Are you looking for an answer to the topic “How is the voltage distributed in a parallel circuit?“? We answer all your questions at the website Chiangmaiplaces.net in category: +100 Marketing Blog Post Topics & Ideas. You will find the answer right below.
Voltage is the same across each component of the parallel circuit. The sum of the currents through each path is equal to the total current that flows from the source.The voltages across each of the components in series is in the same proportion as their resistances . This means that if two identical components are connected in series, the supply voltage divides equally across them.Loads in power distribution systems are mostly connected in parallel with each other in one way or another. A parallel circuit is constructed by connecting the terminals of all the individual load devices so that the same value of voltage appears across each component. The voltage across each branch is the same.

Table of Contents
How is voltage distributed in a series circuit?
The voltages across each of the components in series is in the same proportion as their resistances . This means that if two identical components are connected in series, the supply voltage divides equally across them.
How does the voltage same in parallel circuit?
Loads in power distribution systems are mostly connected in parallel with each other in one way or another. A parallel circuit is constructed by connecting the terminals of all the individual load devices so that the same value of voltage appears across each component. The voltage across each branch is the same.
Voltage distribution in series circuit|Current distribution in circuit|Voltage in parallel circuits
Images related to the topicVoltage distribution in series circuit|Current distribution in circuit|Voltage in parallel circuits

Is voltage shared in a parallel circuit?
From this definition, three rules of parallel circuits follow: All components share the same voltage. Resistances diminish to equal a smaller, total resistance. Branch currents add to equal a larger, total current.
Is voltage constant in parallel?
All parallel components have the same voltage because you have connected them together with wires that are assumed to have no resistance. The voltage at each end of a wire should be the same for all the components.
Does voltage stay the same in parallel?
In a parallel circuit, the voltage across each of the components is the same, and the total current is the sum of the currents flowing through each component.
Why is electric current distributed in a parallel circuit?
The presence of branch lines means that there are multiple pathways by which charge can traverse the external circuit. When resistors are connected in parallel, the potential difference across them is equal and current gets divided in inverse ratio of their resistance.
What is voltage drop in parallel circuit?
In the parallel circuit diagram, the voltage drop across a resistor in a parallel circuit is the same across all resistors in each branch of the parallel circuit. Voltage, expressed in volts, measures the electromotive force or potential difference that runs the circuit.
See some more details on the topic How is the voltage distributed in a parallel circuit? here:
Physics Tutorial: Parallel Circuits
In a parallel circuit, the voltage drops across each of the branches is the same as the voltage gain in the battery. Circuits X and Y are each powered by a 12- …
Parallel Circuits – Basic Electricity – BCcampus Pressbooks
Total voltage of a parallel circuit has the same value as the voltage across each branch. This relationship can be expressed as: ET = E1 = E2 = E3… Figure 20.
Simple Parallel Circuits | Electronics Textbook
Voltage: Voltage is equal across all components in a parallel circuit. Current: The total circuit current is equal to the sum of the individual branch currents.
Distribution of current and voltage in parallel and series
When resistors are connected in parallel, the potential difference across them is equal and current gets divided in inverse ratio of their …
DC parallel circuits explained – The basics how parallel circuits work working principle
Images related to the topicDC parallel circuits explained – The basics how parallel circuits work working principle

