Are you looking for an answer to the topic “How is taste and smell physiologically interdependent?“? We answer all your questions at the website Chiangmaiplaces.net in category: +100 Marketing Blog Post Topics & Ideas. You will find the answer right below.
Ultimately, messages about taste and smell converge, allowing us to detect the flavors of food. Taste and smell are separate senses with their own receptor organs, yet they are intimately entwined. Tastants, chemicals in foods, are detected by taste buds, which consist of special sensory cells.The nose and mouth are connected through the same airway which means that you taste and smell foods at the same time. Their sense of taste can recognize salty, sweet, bitter, sour and savoury (umami), but when you combine this with the sense of smell they can recognize many other individual ‘tastes’.Taste (gustation) and smell (olfaction) are called chemical senses because both have sensory receptors that respond to molecules in the food we eat or in the air we breathe. There is a pronounced interaction between our chemical senses.

Table of Contents
How are taste and smell are linked together?
The nose and mouth are connected through the same airway which means that you taste and smell foods at the same time. Their sense of taste can recognize salty, sweet, bitter, sour and savoury (umami), but when you combine this with the sense of smell they can recognize many other individual ‘tastes’.
What do taste and smell have in common psychology?
Taste (gustation) and smell (olfaction) are called chemical senses because both have sensory receptors that respond to molecules in the food we eat or in the air we breathe. There is a pronounced interaction between our chemical senses.
Taste Smell: Crash Course Anatomy Physiology #16
Images related to the topicTaste Smell: Crash Course Anatomy Physiology #16

Why is smell and taste important for homeostasis?
Taste and other oro-sensory signals from oral cavity affect not only the intake regulation, but also influence hormonal, neural and metabolic pathways to maintain homeostasis. The aim is to utilize effectively food energy and prevent energy instability of organism.
How much of our sense of taste is dependent on the sense of smell?
It is frequently asserted that somewhere between 75 and 95 % of what we commonly think of as taste actually comes from the sense of smell.
Can you taste without smell?
Can you taste without smell? Smell and taste are closely related. Your tongue can detect sweet, sour, salty and bitter tastes. But without your sense of smell, you wouldn’t be able to detect delicate, subtle flavors.
How are the senses of taste and smell related and what term describes this relationship?
The senses of smell and taste are directly related because they both use the same types of receptors. If one’s sense of smell is not functional, then the sense of taste will also not function because of the relationship of the receptors.
How the sense of smell works in psychology?
People perceive particular smells when different combinations of receptors are stimulated. The sense of smell is closely connected with memory. Most people have had the experience of smelling something, maybe a certain perfume or spice, and suddenly experiencing a strong emotional memory.
See some more details on the topic How is taste and smell physiologically interdependent? here:
Taste and Smell – Biology – UH Pressbooks
Taste, also called gustation, and smell, also called olfaction, are the most interconnected senses in that both involve molecules of the stimulus entering …
Overview of Smell and Taste Abnormalities – Merck Manuals
Because distinct flavors depend on aromas to stimulate the olfactory chemoreceptors, smell and taste are physiologically interdependent.
Physiology, Taste – StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf
Taste is sensed by chemosensory receptors known as taste buds. … Basic anatomy and physiology of olfaction and taste.
Taste and Smell | Boundless Biology | Course Hero
The senses of taste and smell are related because they use the same types of receptors and are stimulated by molecules in solutions or air.
Why is smell important in psychology?
One of the key components of the psychology of smell is the tight-knit link between smell and memory. Scents are processed in the olfactory bulb, which has direct connections to the amygdala and hippocampus. These are the parts of the brain that provide emotional reactions and memories.
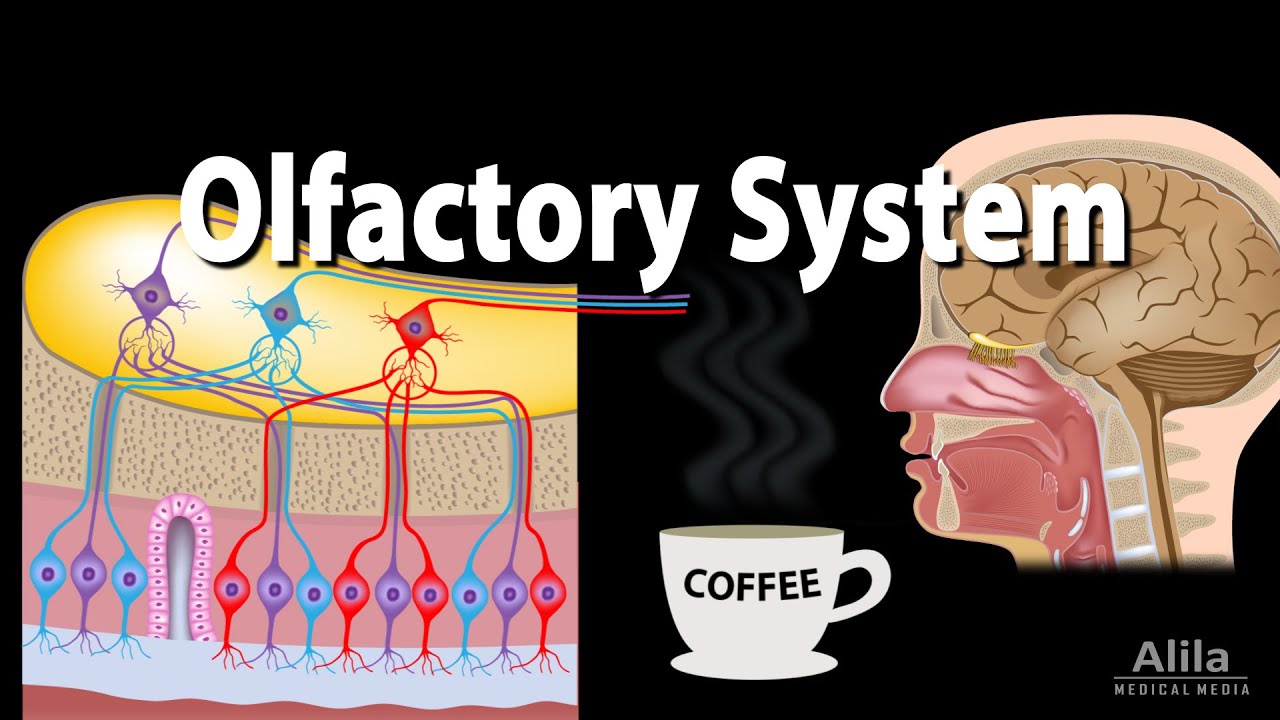
Olfactory System: Anatomy and Physiology, Pathways, Animation.
Images related to the topicOlfactory System: Anatomy and Physiology, Pathways, Animation.
Why are senses of taste and smell important to organisms?
Smell lets an animal sense the presence of food or other animals—whether potential mates, predators, or prey—or other chemicals in the environment that can impact their survival. Similarly, the sense of taste allows animals to discriminate between types of foods.
What role do senses play in maintaining homeostasis?
Answer and Explanation: Your senses help you maintain homeostasis because they allow you to sense changes in the environment and make appropriate changes to keep your… See full answer below.
How can smell affect taste?
When your sense of smell goes south, taste usually follows. That’s because the olfactory area in your nose controls both. When you chew food, odor molecules enter the back of your nose. Your taste buds tell you if a food is sweet, sour, bitter, or salty.
Can you lose smell without taste?
Although it may sound simple enough, it can be tricky to determine if you’ve lost your sense of taste and smell. There are different degrees of loss, so you may still be able to smell, but not as sharp as before (hyposmia). Or your ability to taste may decrease (dysgeusia).
Does 90% of taste come from smell?
Approximately 80–90% of what we perceive as “taste” is in fact due to our sense of smell (think about how dull food tastes when you have a head cold or a stuffy nose). At the beginning of this experiment you may not be able to tell the specific flavor of the candy beyond a general sensation of sweetness or sourness.
What type of sense are both taste and smell?
What Are the Chemical Senses? The chemical senses include taste and smell. The perception of a smell occurs when substances in the air pass through the nose and stimulate the olfactory (smell) nerve.
What part of the brain controls taste and smell?
Parietal lobe
It figures out the messages you receive from the five senses of sight, touch, smell, hearing and taste.
Taste: Anatomy and Physiology, Animation
Images related to the topicTaste: Anatomy and Physiology, Animation

