipole Dipole, H-Bonding
Images related to the topicHow to Identify the Intermolecular Force a Compound Has: London Dispersion, Dipole Dipole, H-Bonding

What is the difference between London dispersion forces and van der Waals?
Van der Waals and London Dispersion Forces
Van der Waals forces are a type of intermolecular force that occurs because of dipole-dipole interactions. London dispersion force is a sub-type of the Van der Waals force that is predominant in non-polar molecules.
How are dipole-dipole forces and dispersion forces similar?
Explanation: Both dipole-dipole forces and London dispersion forces are intermolecular forces, which means that they’re both forces between different molecules. Dipole-dipole forces occur when the molecules are polar, and the positive side of one molecule is slightly attracted to the negative side of another.
Related searches to How is hydrogen bonding different from dipole-dipole forces?
- hydrogen bonding intermolecular forces
- intermolecular forces strongest to weakest
- dipole dipole forces examples
- dipole-dipole forces examples
- ion-dipole forces
- ion-dipole vs dipole-dipole
- ion dipole forces example
- ion dipole forces
- is hydrogen bonding stronger than dipole-dipole
- ion dipole vs dipole dipole
- hydrogen bonding intermolecular forces examples
- types of intermolecular forces
- how is hydrogen bonding different from dipole-dipole forces
- is hydrogen bonding stronger than dipole dipole
Information related to the topic How is hydrogen bonding different from dipole-dipole forces?
Here are the search results of the thread How is hydrogen bonding different from dipole-dipole forces? from Bing. You can read more if you want.
You have just come across an article on the topic How is hydrogen bonding different from dipole-dipole forces?. If you found this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much.