How does current flow in parallel circuit?
Current. In a parallel circuit, charge divides up into separate branches such that there can be more current in one branch than there is in another. Nonetheless, when taken as a whole, the total amount of current in all the branches when added together is the same as the amount of current for the entire circuit.
Is voltage always the same in a series circuit?
2. In a series circuit the current is the same at any particular point on the circuit. 3. The voltage in a series circuit, however, does not remain constant.
Is voltage constant in a circuit?
The voltage can never be a constant parameter in any electrical circuit. Each resistor has a different voltage drop through them in a series combination. Hence, voltage in series circuits is neither same nor constant.
How does voltage change in a series and parallel circuit?
In a series circuit, the current through each of the components is the same, and the voltage across the circuit is the sum of the voltages across each component. In a parallel circuit, the voltage across each of the components is the same, and the total current is the sum of the currents through each component.
Is current the same everywhere in a parallel circuit?
In parallel circuits the current splits up so each branch has a different effective resistance (in each of the separate branches one can use the series rule again). Due to this, the current isn’t the same everywhere in a parallel circuit.
What happens to potential difference in a parallel circuit?
In parallel circuits, the electric potential difference across each resistor (ΔV) is the same. The current in a resistor follows Ohm’s law: I = ΔV / R. Since the ΔV is the same for each resistor, the current will be smallest where the resistance is greatest.
How To Calculate The Current In a Parallel Circuit Using Ohm’s Law
Images related to the topicHow To Calculate The Current In a Parallel Circuit Using Ohm’s Law
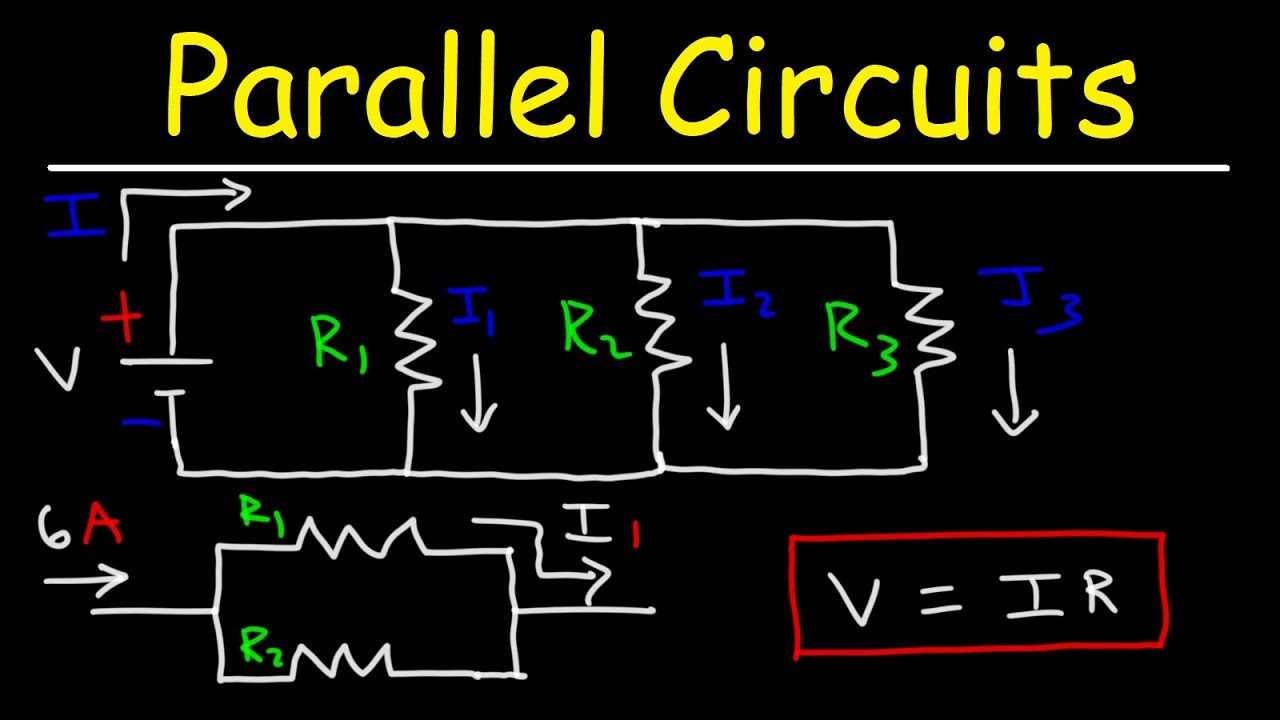
What happens to current in a parallel circuit?
The current in a parallel circuit splits into different branches then combines again before it goes back into the supply. When the current splits, the current in each branch after the split adds up to the same as the current just before the split.
Why is voltmeter connected in parallel?
In order to measure a device’s voltage, a voltmeter is connected in parallel to a device. This setup is important as objects in parallel usually tend to experience the same potential difference. It is connected in parallel with the circuit mainly because the same voltage drop occurs across it.
Related searches to How is the voltage distributed in a parallel circuit?
- parallel circuit formula
- current in a parallel circuit
- characteristics of parallel circuit
- voltage in series and parallel
- resistance in a parallel circuit
- what happens to the voltage in a parallel circuit
- how is voltage distributed in a parallel circuit
- does voltage split in parallel
- how is the voltage distributed in a parallel circuit with two resistors
Information related to the topic How is the voltage distributed in a parallel circuit?
Here are the search results of the thread How is the voltage distributed in a parallel circuit? from Bing. You can read more if you want.
You have just come across an article on the topic How is the voltage distributed in a parallel circuit?. If you found this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much.