Do you have Covid if you can’t smell?
With COVID-19, smell loss one of the first signs of infection. “Smell loss is actually an early sign of COVID-19 and usually occurs for those who have a mild form of the virus,” says Tajudeen. “Patients with smell loss are normally at home recovering and not admitted into the hospital or on a ventilator.”
Can you taste if you hold your nose?
Try holding your nose the next time you eat something. You’ll notice that your taste buds are able to tell your brain something about what you’re eating — that it’s sweet, for instance — but you won’t be able to pick the exact flavor until you let go of your nose.
Related searches to How is taste and smell physiologically interdependent?
- what percentage of taste is smell
- how are taste and smell different
- how does smell affect taste experiment
- what is the cause of loss of taste and smell?
- how is taste and smell physiologically interdependent quizlet
- how is taste and smell physiologically interdependent or negative
- how the senses of smell and taste operate in ways that help the body maintain a homeostatic balance
- how are the sensory receptors for smell and taste similar gizmo
- how is taste and smell physiologically interdependent synonym
- how is taste and smell physiologically interdependent in the brain
- what is the cause of loss of taste and smell
- smell is 70 of taste
- what part of the brain controls taste and smell
- how is taste and smell physiologically interdependent in the workplace
- how is taste and smell physiologically interdependent in relationships
Information related to the topic How is taste and smell physiologically interdependent?
Here are the search results of the thread How is taste and smell physiologically interdependent? from Bing. You can read more if you want.
You have just come across an article on the topic How is taste and smell physiologically interdependent?. If you found this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much.